 Short Communication
Short Communication
Installation of Pit Fencing in Cramped Conditions
Sokolov NS, Chuvash State University, Russia.
Received Date: February 03, 2022; Published Date: March 04, 2022
Abstract
Construction of facilities in cramped conditions is always a complex geotechnical problem associated with ensuring the basal emergency operation of buildings and structures of the surrounding buildings. In the arsenal of geotechnicians, a great potential of geotechnical technologies for the installation of pit fences has been accumulated. Often, not everyone is suitable for the conditions of their use in cramped conditions. The most suitable technologies for such cases are the drilled wells used (wells for drill piles and soil anchors) with their subsequent filling with concrete and at the same time not disturbing the stress-strain state of the surrounding soil. The use of drilling piles and soil anchors arranged using electric discharge technology (ERT technology) in many cases successfully solves the problem of construction in cramped conditions. The article cites one of the geotechnical cases of fencing the pit in particularly cramped conditions. The work is an overview.
Keywords: Geotechnical construction; Electric discharge technology of ERT; Drill injection pile ERT; Soil anchors ERT
Introduction
The construction of buildings and structures in cramped
conditions requires from builders and geotechnicians close
attention [1-12] related to the need to preserve the objects of
the surrounding buildings. In this article, a successful example of
fencing the pit of a building under construction, located surrounded
by existing structures, is given.
Administratively, the construction site of a six-storey residential
building is located in Nizhny Novgorod in cramped conditions
of urban development. It was built on a non-developmental
territory. Surrounded by a house under construction in the zone of
geotechnical influence, there are six objects of existing development
(see Figure 1), including two objects of the OKN (objects of cultural
heritage).
Geomorphologically, the survey site is located on the watershed
plateau of the Oka and Volga rivers. Elevations of the surface of the
earth within the site vary from 135.9 to 136.3 B.S. (at the mouths of
engineering and geological workings). The terrain is planned. The
engineering and geological structure of the site to a depth of 20.0
m is represented by undissected upper-middle quaternary loess
loams (prQII-III), opened with a capacity of 1.7-2.5 m, undissected
