 Mini Review
Mini Review
Ozone Therapy in Periodontology
Semih Akgül, Mehmet Kızıltoprak and Mustafa Özay Uslu*
Department of Periodontology, Inonu University, Turkey
Mustafa Ozay Uslu, Inonu University, Faculty of Dentistry, Department of Periodontology, Malatya, Turkey.
Received Date: September 12, 2018; Published Date: November 08, 2018
Abstract
Ozone is a strong oxidant and an effective antimicrobial agent. Ozone therapy has been successfully applied in the treatment of various diseases in medicine and dentistry for many years. Ozone has antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, metabolic and biosynthesis-enhancing effects. In this review, the use of ozone in periodontology is evaluated along with past studies.
Keywords:Ozone; Periodontology; Periodontal treatment
Introduction
Ozone therapy, due to its various effects on periodontal tissues, is used in periodontology as well as in many branches of dentistry [1]. The first person to consider using ozone gas or ozonated water in dentistry practice is the Swiss dentist, EA Fisch [2] used ozonated water in the early 1930s for surgical disinfection and wound healing.
Biological effects of ozone
Ozone has antimicrobial effects on the human body, stimulating the immune system, increasing blood circulation, biosynthetic, analgesic and detoxification effects [3].
Antimicrobial effect
Ozone shows a cytotoxic effect on bacteria, fungi and viruses. The antimicrobial effect of ozone is selective against microbial cells and does not harm human cells. Ozone is also very effective in antibiotic resistant species. The effect of ozone on viral infections; it is based on the sensitivity of the infected cells to changes in peroxide and reverse-cryptase activity [1,3].
The immune system stimulating effect: Ozone has a strong effect on the cellular and humoral immune system. It contributes to the proliferation of defense cells, immunoglobulin synthesis, as well as the phagocytosis function of macrophages. Ozone causes the expression of anti-inflammatory and wound healing cytokines such as interleukin, leukotriene and prostaglandin [3]. While low concentration of ozone causes immunostimulatory effect, high concentration of ozone creates immunodepressive effect [1,4].
Antihypoxic effect: Ozone causes partial oxygen pressure in the tissues and oxygen transport in the blood to cause changes in cell metabolism. Superoxide dismutase, catalase, dehydrogenase, glutathione peroxidase enzymes are activated with low-dose ozone. These enzymes protect the organism from free oxygen radicals [3]. Increases the contact surface of erythrocytes for oxygen transport. It is important in circulatory disorders, in stimulating circulation and in revitalizing organ functions [5,6].
Biosynthetic effect: Activates the mechanism of protein synthesis. Increase the amount of ribosome and mitochondria in cells. These changes at the cell level; stimulates the potential of regeneration in tissues and organs by raising functional activities [3].
Analgesic and detoxification effect: It causes the release of vasodilators such as nitric oxide (NO) and causes dilatation of arterioles and venules [6].
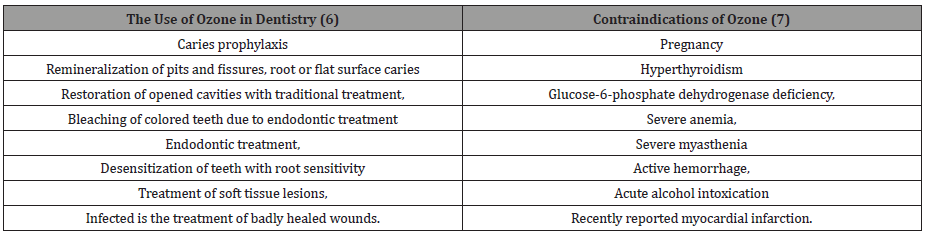
Ozone toxicity: Inhalation of ozone may be toxic to the pulmonary system and other organs. Therefore, long-term exposure to ozone may indicate some side effects such as epiphora, upper respiratory irritation, bronchoconstriction, rhinitis, cough, headache and vomiting. In ozone poisoning, the patient is brought to supine position and treated with vitamin E and N-acetyl-cysteine [7-9] (Table 1 & Table 2).
Table 1

Table 2:
Ozone Studies in Periodontology: In periodontology, ozone is used to eliminate pathogenic bacteria and to treat periodontal/ peri-implanter diseases. A number of studies have been conducted investigating the antimicrobial activity of ozone, its contribution to wound healing, its effects on peri-implant/ periodontal diseases and implant osteointegration.
Microbiological and histopathological Studies of Ozone Microbiological and histopathological Studies of Ozone
Positive effects
When these studies are examined; it showed significant improvement in clinical parameters such as periodontal pocket depth, clinical attachment level, gingival index, plaque index and it has been observed that the number of microorganisms such as Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and Spirochetes decreases significantly [10-17]. It has been reported to be effective in decreasing gingival inflammation and decreasing lactate dehydrogenase enzyme level [18]. The effect of ozone gas on mechanical treatment was similar with Er: Yag laser [19].
