 Research Article
Research Article
Effect Analysis of Different Treatment Methods for Soft Soil Foundation of Highway
Lu-Hao He and Hong-Jun Liu*
School of Civil Engineering and Architecture Wuyi University, Jiangmen, Guangdong, China
Hong-Jun Liu, Geotechnical engineering and road engineering, School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Wuyi University, Jiangmen City, Guangdong Province, China.
Received Date: June 25, 2020; Published Date: July 10, 2020
Abstract
With the rapid development of Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao Bay area, the intercity rapid traffic network with high-grade highway as the main part has been developed rapidly. At the same time, the technology related to the soft soil foundation treatment of highway has also been developed. Based on a highway project in Foshan, Guangdong, this research used on-situ monitoring to study 4 kinds of soft soil foundation treatment methods, including preloading method, cement mixing pile, high-pressure jet grouting pile and Cement Flying-ash Gravel (CFG) pile, and then comparatively analyzed the influence of different treatment methods on the settlement of soft foundation. Finally, hyperbolic method was used to calculate the final settlement and post-construction settlement. The results showed that under the similar thickness of soft soil layer, treatment depth and filling height, CFG pile and high-pressure jet grouting pile have the best effect of controlling settlement after construction, which are 8.638mm and 14.584mm respectively; Cement mixing pile was followed by 23.196mm; preloading method are the worst at 71.731mm. In addition, the cumulative settlement of the preloading method is the largest, which are 212mm; the cement mixing pile is the second, which are 160mm; the CFG pile and the high-pressure jet grouting pile are the smallest, which are 120mm and 132mm, respectively. The research results provide a basis for the design and construction of soft soil foundation treatment for highway in the future.
Keywords: Treatment effect of highway soft soil foundation; Bagged sand well; Cement mixing pile; High- pressure jet grouting pile; CFG pile
Introduction
Soft soil [1] refers to fine-grained soil which natural void ratio is greater than 1.0 and natural water content is greater than the liquid limit. It includes silt, silty soil, peat and peaty soil, etc. In the construction of highway, due to the soft soil has low bearing capacity and high compressibility, the subgrade will inevitably collapse and uneven settlement if proper methods are not taken to deal with it. At present, there are many treatment methods for highway soft soil foundation, such as sand wick stacking load and consolidated drained technique, cement mixing pile, high-pressure jet grouting pile and CFG pile.
The bagged sand well [2] is by applying a load step by step on the soft soil foundation and draining the pore-water from the soil by vertical drainage such as bag sand-well, so that the soft soil foundation is consolidated and settled, which will improve the strength of soft soil. The cement mixing pile [3] is a method to make the soft soil harden gradually and improve foundation strength through injecting cement into the depth of foundation and mixing with soft soil with special mixing equipment. High-pressure jet grouting pile [4] is a method to replace soft soil layer and squeeze around the pile through spraying cement slurry into soil rapidly. CFG pile [5] is made of cement, fly ash, crushed stone, gravel or sand mixed with water to form a high bonding strength pile, and it forms a composite foundation together with pile layer and mattress.
Based on the highway project from Gaoming Bridge to Fulong Bridge in Foshan, the subsidence monitoring analysis of the above 4 kinds of soft soil foundation treatment is carried out. By using hyperbolic method, the final settlement of highway roadbed and post-construction settlement of highway roadbed are calculated. Relying on the quantitative data, this paper analyzes the treatment effect of soft soil foundation from the perspective of engineering technology and provides the basis for the design and construction of similar soft soil foundation treatment.
Project Overview and Geological Situation
Project overview
The project is the highway project from Gaoming Bridge in Foshan city to Fulong Bridge, namely the north extension line of Yangxi Avenue. The length of the route is about 9.020km, and the stake number ranges from K27+ 780 to k36+800. It is arranged according to the two-way 6-lane section and adopts the first-class highway standard to take into account the function of urban roads. The design speed of the main road is 80km/h, and the design speed of the auxiliary road is 40km/h.
