 Research Article
Research Article
Hybrid Teaching Practice of Structural Mechanics Based on Deliberate Practice Theory
Xiaowei Wang* and Zhide Li
School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Wuyi University, China
Xiaowei Wang, School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Wuyi University, China, Email: ID:34492929@qq.com
Received Date: February 19, 2022; Published Date: February 28, 2022
Abstract
The reduced class time for Structural Mechanics and the lack of interaction in large classes have led to the lack of students’ interest and motivation in learning. Facing the new engineering discipline, combined with the objective of this course to cultivate students’ mechanical thinking and thus enhance the ability of model simplification and computational analysis of complex engineering, the modular design of the course content, timely feedback on learning effect through cloud class lessons, design a large number of repetitive and progressive deliberate exercises for the three-stage teaching, integrate hybrid teaching, and try to guide students’ courage to step from the comfort zone into the challenge zone.
Keywords: Structural mechanics; Deliberate practice; Hybrid teaching
Current Status of Teaching
The course “Structural Mechanics” is an important professional
foundation course for civil engineering majors. The following
problems exist in teaching.
• Since2016 the “New Engineering” was formally
proposed [1], there is often a disconnect between theory and
engineering practice in students’ learning process, and there is
a lack of organic connection between mathematics, mechanics
principles, and engineering.
• Class hours in basic mechanics courses have been
compressed. The streamlining of class time with the same
teaching content leads to teachers being tired of catching up.
• Large classes lead to a lack of effective teacher-student
interaction, resulting in a lack of motivation and interest in
learning.
In order to solve the above problems, and in response to the current
situation that the overall mechanical thinking of civil engineering
students in our school is weak, we tried to carry out a hybrid
teaching reform based on deliberate practice [2] theory in the
course of Structural Mechanics.
Teaching Reform Ideas
The teaching reform of mechanics courses for the new engineering should cultivate students’ mechanics thinking through mechanics course learning. Mechanics thinking contains three landing points and the three landing points refer to engineering (or natural phenomena), mechanics, and mathematics (hereinafter referred to as the three segments). For the cultivation of mechanical thinking, it is appropriate to use the three-step teaching method [3]. Combined with the objective of this course to cultivate students’ mechanical thinking so as to enhance the ability of model simplification and computational analysis of complex engineering, the modular design of the course content, the timely feedback of learning effect through cloud classroom, the design of a large number of repetitive and progressive deliberate exercises for the three-stage teaching, and the integration of hybrid teaching, try to guide students’ courage to step from the comfort zone into the challenge zone.
Implementation of Curriculum and Teaching Reform
The modularity of course content
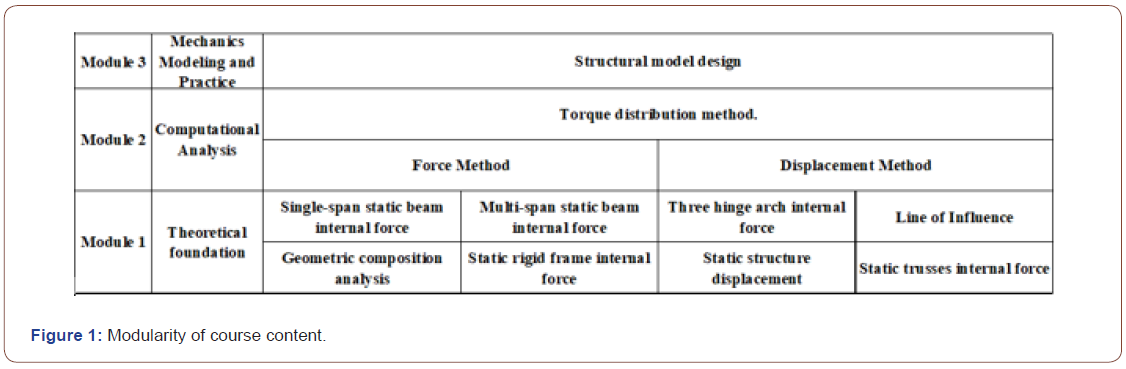
Combined with the school’s positioning of training highquality applied talents and the requirements of the construction of engineering education accreditation standards, based on the OBE concept, benchmarking this course supports the graduation requirements in the talent training program indicator points 1.2, 2.2, the course objectives identified: knowledge objectives (objectives 1) and ability objectives (objectives 2). According to the course objectives, the content of this course is divided into a total of three 11chapters, a total of 72 credit hours (see Figure 1). In the three-stage teaching, students are required to reconstruct the course content according to the three-stage structure: combing the knowledge points of each chapter with the mainline of “engineering background, mathematical foundation, and mechanics principle”, drawing a three-stage mind map of each chapter and writing study notes. Students and faculty members will work together to construct a knowledge map for the course.