Ineffective results
The studies showing that ozone treatment does not provide additional benefit to mechanical therapy is available in the literature [20-23]. In an in vitro study, it was reported that ozone was effective on E.fecalis but did not show this effect in biofilm [24]. In another in-vitro study, it was observed that the effect of ozone on microorganisms within organized cryogenic biofilms was minimal. (25).
Wound Healing Studies of Ozone
Positive effects
When the studies that ozone is applied in wound healing; ozone administration has been reported to increase blood perfusion, significantly reduce genotoxic damage, contribute positively to wound healing and improve post-operative quality of life, and the results confirm that ozone has an antimicrobial potential [26-31].
Ineffective results
There were no studies in the literature that showed negative effects.
Peri-implant disease studies of ozone
Positive effects: Considering the studies in which ozone is applied in the treatment of peri-implant disease; it has been concluded that ozone has a good potential in the treatment of peri-implant mucositis, its additional use in surgical regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis has positive results in implant surface decontamination and the use of ozone also increases the immediate implant stability in the posterior mandible [32-34].
Ineffective results: In an in-vitro study, the antibacterial effect of ozone gas on the implant surface was investigated. While ozone gas had a selective effect on bacteria, no effect was found on the adherence of osteoplast-like cells[35].
Lichen planus studies of ozone
Positive effects: When we look at the studies of ozone in the case of oral lichen planus; It was concluded that combined ozone and steroid treatment were safe and effective and provide lesions healing [36,37].
Ineffective results There were no studies in the literature that showed negative effects.
Conclusion
There are many studies showing that the use of ozone in periodontal treatments is found useful in the literature. Further studies are needed to fully understand the effects of ozone and to increase clinical use.
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
References
- Gupta G, Mansi B (2012) Ozone therapy in periodontics. Journal of medicine and life 5(1): 59-67.
- Reddy S, Reddy N, Dinapadu S, Reddy M, Pasari S (2013) Role of ozone therapy in minimal intervention dentistry and endodontics-a review. Journal of international oral health JIOH 5(3): 102-108.
- Seidler V, Linetskiy I, Hubalkova H, Stankova H, Smucler R, et al. (2008) Ozone and its usage in general medicine and dentistry: A review article. Prague Med Rep 109(1): 5-13.
- Srikanth A, Sathish M, Harsha AVS (2013) Application of ozone in the treatment of periodontal disease. Journal of pharmacy & bioallied sciences 59(1): S89-S94.
- Saini R (2011) Ozone therapy in dentistry: A strategic review. Journal of natural science, biology and medicine 2(2): 151-153.
- Bhateja S (2012) The miraculous healing therapy–“Ozone therapy” in dentistry. Indian Journal of Dentistry 3(3): 150-5.
- Nogales CG, Ferrari PH, Kantorovich EO, Lage-Marques J (2008) Ozone therapy in medicine and dentistry. J Contemp Dent Pract 9(4): 75-84.
- Bocci V, Aldinucci C (2006) Biochemical modifications induced in human blood by oxygenation‐ozonation. Journal of biochemical and molecular toxicology 20(3): 133-138.
- Bocci V (2006) Is it true that ozone is always toxic? The end of a dogma. Toxicology and applied pharmacology 216(3): 493-504.
- Schlagenhauf U, Horlacher V, Netuschil L, Brecx M (1994) Repeated subgingival oxygen irrigations in untreated periodontal patients. Journal of clinical periodontology 21(1): 48-50.
- MI R GH, MI M ZB (2005) Management of aggressive periodontitis using ozonized water. Egypt Med JNR C 6(1): 229-45.
- Kshitish D, Laxman VK (2010) The use of ozonated water and 0.2% chlorhexidine in the treatment of periodontitis patients: A clinical and microbiologic study. Indian Journal of Dental Research 21(3): 341-348.
- Dodwad V, Gupta S, Sethi M, Kumar K, Masamatti S (2011) Changing paradigm in pocket therapy–Ozone versus Conventional irrigation. International Journal of Public Health Dentistry 2(2): 7-12.
- Hayakumo S, Arakawa S, Mano Y, Izumi Y (2013) Clinical and microbiological effects of ozone nano-bubble water irrigation as an adjunct to mechanical subgingival debridement in periodontitis patients in a randomized controlled trial. Clinical oral investigations 17(2): 379- 388.
- Iliadis D, Millar BJ (2013) Ozone and its use in periodontal treatment. Open Journal of Stomatology 3(02): 197.
- Shoukheba M, Ali SA (2014) The effects of subgingival application of ozonated olive oil gel in patient with localized aggressive periodontitis: A clinical and bacteriological study. Tanta Dental Journal 11(1): 63-73.
- Eltas A YD (2012) An Assessment of Clinical Effects of Gaseous Ozone on Treatment of Gingival Inflammation. Inonu University Health Sciences Journal 2: 29-32.
- Dhingra K, Vandana K (2011) Management of gingival inflammation in orthodontic patients with ozonated water irrigation–a pilot study. International journal of dental hygiene 9(4): 296-302.
