 Clinical
Clinical
Association Between Leptin and Lipid Profile in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Wafa Zughair Mohi*
Chemistry and Biochemistry, National University for science and technology thiqar, Iraqi
Wafa Zughair Mohi, Chemistry and Biochemistry, National University for science and technology thiqar, Iraqi
Received Date: March 13, 2025; Published Date: March 25, 2025
Abstract
It is not contagious to have diabetes mellitus, high prevalence worldwide disease, the levels of lipids are also affected in diabetes high prevalence worldwide disease due to a variety of factors, as carbohydrate metabolism a lipid metabolism influence objectives. This investigation evaluated, leptin, levels of lipids in people with DM. The study’s participants included A total of 90 participants and 30 healthy controls (Group 1) 30 Dm type 2 patients (Group 2) as well DM with atherosclerosis was identified by utilizing the high value of ELISA and spectrophotometer in DM patients (Group 2) contrasted compared to the wholesome controls (Group 1) at (54.68±9.67), (42.18±4.38) were much greater in group 2 than in group 3 at (54.68±9.67), (25.69±2.61). However additional research involving more people of patients is necessary to establish which marker’s precise function.
Keywords: Leptin; cholesterol; TG, LDL, HDL
Introduction
Chronic diabetes mellitus is a disease that occurs when the pancreas malfunctions the body produces enough insulin or the body produces insulin inefficiently [1]. In accordance with prior medical records is yet no diabetic cure although it is possible to balance the impacts with proper health management and consistent medical check-ups [2]. Greater thirst and greater frequency of urination hunger are all indicators of increased diabetes if untreated blood sugar can have a number of negative effects. Chronic renal failure cardiovascular disease and stroke foot ulcers, poor vision, and all significant long-term issues [3]. The conditions of ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycaemia the worst clinical consequences that can result in a lack of fluids being unconscious and Death in the absence of sufficient therapy [4]. Leptin Adipose tissue is thought to be as a primary repository for fat plays a passive part in the metabolism of energy.
The adipose system is universally acknowledged the biggest endocrine organ ever tissue [5]. It releases lots of hormone Adipokines that regulate nutrition, immunity, and reproduction neuroendocrine function and hormones Adipocyte tissue has been identified since the finding of the leptin gene and obesity [6]. Is a signal of fullness sent by the brain via that adipose cell insulin and glucose metabolism control mechanism and contributes to the balance of energy by using a neuroendocrine mechanism and body weight [7]. Leptin decline mediates weight loss gain through the hypothalamus to boost hunger reduce energy consumption altering neuroendocrine processes [8]. The total plasma lipid ranges from 400 to 600 mg/dl. Cholesterol makes up one third Triacylgycerol makes up one third in addition to others phospholipids are lipids being insoluble in water they aid in they are transported in plasma complexed to create lipoprotein from protein. The lipoprotein’s component protein is identified as APO lipoprotein [9]. Among them are chylomicrons, Extremely Low Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) (LDL) or low density lipoprotein (IDL) or intermediatedensity lipoprotein (HDL) or high density lipoprotein. Protein and fat content varies components, dimensions, density, and place of origin. Work to maintain both of their components being lipid soluble they move in the Plasma will offer an effective method for transferring the tissue’s lipid content [10].
Materials and Methods
Patients and Control
The equation for Daniels sample size formula was used to calculate sample size includes three sets of (90) individuals each the first group consists of the 30 patients mentioned earlier T2DM diagnosis the specified category consists of (30) seemingly healthy controls and 30 patients from the third group have been diagnosed with T2DM and atherosclerosis. Exclusion Criteria
a. Patient with heart diseases and hypertension
b. Pregnant women
c. Smokers
d. Type 1 diabetes patient
e. Chronic liver disease
f. Thyroid disease
Determination of serum leptin
ELISA kits for diagnostics were employed to Calculate the leptin levels in the patient and control groups.
Determination of serum lipid profile
Lipid concentration was measured using spectrophotometer method.
Results
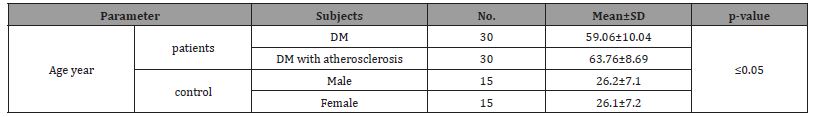
Categories based on age and related groups research reveals a substantial rise patients and D.M. patients’ ages more than with D.M. and atherosclerosis There is a control person significant age reduction in D.M fewer patients than those who have D.M. with atherosclerosis (Table 1 & Figure 1).