Geological situation
The landform along the project is mainly alluvial plain and denudation monadnock. Most of the surface is farmland and fishpond, with abundant water source. The research area is alluvial plain, which is the plain area on the West Bank of the Pearl River Delta. The main mileage is from K27+800 to K30+150, K31+450 to K31+750, k32+000 to k33+650, k33+900 to K37+150. It belongs to the first terrace of Quaternary sedimentation, with flat terrain and abundant water sources around. The ground elevation is generally 3.0-11.0m. The overlying soil layer is mainly quaternary alluvial cohesive soil and sand, and some of the overlying soil layers are special soil layers, such as developed soft soil and saturated liquefied soil, in local fishponds, rivers and ditches. The underlying bedrock is the upper Cretaceous (K2ss), upper Triassic (T3x) and lower Carboniferous (C1s).
According to the survey results, the foundation overburden along the line was composed of artificial fill (Q4ml), Quaternary Holocene fluvial facies alluvium (Q4al), (Q3el), the upper Cretaceous (K2ss), upper Triassic (T3x) and lower Carboniferous (C1s). The basic physical and mechanical properties of soft soil are shown in Table 1.
Table 1:Quality indicators to assess the oil on the “spot test».
Surface Subsidence Monitoring
Installing and monitoring settlement plates
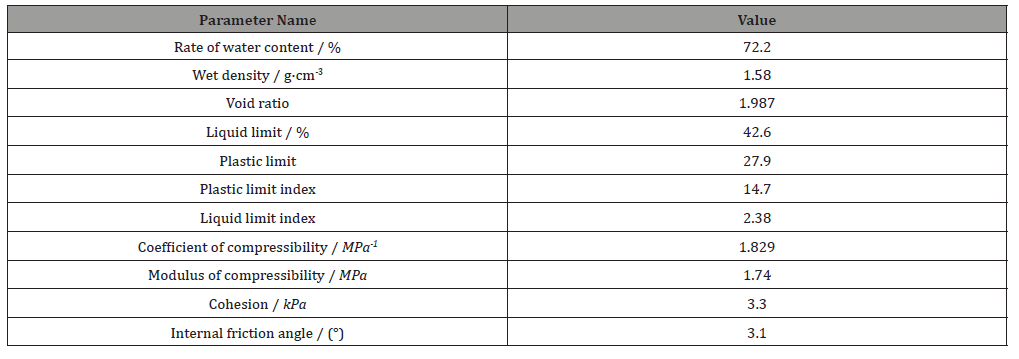
The settlement plate consisted of a steel plate, a measuring rod and a protective sleeve, as shown in Figure 1. The site setting out was carried out according to the coordinates of the design drawing, and the excavation was carried out manually to the original ground. After clearing the pit bottom, lay a 3~5cm thick fine sand cushion and then put the settlement plate on the sand cushion to ensure the bottom plate was flat and stable. Subgrade settlement monitoring was mainly carried out by geometric leveling method. During the filling stage, the accuracy level of leveling was grade III. But during the preloading period, the accuracy level of leveling was grade II. As the embankment was filled high, the settlement plate pole and protective casing were increased section by section. The height of each section was 50cm. In order to obtain the settlement of this period and the initial elevation before the next measurement, elevation was measured before and after connecting the rod, as shown in Figure 2.

Selection of monitoring section for surface subsidence
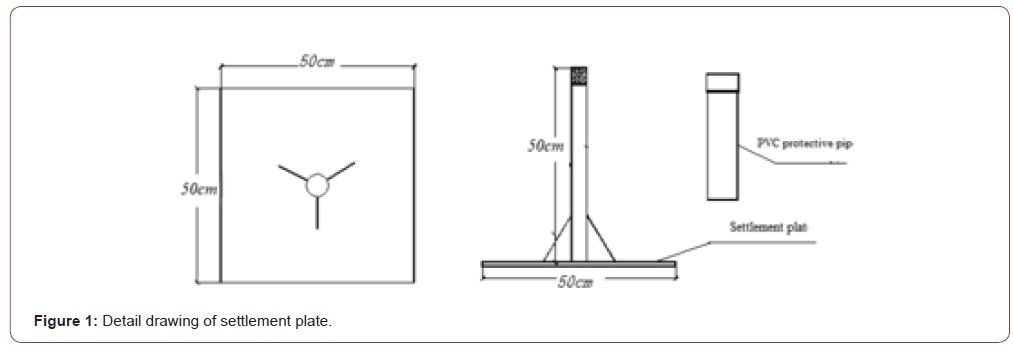
The layout of settlement monitoring points is shown in Figure 3.