- Yılmaz S, Algan S, Gursoy H, Noyan U, Kuru BE, et al. (2013) Evaluation of the clinical and antimicrobial effects of the Er: YAG laser or topical gaseous ozone as adjuncts to initial periodontal therapy. Photomedicine and laser surgery 31(6): 293-298.
- Skurska A, Pietruska M, Paniczko-Drezek A, Dolinska E, et al. (2010) Evaluation of the influence of ozonotherapy on the clinical parameters and MMP levels in patients with chronic and aggressive periodontitis. Advances in medical sciences 55(2): 297-307.
- Katti SS, Chava VK (2013) Effect of ozonised water on chronic periodontitis-a clinical study. Journal of international oral health: JIOH 5(5): 79-84.
- Al Habashneh R, Alsalman W, Khader Y (2015) Ozone as an adjunct to conventional nonsurgical therapy in chronic periodontitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Journal of periodontal research 50(1): 37-43.
- Eltas A YS (2013) Effect on Halitosis the use of Gase Ozone in Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis. Inonu University Health Sciences Journal 1: 1-4.
- Hems R, Gulabivala K, Ng YL, Ready D, Spratt D (2005) An in vitro evaluation of the ability of ozone to kill a strain of Enterococcus faecalis. International Endodontic Journal 38(1): 22-29.
- Muller P, Guggenheim B, Schmidlin PR (2007) Efficacy of gasiform ozone and photodynamic therapy on a multispecies oral biofilm in vitro. European journal of oral sciences 115(1): 77-80.
- Filippi A (2001) The influence of ozonised water on the epithelial wound healing process in the oral cavity. Clinic of Oral Surgery, Radiology and Oral Medicine, University of Basel, Switzerldand.
- Patel PV, Kumar V, Kumar S, Patel A (2011) Therapeutic effect of topical ozonated oil on the epithelial healing of palatal wound sites: a planimetrical and cytological study. Journal of investigative and clinical dentistry 2(4): 248-258.
- Sivalingam VP, Panneerselvam E, Raja KV, Gopi G (2017) Does topical ozone therapy improve patient comfort after surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molar? A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 75(1): 51.e1-51.e9.
- Tasdemir Z, Alkan BA, Albayrak H (2016) Effects of Ozone Therapy on the Early Healing Period of Deepithelialized Gingival Grafts: A Randomized Placebo‐Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of periodontology 87(6): 663- 671.
- kdeniz SS, Beyler E, Korkmaz Y, Yurtcu E, Ates U, et al. (2018) The effects of ozone application on genotoxic damage and wound healing in bisphosphonate-applied human gingival fibroblast cells. Clinical oral investigations 22(2): 867-873.
- Isler SC, Uraz A, Guler B, Ozdemir Y, Cula S, et al. (2018) Effects of Laser Photobiomodulation and Ozone Therapy on Palatal Epithelial Wound Healing and Patient Morbidity. Photomed Laser Surg.
- McKenna DF, Borzabadi-Farahani A, Lynch E (2013) The effect of subgingival ozone and/or hydrogen peroxide on the development of peri-implant mucositis: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. The International journal of oral & maxillofacial implants 28(6): 1483-1489.
- Isler SC, Unsal B, Soysal F, Ozcan G, Peker E, et al. (2018) The effects of ozone therapy as an adjunct to the surgical treatment of peri-implantitis. Journal of periodontal & implant science 48(3): 136-151.
- Karaca I, Ergun G, Ozturk D (2018) Is low‑level laser therapy and gaseous ozone application effective on osseointegration of immediately loaded implants? Nigerian journal of clinical practice 21(6): 703-710.
- Hauser-Gerspach I, Vadaszan J, Deronjic I, Gass C, Meyer J, et al. (2012) Influence of gaseous ozone in peri-implantitis: bactericidal efficacy and cellular response: An in vitro study using titanium and zirconia. Clinical oral investigations 16(4): 1049-1059.
- Kazancioglu HO, Ezirganli S, Aydin MS (2013) Effects of laser and ozone therapies on bone healing in the calvarial defects. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 24(6): 2141-2146.
- Mostafa B, Zakaria M (2018) Evaluation of Combined Topical Ozone and Steroid Therapy in Management of Oral Lichen Planus. Open access Macedonian journal of medical sciences 6(5): 879-884.
-
Semih Akgul, Mehmet Kiziltoprak, Mustafa Ozay Uslu. Ozone Therapy in Perıodontology. Sci J Research & Rev. 1(1): 2018. SJRR. MS.ID.000502.
-
Antimicrobial, Biosynthetic, Analgesic, Detoxification, Immunoglobulin, Dehydrogenase, Glutathione, Peroxidase, Analgesic, Detoxification, Nitric Oxide, Pathogenic Bacteria, Aggregatibacter, Actinomycetemcomitans, Lactate, Lichen Planus, Peri-Implantitis, Biofilms, Myasthenia Hemorrhage
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