upper-middle quaternary loam loams (prQII-III), with a capacity of
14.5-16.6 m, from the surface of the sediments covered with bulk
soil (tQIV), with a capacity of 1.7-3.0 m.
All engineering and geological workings are plotted on the
layout plan of engineering and geological workings. The geological
and lithological structure of the site is characterized by columns
of wells and engineering-geological sections. The hydrogeological
conditions of the site to a depth of 20.0 m at the time of the survey
(July-August 2017) are characterized by the presence of an aquifer
confined to Quaternary sediments. The groundwater level was
recorded at depths of 4.5-6.4 m. The aquifer is non-pressure, the
water-containing soils are loess loam. Water wells have not been
opened. The aquifer is fed by atmospheric infiltration precipitation
and leaks from water-carrying communication.
The geological and lithological structure of the site is presented
in Table 1 (Table 1) (Figures 1-6).
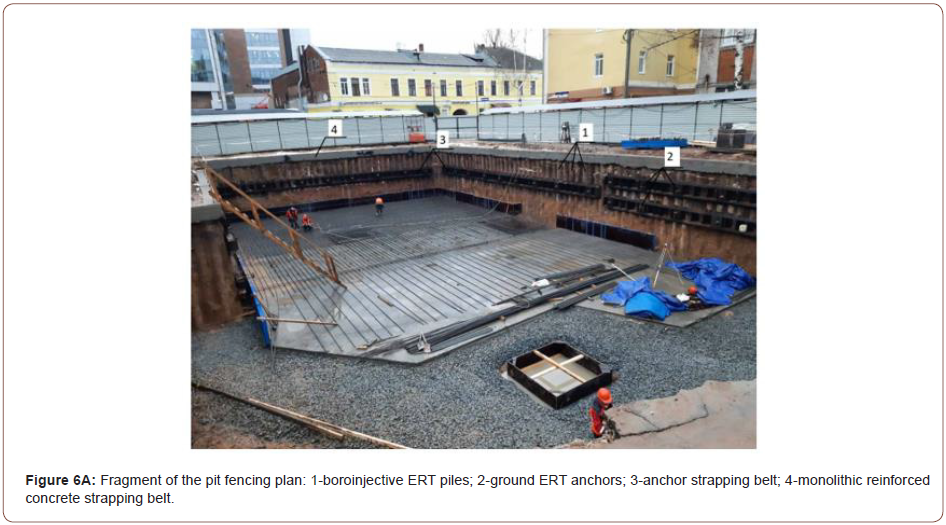
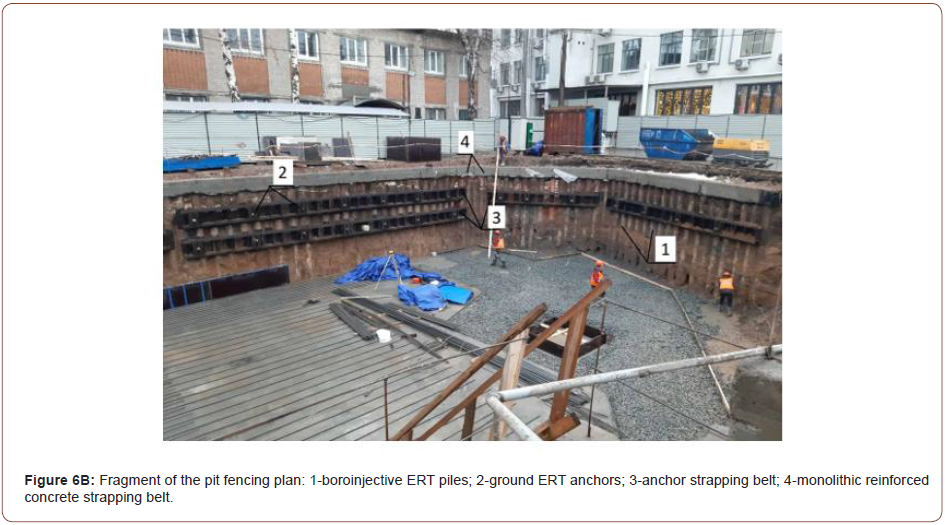
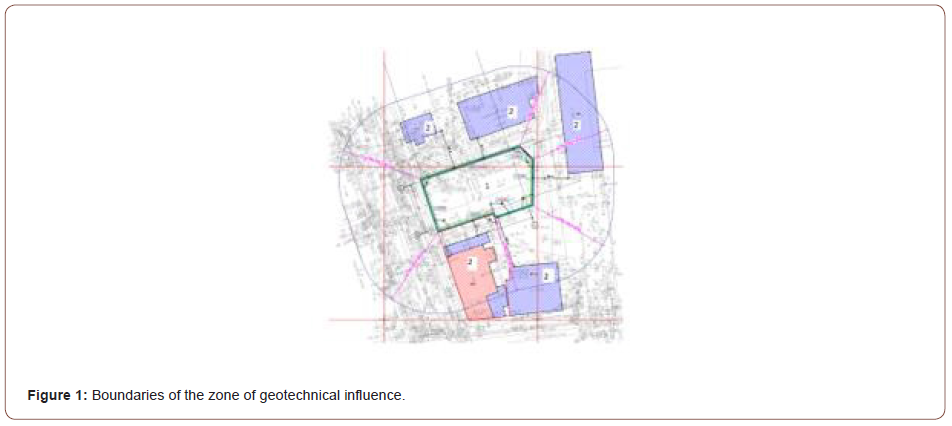
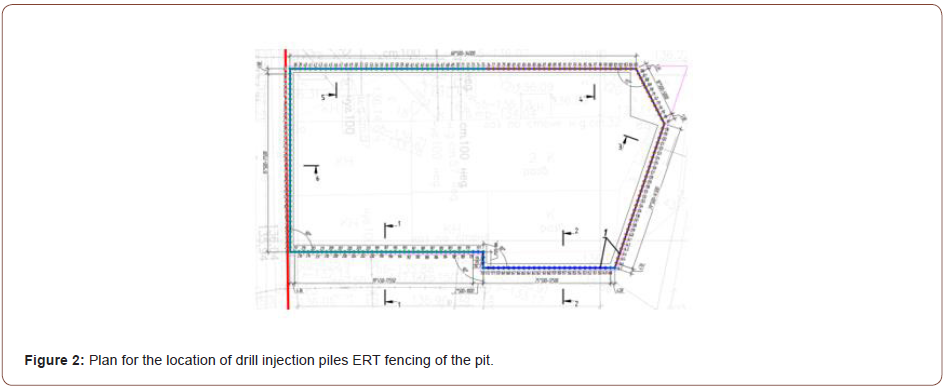
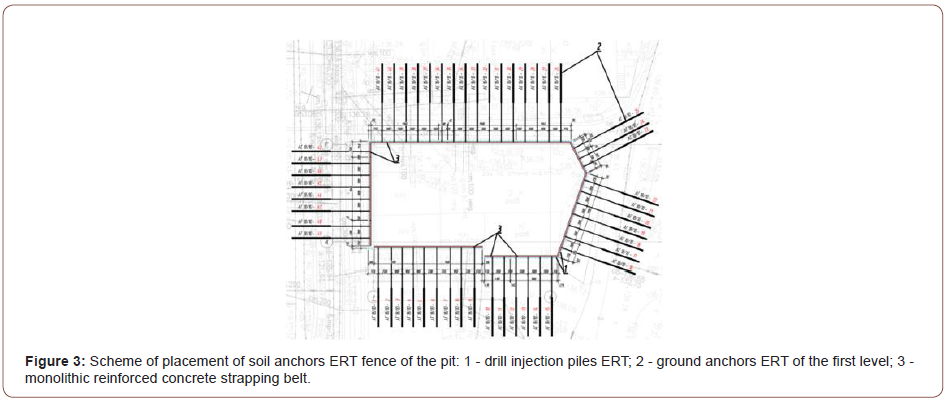
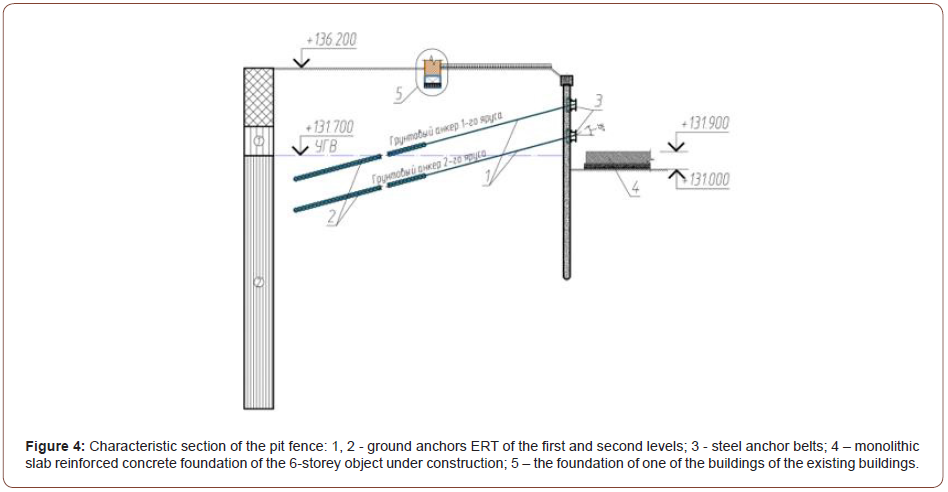
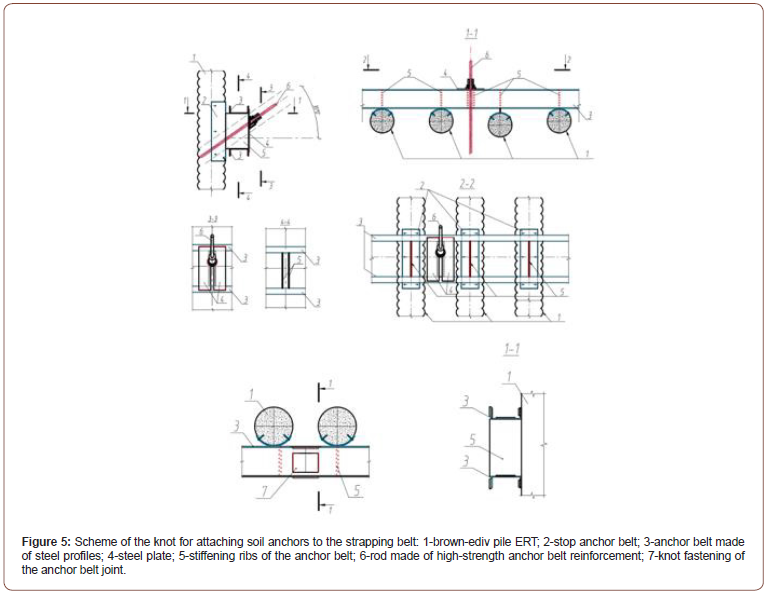


Table 1: Resource requirements by component.