In order to compare and analyze the effects of the four treatment methods, four monitoring sections with similar soft soil thickness, filling height and treatment depth were selected for study. The soft soil thickness, filling height and treatment depth of each monitoring section are shown in Table 2.
Site map of various soft-based approach
The site construction of the four soft-based methods is shown in Figure 4.
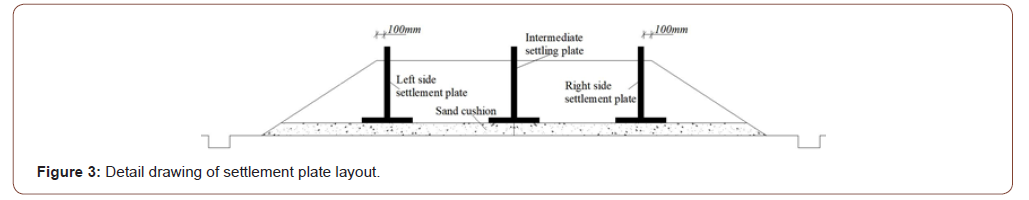
Table 2:Treatment of each section.
Effect Analysis of Four Soft Soil Foundation Treatment Methods
Analysis of ground settlement
Ground settlement was the basis for the analysis of soft ground settlement. Its change rule was not only the most important target for controlling the construction schedule and arranging later construction, but also the most direct test standard for judging whether the theoretical research results were correct. In this project, thin-Layer Intermittently Adding Method [6] was adopted for filling, and each layer of filling was about 40cm. During the monitoring of soft soil foundation, each fill layer was monitored