Design of “deliberate practice + three-stage” teaching method
Deliberate practice emphasizes purposeful practice that breaks out of the comfort zone, which is the only way to make rapid progress. The most important feature of the deliberate practice lies in purposeful mass repetition, the use of spaced, interspersed, and diverse exercises, and the giving of timely feedback. The three-stage teaching design of this course based on the theory of deliberate practice is as follows (see Figure2).
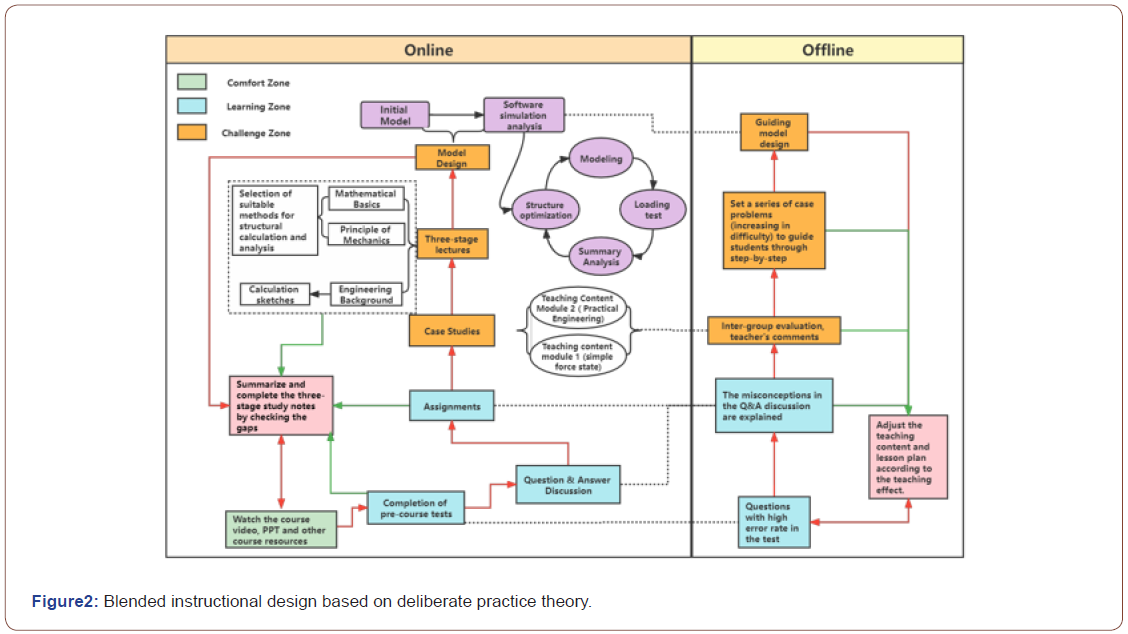
Online teaching
• Combined with the theory of deliberate practice, the
three-stage teaching of the course “Structural Mechanics”
relies on MOOC and beeping websites, and students use their
cell phones or computers to watch the course videos online in
fragmented time and arrange their learning progress flexibly
according to their own conditions. This stage is the comfort
zone.
• Then we move on to the study area: students are required
to complete a pre-test. The teacher selects the appropriate level
of difficulty in the exercise bank and assigns the pre-class test,
which is based on multiple-choice and judgment questions.
• Teachers set up Q&A discussion topics in the cloud class
for the misconceptions of the pre-class test, as well as the key
points and difficulties in teaching, and teachers and students
participate together and arrange them at intervals according to
the students’ real-time mastery.
• The teacher assigns homework in Cloud Class and
depending on the students’ mastery online and offline, the
questions increase in difficulty, requiring students to “tiptoe” to
reach them.
• The “test, question and answer, homework” type of
deliberate practice is mainly to test students’ mastery of the
knowledge objectives, based on this, set higher-order deliberate
practice for the ability objectives, this paper set as a challenging
area, through the flipped classroom to implement.
• The case study is mainly to train students to calculate the
sketch + structural rationality analysis ability, in the course
content module part of the selected case is a simple state of
force (such2021 as the year1218 in Ezhou City, Hubei Province,
Wu Huang high speed and Da Guang high-speed interchange
approach bridge section bridge overturn). It is required to
complete the case analysis and write a report in advance by
cooperating with the structural mechanic’s study group. The
case chosen in the module II part of the course content is a
complex practical project, which needs to be combined with the
subsequent collection of specialized courses to choose a suitable
engineering case. This deliberate exercise is interspersed and
set 2-4 times depending on the students’ learning situation and
status.
• The purpose of the three-stage lecture is to cultivate
students’ mechanical thinking so as to enhance students’ ability
to calculate sketch + calculating analysis. In one part of the
course content module, we choose the internal force diagram of
a static rigid frame which most students are weak in mastering,
and in the second part of the course content module, we choose
the lecture content: solving super-static structure by force
method and displacement method. It is required to finish the
lecture with group discussion, organize the teaching content in order according to engineering background, mathematical
foundation, and mechanics principle, and submit the results as
lecture PPT, video, and summary.