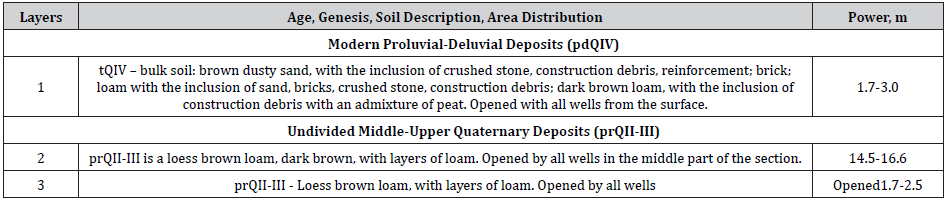
Table 2: Resource requirements by component.
Below in Table Figure 2 shows the algorithm for the device of ERT drill injection anchors (Table 2).
Conclusion
1. Brown-injection piles and soil anchors ERT, being buried
reinforced concrete structures of the pit fence during the
construction of a six-story residential building, made it possible
to build an object without negative consequences for buildings
of the surrounding buildings.
2. The algorithm for the installation of soil anchors ERT has
been tested on many objects of geotechnical construction. It is
mandatory in the manufacture of brown injection ERT anchors.
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
References
- Ilyichev VA, Mangushev RA, Nikiforova NS (2012) Experience of mastering the underground space of russian megalopolises. Osnovy, foundations and mechanics of soils. 2: 17–20.
- Ulitskiy VM, Shashkin AG, Shashkin KA (2010) Geotechnical support of urban development. SPb.: Georeconstruction p.551.
- Ilichev VA, Konovalov PA, Nikiforova NS, Bulgakov LA (2004) Deformations of the Retaining Structures Upon Deep Excavations in Moscow. Proc. Of Fifth Int. Conf on Case Histories in Geotechnical Engineering, New York, USA. pp.5–24.
- Ilichev VA, Nikiforova NS, Koreneva EB (2007) Computing the evaluation of deformations of the buildings located near deep foundation tranches. Proc. of the XVIth European conf. on soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering. Madrid, Spain. Geo-technical Engineering in urban Environments, 2: 581–585.
- Nikiforova NS, Vnukov DA (2011) Geotechnical cut-off diaphragms for built-up area protection in urban underground development. The pros, of the 7thI nt. Symp. Geotechnical aspects of underground construction in soft ground, tc28 IS Roma, AGI, 2011, No.157NIK.
- Nikiforova NS, Vnukov DA (2004) The use of cut off of different types as a protection measure for existing buildings at the nearby underground pipeline’s installation. Proc. of Int. Geotech. Conf. dedicated to the Year of Russia in Kazakhstan. Almaty, Kazakhstan, pp.338–342.
- Petrukhin VP, Shuljatjev OA, Mozgacheva OA (2003) Effect of geotechnical work on settlement of surrounding buildings at underground construction. Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering. Prague.
- Sokolov NS (2018) Ground Anchor Produced by Electric Discharge Technology, as Reinforced Concrete Structure. Key Engineering Materials. pp.76–81.
- Sokolov NS (2018) Use of the Piles of Effective Type in Geotechnical Construction. Key Enginiring Materials. pp.70–74.
- Sokolov NS (2021) Electro Discharge Technology strengthening the foundation of the foundations. Housing construction. 9: 36-42.
- Sokolov NS (2021) One of the cases of reinforcement of the base of the deformed anti-landslide retaining wall. Housing construction. p.12.
- Sokolov NS (2022) Technological aspects of increasing the reliability of existing retaining walls. Housing construction. No.1-2.
-
Bosong Jiao, Harry Evdorides and Mostafa Massoud. A Systematic Review of Existing Methods plus the State-of-the-art Technologies Used to Collect Road-Related Data and its Usage. Cur Trends Civil & Struct Eng. 8(3): 2022. CTCSE.MS.ID.000690.
-
Geotechnical construction, Electric discharge technology of ERT, Drill injection pile ERT, Soil anchors ERT
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