once. After the completion of embankment filling, it would be monitored every 5 days until the preloading period was completed. The cumulative settlement time-history curves of the four types of soft ground treatment are shown in Figures 5-8.
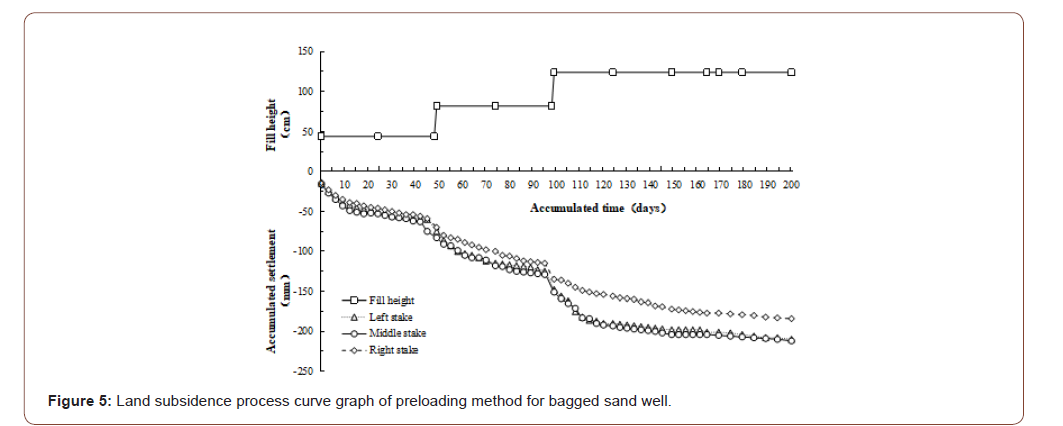
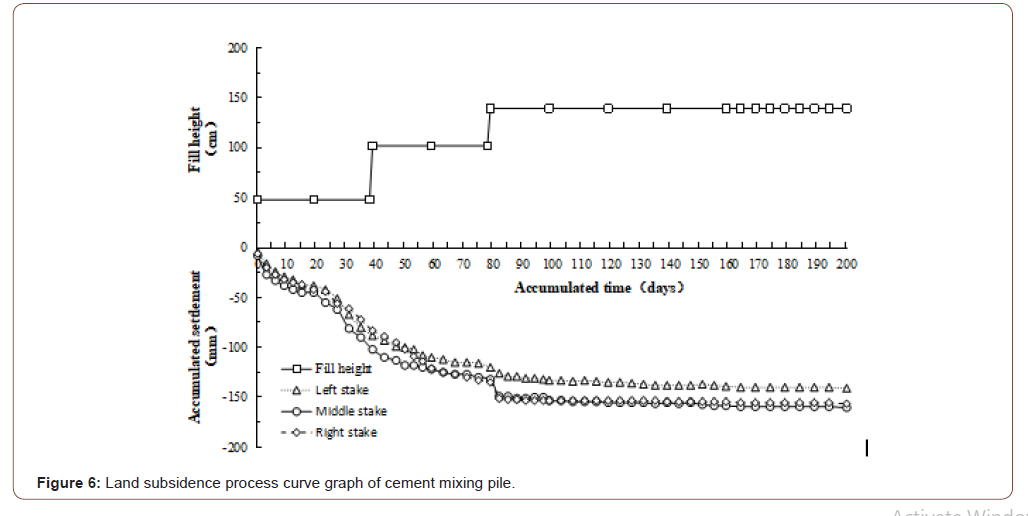
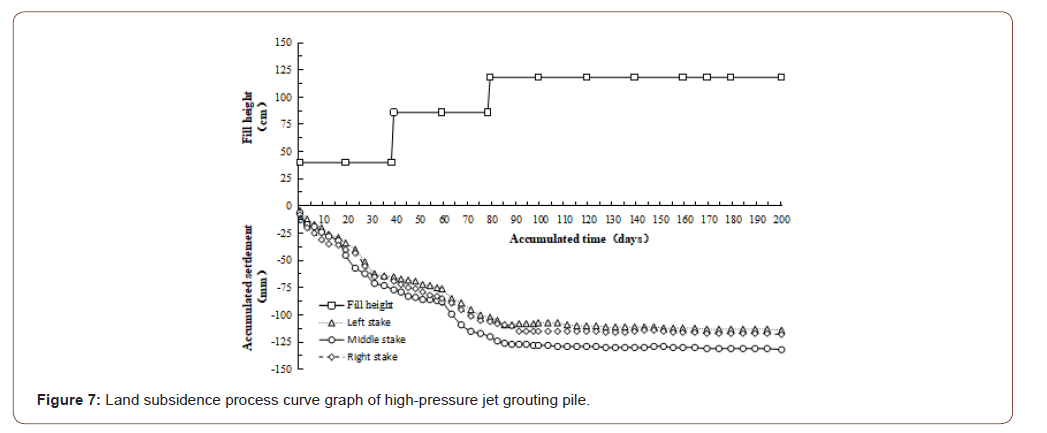
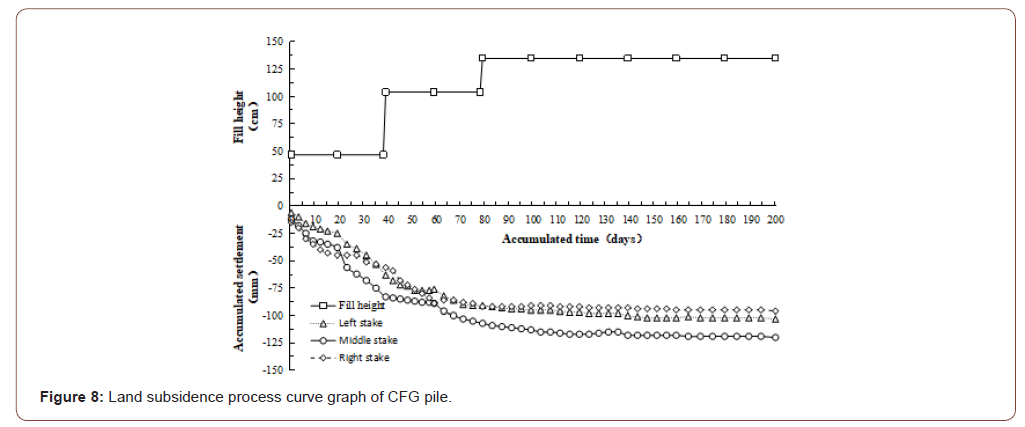
By analyzing the above curves, the following conclusions can be drawn:
• At the same filling height, the settlement of foundation was closely related to the filling thickness. The total settlement of the above four soft foundation treatments increased with the increase of filling height, and all of them show certain regularity. During the filling, the settlement curve generally appeared obvious subsidence phenomenon, and the change was steep; During the period of constant load, the settlement changed slowly and gradually flattens out in the later period. In addition to the preloading method of packed sand well, the curve convergence of the other three methods was faster in the preloading period.