• Structural model design aims to cultivate students’
engineering innovation ability, corresponding to the course
content module 3, by organizing students to participate in our
school academic science and technology festival - structural
design competition project implementation in small groups,
requiring group cooperation and discussion to complete: initial
model → software simulation analysis → structural optimization
→ model making → loading test → summary. The results to be
submitted are structural model, design proposal, and video.
• Write three-stage study notes for each chapter, in
addition to drawing a three-stage mind map for each chapter,
self-summarize the deficiencies in each deliberate exercise,
check the gaps, and integrate them into the study notes of each
chapter to form a closed loop of online teaching.
Off-line teaching: Offline teaching with online teaching, the focus is on teachers organizing classroom teaching based on the teaching feedback from the cloud classroom, timely checking and remediation, and students are always in the learning zone + challenge zone.
• The teacher sets a series of class quizzes of increasing
difficulty and guides students to complete them step by
step according to the pre-class tests, Q&A discussions, and
misconceptions in the homework based on feedback from
the cloud class sessions. For example, drawing a deformation
displacement diagram to determine nodal displacement is a
weak point for students. The teacher will first choose a corner
+ a lateral displacement example, students complete the class
quiz, the teacher speaks and analyzes the ideas, announces
the reference answers and grading criteria, students use a red
pen to correct and revise and then upload the cloud class as
required; next, the horizontal rod is changed to a rigid rod;
on this basis, the vertical rod is changed to a two-force rod,
and three deliberate exercises of increasing difficulty are set
to guide students’ thinking progression and develop their
mechanical thinking The next step is to change the horizontal
rod to a rigid rod; and the vertical rod to a diametrical rod.
• Case studies and three-part lectures are evaluated among
groups, and group comments + teacher comments are given in
a timely manner.
• The teachers follow up and provide guidance in a time
when students encounter problems in the design of structural
models. According to the teaching effect of each link of offline
teaching, the teaching content and teaching progress are
adjusted to form a closed loop of offline teaching.
The entire online + offline teaching from the comfort zone → learning zone → challenge zone set interval, interspersed, diversified deliberate exercises, from easy to difficult, from basic to advanced progressive deliberate exercises, offline and online teaching with each other, through the teacher’s careful design, so that students online learned the basic knowledge to consolidate and flexible application, stimulate students’ interest in learning, led by the sense of achievement to make mechanics learning It is easy and challenging.
Cloud classes provide timely feedback on learning results
Deliberate practice requires a lot of timely feedback. This course provides timely feedback through Cloud Classroom, a learning platform. The instructor publishes a list of tasks and corresponding activities for each class a week in advance in Cloud Classroom, and each deliberate exercise has a corresponding assessment rule, and students can log in to Cloud Classroom to check their grades and comments, which constitute the usual grade for the course. The online and online deliberate exercises provide students with the opportunity to repeat and correct their mistakes in a timely manner, creating a sense that “making mistakes is an opportunity to learn”. When mistakes are made, teachers should encourage students to face up to them and not be afraid to make mistakes, and correcting mistakes is progress.
Conclusion
The attainment of structural mechanics (1) for civil engineering students was: 2017 grade for 0.72, 2018 grade for, 0.76 and 2019 grade for 0.76. 2019. The level students, despite their weak foundation and after adding deliberate practice, have the same learning effect as 2018 the level. In the author’s opinion: by guiding students to complete deliberate practice from comfort zone → learning zone → challenge zone, from easy to difficult, from basic to advanced progressive, the harvest after the effort is more accomplished, enhance students’ learning enthusiasm, develop their mechanical thinking and vision, stimulate their learning potential, and promote the achievement of the course teaching objectives. In this process, the role of the teacher is particularly important.
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by Guangdong Provincial Teaching Reform Project “Teaching Reform and Practice of Mechanics Course for New Engineering” (GDJX2018016); Wuyi University Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project (2020CX04)
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
References
- Wu AH, Hou YF, Yang QB, et al. (2017) Accelerating the development and construction of new engineering disciplines to actively adapt to and lead the new economy [J]. Research on Higher Engineering Education 1: 1-9.
- Anders Eriksson, Wang Zhenglin (2016) Deliberate practice [M]. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press, pp. 10.
- Wang Xiaowei, Wang Minrong, Chen Kongliang, Yan Shaorong (2021) A three-stage teaching method for Structural Mechanics. Science and Technology Wind 6: 49-50.
-
Xiaowei Wang, Zhide Li . Hybrid Teaching Practice of Structural Mechanics Based on Deliberate Practice Theory. Glob J Eng Sci. 9(2): 2022. GJES.MS.ID.000709.
-
Structural mechanics, Deliberate practice, Hybrid teaching
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