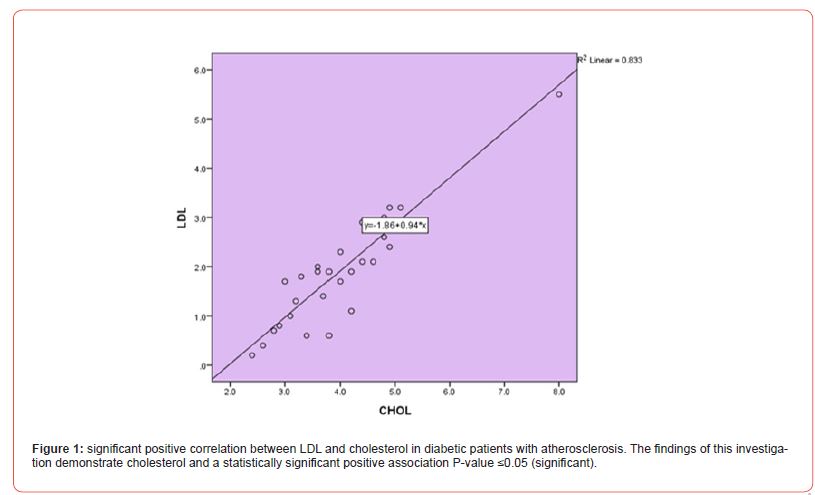
Table 1: Age of Diabetic and Control Groups.
Discussion
The findings of the present study are (Table 1) age-related changes and prevalence T2DM or type 2 diabetes is similar atherosclerosis T2DM is a metabolic condition a disorder frequently connected to fat poor eating patterns and a sedentary lifestyle the possibility of producing T2DM grows as you get older The other hand on the other side atherosclerosis is marked by the plaque accumulation in the arteries which may cause serious cardiovascular issues including heart attacks and strokes Atherosclerosis development risk is also increases with age [11]. These atherogenic factors are a significant part of Apolipoprotein B (Apo B) is a lipoprotein that supports the build up of LDL in the blood Atherosclerosis is started by the intima and is mediated by increased permeability of the endothelium and elevated intimal retention of LDL [11].
There is evidence that diabetes patients Leptin and HDL have a relationship levels In particular research have revealed that Leptin levels that are greater could connected to reduced HDL values cholesterol in people with diabetes one potential The reason behind this link is that Leptin could help with the growth a condition called insulin resistance that can a dyslipidemia (irregular lipid levels) low HDL cholesterol levels Additionally oxidative stress and inflammation are connected to diabetes as well as contributing to lower HDL levels [12].
Conclusions
a. Leptin hormone has a predictive capacity to predict T2DM as they significantly associated with IR and fraction lipid profile.
b. The study showed wide spread abnormalities lipid in the course of D.M. triggered dyslipidemia as hypercholesterolemia hypertriglyceridemia higher LDL and decreased HDL.
References
- D Bora, MP Barman (2022) Diabetes Risk Classification Comparison of Machine Learning Techniques. Neuro Quantology 20(14): 303-308.
- M Rout, A Kaur (2019) Prediction of Diabetes Based on Data Mining Techniques. Think India Jvol 22(16): 3743–3750.
- S Preethikaa, MP Brundha (2018) Awareness of diabetes mellitus among general population. Res J Pharm Technol 11(5): 1825–1829.
- A Rahman, B Babar, A Sebtain, H Gul, M Qasim, et al. (2022) Frequency of Proteinuria in Newly Diagnosed Diabetic Patients. Pakistan J Med Heal Sci 16(06): 935-938.
- S Kaur, C Auger, MG Jeschke (2020) Adipose tissue metabolic function and dysfunction: impact of burn injury. Front Cell Dev Biol 8(1): 599576-599580.
- S Kaplan (2018) Nucleotide polymorphism of leptin gene in Anatolian Water Buffaloes. Pak J Zool 50(5): 1-5.
- A Nunziata, Jan Bernd Funcke, Guntram Borck, Julia von Schnurbein, Stephanie Brandt, et al. (2019) Functional and phenotypic characteristics of human leptin receptor mutations. J Endocr Soc 3(1): 27-41.
- B Yau, Lori Hays, Cassandra Liang, D Ross Laybutt, Helen E Thomas, et al. (2020) A fluorescent timer reporter enables sorting of insulin secretory granules by age. J Biol Chem 295(27): 8901-8911.
- R Ledesma, Raúl B Martínez Pérez, David A Curiel, Laura M Fernández, María L Silva, et al. (2022) Potential benefits of structured lipids in bulk compound chocolate: Insights on bioavailability and effect on serum lipids. Food Chem 375(8): 131824-131829.
- BS Hedegaard, Christian Sørensen Bork, Morten Kaltoft, Ib Christian Klausen, Erik Berg Schmidt, et al. (2022) Equivalent impact of elevated lipoprotein (a) and familial hypercholesterolemia in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 80(21): 1998-2010.
- Turner MC, Neil RW Martin, Darren J Player, Richard A Ferguson, Patrick Wheeler, et al. (2020) Characterising hyperinsulinemia-induced insulin resistance in human skeletal muscle cells. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology 64(3): 125-132.
- Vergès B (2015) Pathophysiology of diabetic dyslipidaemia: where are we? Diabetologia 58(5): 886-899.
-
Wafa Zughair Mohi*. Association Between Leptin and Lipid Profile in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Sci J Biol & Life Sci. 4(1): 2025. SJBLS.MS.ID.000579.
-
Leptin; cholesterol; TG, LDL, HDL
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