• By comparing the settlement process of the left, middle and right settling plates, it could be found that the settlement amount of the middle settling plate was generally greater than that of the left and right settling plates, which was consistent with the distribution principle of additional stress.
• That was to say, the additional stress on the horizontal plane at the same depth under the ground was different, the additional stress along the line of action of the force was the largest, and gradually decreases toward both sides.
• At a similar filling height, when the pile was loaded to the 200th day, the accumulated settlement of the bagged sand well was 212mm; the cement mixing pile was 160mm; the highpressure jet grouting pile and the CFG pile were 132mm and 120mm respectively. From the perspective of technology, the bagged sand well method was different from the other three methods. The bagged sand well method was to put the sand and gravel into the long bag of pervious geotextile and set it in the soft soil foundation to form a drainage channel. And under the load, as the excess pore-water pressure dissipated gradually, the effective stress of the soil itself increased gradually to make the strength of the foundation soil increase gradually. However, the foundation treated by cement mixing pile, high pressure jet grouting pile and CFG pile was composite foundation with piles and cushion [7]. It was composed of two parts, the matrix and the reinforcement, which were two kinds of materials with different stiffness modulus. Under the load, the pile and the soil between the piles shared the upper load and coordinated the deformation; Therefore, the settlement control effect of composite foundation with piles and cushion was better than that of bagged sand well under the similar filling height.
Analysis of surface subsidence rate
Settlement rate could directly reflect the speed of embankment settlement in the process of loading and it was one of the important indexes to control the speed of filling. In the process of loading, the settlement and stability should be monitored synchronously. The filling rate was strictly controlled, and the control standard was the central settlement rate of embankment less than 10mm/d.
According to the monitoring data, the intermediate settling plates in the four methods were selected for settlement rate analysis. The settlement rate cure is shown in Figure 9.
By analyzing the settlement rate curve in Figure 9, the following conclusions can be drawn:
• “Thin-Layer Intermittently Adding Method” was used for filling, and the monitoring data results showed that the settlement rate was not more than 10 mm / D, and there was no overall sliding failure on site. It had been proved that this method, which was an economic, applicable and reasonable scientific method, increased the stability of embankment construction and is
• The maximum settlement rate of bagged sand well, cement mixing pile, high-pressure jet grouting pile and CFG pile appeared in the loading period, the values were 6.33mm/d, 5.50mm/d, 3.67mm/d and 4.50mm/d respectively.
This showed that the settlement rate had a rapid increase process with each stage of loading, and then gradually became slow convergence;
In the later period of constant load, the settlement rate gradually tended to be stable.
In the whole process, the curve changed very slowly until the curve tended to level, which showed that the settlement process of the whole embankment was basically completed.
• In terms of the above four kinds of soft foundation treatment effect, the settlement effect of composite foundation with piles and cushion should be better than that of bagged sand wells. This was because under the load, the friction between pile and soil was increased through deformation, which improved the bearing capacity of foundation. In this way, the settling rate decreased in the later period of constant load, which indicated that the settlement of the foundation was limited.
