 Complementary
Complementary
Digital Optical Biopsy of the Retina. (Pixelometria Cuantica)
Jorge Oscar Zarate*
Department of Psychology, Western Carolina University, Cullowhee, USA
Jorge Oscar Zarate, Professor Consulto Titular, faculty of medicine, Universidad de Buenos, Aires, Argentina.
Received Date: April 08, 2019; Published Date: April 30, 2019
Complementary
“When it seems diminished the possibilities of new molecules to unravel the mysteries of life and death, a new physical design as sequential core of the dynamic structures arises: The Pixel”
The geometry of the pixels denotes a certain combination of eucldiana and two-dimensional elliptical, especially with options 3 D allowed in the construction scheme geométric Riemannian, and the stocks of subpixels (red, green and blue) dead pixels and stuck, expressing where color and resolution monitors have reached almost improbable geometric expressions, graphics cards such as the S3, NVIDIA, or ATI among others., giving the opportunity to overcome infinitely genome combination possibilities of identification, in this case with 16.8 million colors. (32 bits). The QRS, the old fingerprint, facial detectors FBT face detection, bar codes, different forms of interferometry and spectrometric, have led to the possibility of using non-invasive methods of identity uncalculated limits or different particles [1].
We used the pixelometric new non-Euclidean geometry described, about the pixel, as measurement converter, density, metric, shapes, etc. The group of experts JPG (Joint Photographic Experts Group), have advanced significantly to the compression of images, both color and grayscale high quality) form, giving the fabulous figure of 16,000,000 colors in the save’s images. The pixeloarquitectura that information across multiple cuts allows us to acquire of optical coherence tomography of retina, the structure of a cell or a protein, focal and morphologically ready.
Is the world of pixels identified by images square, hexagonal, rectangular, round, dead, etc., ie no information propia? No morphology forgets that the image (pixel), decoded, it is morphology pure. Quantum computing is a computing paradigm different from classical computing. It is based on the use of qubits instead of bits and gives rise to new logic gates that make possible new algorithms. In the digital computing, a bit can take only two values: 0 or 1. However, in quantum computing, involving the laws of quantum mechanics, and the particle can be in coherent superposition: can be 0, 1 and can be 0 and 1 at a time (a two orthogonal states subatomic particle). This allows you to perform several operations at once, depending on the number of qubits [2-4].
The number of qubits indicates the number of bits that can be in superposition. With conventional bits, if we had a record of three bits, there were eight possible values and the registry only could take one of those values. But if we have a vector three qubits, the particle can take eight different values simultaneously due to quantum superposition. Thus, a three qubits vector allow a total of eight parallel operations. As expected, the number of operations is exponential with respect to the number of qubits [5-7].
However, the possibility of storing their own information, a unit, which is the pixel, makes it more accurate, dynamic and reliable. Quantum physics is the physics of the possibilities of change, management of unified fields of the four forces: gravity, electromagnetism and the strong and weak force of the atomic nucleus.
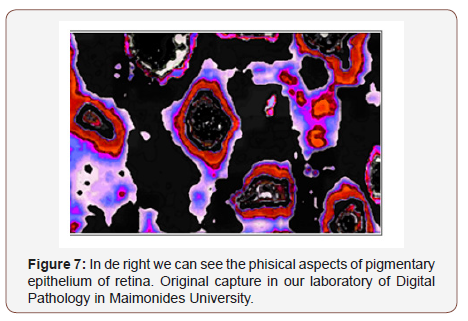
Einstein suggested in his theories, the existence of a field holding space-time transformations and mass - energy. This field is the pixel. In the different photos that we show, can be seen digital secuentiation of the retina tissue, detection technique based in sequencing images, obtained in our Digital Laboratory (Maimonides University) (Figures 1-7) [8,9].