• As far as bagged sand wells were concerned, the larger value of the settlement rate usually occurred in the filling period. While during the preloading period, the settlement rate was obviously reduced, which showed that the bagged sand well played a good role in drainage consolidation to make the consolidation degree of the soft soil foundation improve and to control the subgrade settlement.
• As far as the pile composite foundation is concerned, the effect of high-pressure jet grouting pile and CFG pile was better than that of cement mixing pile on controlling settlement rate. This showed that the method of spraying cement slurry into the soil layer through a high-pressure rotating nozzle was better than the method of mixing cement into the soil layer through a mixer at a low speed.
Compared with the cement mixing pile, CFG pile was mixed with gravel, sand, fly ash, which could increase the stiffness of the pile and improved the bearing capacity of the foundation, so the effect of settlement control was increased by about 25%.
Calculation and Analysis of Subgrade Final Settlement and Post-Construction Settlement
At present, the methods to predict the settlement by the monitoring data included hyperbolic method [8], exponential curve method, settlement rate method, three-point method, Poisson method, etc.
Among these common methods, the consolidation degree calculated by hyperbolic method was conservative, which was more favorable for engineering practice, so hyperbolic method was commonly used in engineering.
In the analysis of the monitoring data, it was found that the settlement had a good hyperbolic relationship with time, so the hyperbolic method was used in this project to calculate the final settlement and post construction settlement.
According to the monitoring results of surface subsidence, the final settlement and post construction settlement were calculated by hyperbolic method. On the basis of specification, the middle pile was selected as the calculated object. The steps to determine the settlement calculation are as follows:
• Determine the starting time (T0). In this paper, the starting time was taken after the last stage of subgrade filling construction was loaded;
• According to the monitoring data, “Δt-Δt /ΔS” curve was drawed to determine the coefficient ɑ and β;
• Calculated S∞;
• Calculated St;
• Fitting and comparison were carried out according to the formula.
y = βx +α (1)
The final settlement and post-construction settlement calculated by hyperbola are shown in Table 3. The fitting curve is shown in Figure 10.
By analyzing Table 3 and Figure 10, the following conclusions can be drawn:
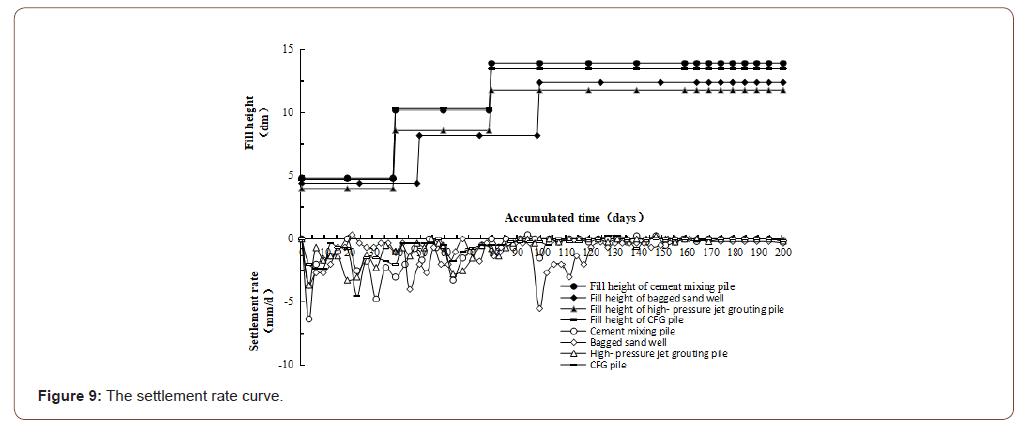
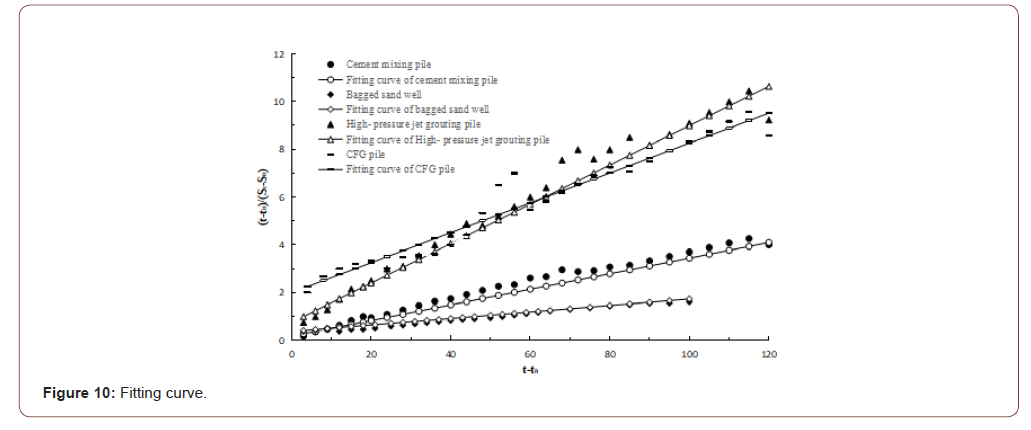
Table 3:Calculation of final settlement and post construction settlement by hyperbolic method.
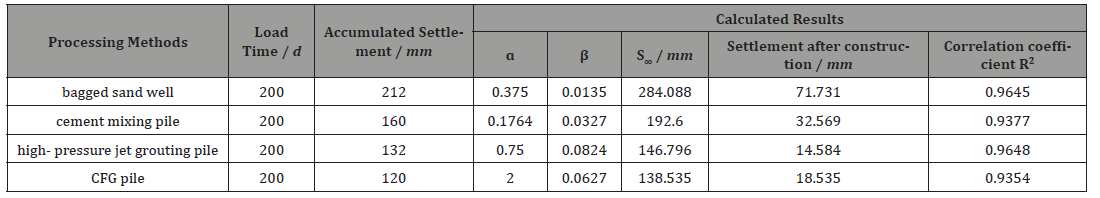
• According to the calculation results of the hyperbolic method, it could be found that the post-construction settlement of the above four treatment methods was less than the 20cm required by the specification. This indicated that these four methods were feasible and effective for the treatment of soft soil subgrade in highway engineering. Among them, high-pressure jet grouting pile and CFG pile had the best effect in controlling post construction settlement, with post construction settlement values of 8.638 mm and 14.584 mm respectively; followed by cement mixing pile and bagged sand well, which was 23.196 mm and 71.731 mm respectively.
• Compared with the actual post-construction settlement, the final settlement calculated above might not be absolutely accurate. This was due to the complexity, variability, and randomness of the geological conditions. For example, the damage of the settlement plate would bring certain errors to the calculated settlement results. However, it could show the subsidence volume and its development trend from the macroscopic view.
• The hyperbolic method was used to calculate the settlement after construction of four soft foundation treatment methods, and the correlation coefficient “R2” of curve fitting was greater than 0.93, which showed that the results of the hyperbolic calculation and the monitoring data were highly correlated and credible.
However, it could be found that the large deviation between the fitting curve and the monitoring data mainly occurred 80 days before the constant load, and then the deviation between the two decreased after 80 days from Figure 10. This error was mainly due to the preliminary construction machinery for embankment frequently caused by the repeated rolling. Although the time of the construction machinery passing on the embankment was short, the additional stress of the self-weight on the soft soil foundation could not be ignored, especially the rolling of the embankment by the construction machinery with large tonnage (such as the full load dump truck, roller, etc.). This is the main reason for the settlement in the early period of preloading, but the law of settlement growth in the preloading period of soft soil foundation was obscured. Therefore, the fitting deviation of the settlement curve in the early period of preloading was obviously lower than that in the middle period.