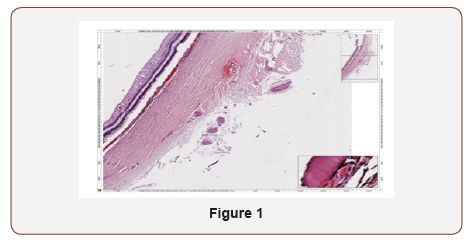
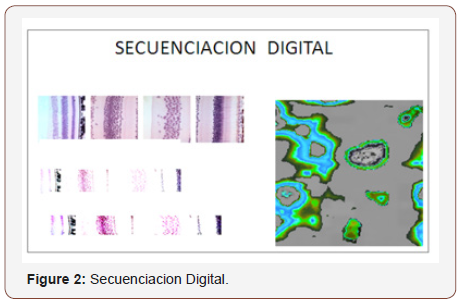
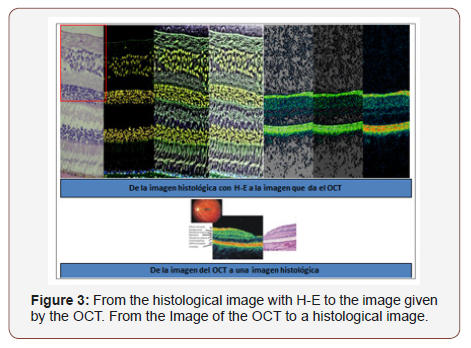


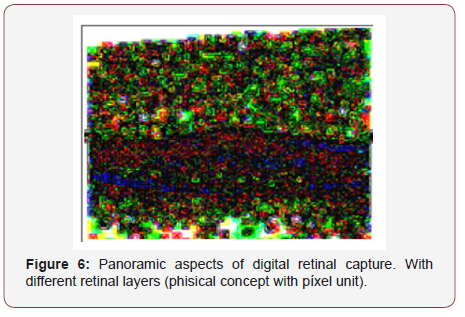
• The basics of different methods of detection are:
• Chemical for Haematoxilin and eosin
• Immunological in Immunohistochemical tecqunics
• Resolutive expectative, for the transmission electronic microscopy
• And Pixel in digital capture detection.
Acknowledgment
None.
Conflicts of Interest
No Conflicts of interest.
References
- Wojtkowski M, Bajraszewski T, Gorczynska I, Targowski P, Kowalczyk A, et al. (2004) Ophthalmic imaging by spectral optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 138(3): 412-419.
- Zarate JO, Pelayes D, Singh A (2012) Optical digital biopsy: A new method of tissue and cell identification with ophthalmic applications. Patología 50(3):179-181.
- Zárate JO (2013) Optical Digital Biopsy. Brush strokes and pixels in the wonderful Latin-American iconography. Patología 51(3):206-209.
- Zárate JO (2014) Digital optical biopsy. Possible extension to no other ophthalmic tissue. Patología Rev Latinoam 52: 246-247.
- Zarate JO (2014) The pixelometría. New non-Euclidian geometry, biological importance. Patologia (Mex).
- Zárate JO, Pelayes David, Folgar Martín, Lacarta Guillermo, Alvarado Miguel (2015) Optical Digital Biopsy: Uveal Choroidal Melanoma: Case Report and Update of Technology. Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine. 3(2): 59-63.
- Zárate Jorge Oscar, Pelayes David, Folgar Martin, Lacarta Guillermo, Alvarado Miguel. (2015) Optical Digital Biopsy: Subcellular Identification and Update of Technology. Open Science Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering 2(2): 29-32.
- El pixel, Jorge O Zárate (2016) ampliadaCABA.Univ. Maimonides ISBN 978-987-1699-24-7(REUP)
- Zarate JO, Racca ML (2008) Historia y Filosofia de la patología latinoamericana-Acuarelas micrográficas impresionistas de America Latina. Patologia (Mexico). 46(3): 295-296.
-
Jorge Oscar Zarate. Digital Optical Biopsy of the Retina. (Pixelometria Cuantica) W J Opthalmol & Vision Res. 1(5): 2019. WJOVR. MS.ID.000524.
-
Vision sciences, Analyzing information, Visual health, Commercial prejudices, Ophthalmology, Optometry, Visual science.
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