Conclusion
Taking a highway project in Foshan, Guangdong as an example, the four soft foundation treatment methods of bagged sand well, cement mixing pile, high-pressure rotary jet pile and CFG pile were studied, and the following conclusions were drawn:
• Under the similar thickness of soft soil, treatment depth and filling height, the settlement of the foundation treated by the above four soil soft foundation treatment methods is closely related to the filling height, and the total settlement of the foundation increases with the increase of filling height. In addition, the slope of the settlement curve of the four treatment methods is relatively steep during the stage loading. But after the loading is completed, the settlement curve gradually tends to be gentle, which shows that the settlement of the foundation is limited. It conforms to the compression settlement law of the foundation.
• Based on the analysis of monitoring data, at a similar filling height, the accumulated settlement of the bagged sand well reach the maximum at the 200th day of stacking, reaching 212mm, followed by the cement mixing pile, reaching 160mm. and the high-pressure jet grouting pile is similar to the CFG pile, reaching 132mm and 120mm respectively. And four kinds of soft soil foundation treatment methods can effectively control the total settlement of the foundation.
• In the process of preloading, on-site monitoring was used to effectively control the loading rate and reasonably arrange the construction schedule, in which the maximum daily settlement rate was 6.33mm/d for the bag sand well and 3.67mm/d for the CFG pile. And during this period, the soft soil foundation did not appear obvious slip phenomenon, which ensured the stability and safety of embankment in the loading process.
• The hyperbolic method is used to calculate the final settlement and post construction settlement of soft soil subgrade. The results show that the high-pressure jet grouting pile and CFG pile have the best effect in controlling post construction settlement, with the minimum value of post construction settlement of 8.638 mm and 14.584 mm for each, followed by cement mixing pile, with 23.196 mm, and the bagged sand well is poor, with 71.731mm.
• After considering the construction cost, construction period and construction difficulty, cement mixing pile has a higher property value in the treatment of soft foundation in these four methods, which provides a reference for the comparison and selection of early schemes for similar projects.
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
References
- Liu Hanlong, Zhao Minghua (2016) Review of ground improvement technical and its application in China[J]. China Civil engineering Journal 49(01): 96-115.
- Yu Chenghua, Li Jufeng (2010) Fluid-solid coupling simulation of settlement process in soft ground based on drainage consolidation method with sand well[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics 31(03): 939-943.
- Xin Hong Guo, Guang De Wu, Xin Huan Guo (2013) Study on the Scope of Application of Cement Deep Mixing Pile to Consolidate Soft Soils[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, pp. 2746.
- Wang Yan Ning, Jiang Bin Song, Yu Jian, Gao Chao, Fang Da Yong (2017) In-situ experiment on composite foundation of high-pressure jet grouting piles of Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 36(06): 1514-1521.
- Li San Ming, Yan Bo, An Hai Tang, Cheng Zong Liang, Xu Wei (2017) Causes and processing methods for quality defects of soft foundation reinforcement using CFG piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 39(S2): 216-219.
- Liang Bin Bo (2009) The Application of the Thin-Layer Intermittently Adding Method to the Construction of Soft Soil Foundations for Expressways[J]. Traffic Engineering & Technology for National Defence 7(05): 57-58+64.
- Yang GuangHua, Li DeJi, Guan Da Shu (2011) Optimization Design of Rigid Pile Composite Foundation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 30(04): 818-825.
- Lihua Yin, Xudong Sun, Ping Yang, Meixia Li (2018) Stability Analysis for Subgrade Settlement Prediction by Curve Fitting Methods[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 170(3).
-
Lu-Hao He, Hong-Jun Liu. Effect Analysis of Different Treatment Methods for Soft Soil Foundation of Highway. Glob J Eng Sci. 6(1): 2020. GJES.MS.ID.000629.
-
Treatment effect of highway soft soil foundation, Bagged sand well, Cement mixing pile, High- pressure jet grouting pile, CFG pile
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Project Overview and Geological Situation
- Surface Subsidence Monitoring
- Effect Analysis of Four Soft Soil Foundation Treatment Methods
- Calculation and Analysis of Subgrade Final Settlement and Post-Construction Settlement
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgement
- Conflict of Interests
- References






