Research Protocol
Research Protocol
An Audit of the Predictive value of SNOT 22 Test in Evaluating Nasal Surgeries Emersons Green /Devizes NHS Treatment Centers-UK
Samir Gendy, Department of ENT Surgery, Ireland.
Received Date: May 16, 2019; Published Date: May 24, 2019
Abstract
The Sino-nasal outcome test (SNOT22) has been widely adopted in clinical practice and has been declared as the most suitable sinonasal outcome scoring system. It is simple disease specific encompassing 22 symptoms reflecting health burden of the rhino- logical patients. Each item quantifies symptoms severity from 0 (no problem) to 5 (worst symptom). The sum of each item results in a maximum score of 110. High score indicates poor outcome. The SNOT22 is a validated questionnaire of disease specific, quality of life-related measures of sinonasal function that has demonstrated good reliability, validity, and responsiveness and is been used in various Rhinological procedures for example septoplasty, Functional endoscopic sinus surgery, Endoscopic turbinoplasty. SNOT22 is recommended by the European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal polyps EPOS 2012 as the most adequate tool to evaluate the effectiveness of surgery for chronic rhino sinusitis [1]. This Audit reflects a single Surgeon experience of using SNOT22 in evaluating a cohort of patients with Rhinological disease comparing the preoperative and postoperative scoring to reflect the outcome of various Rhinological procedures.
Materials and Methods
A Total of 15 patients were randomly selected who hard various nasal surgeries performed by named ENT surgeon at Emersons Green/Devizes NHS treatment Centres in the period from May 2018-November 2018.
Every patient was seen preoperatively in the outpatient clinic where he/she scored his /her symptoms using the SNOT 22 questionnaire chart, 6 weeks postoperatively he/she scored again her symptoms using SNOT22 questionnaire unaware of their preoperative SNOTT -22 scores. The Cohort Age varied from the youngest of 20 years old to the oldest of 65 years old, Various Rhinological Procedures was performed including: Septoplasty with or without Turbinoplasty, FESS Polypectomy, and Endoscopic Turbinoplasty.
All patients had a preoperative Counselling and received an information leaflet about their nasal procedure in addition to SNOT22 Questionnaire chart. Routine blood investigations, informed Consent was signed in the clinic. Postoperatively all patients received oxymetazoline nasal drops 0.05% 2 drops twice daily for 5 days followed by isotonic Sterimar nasal sprays for 2 weeks, A 10 days course of 500mg Clarithromycin antibiotic 12 hourly was prescribed in selected FESS Polypectomy patients where signs of active infection were illustrated intra-operatively. All patients were seen 6 weeks postoperatively to assess their symptoms clinically and by SNOT22 questionnaire chart. The mean Pre-operative SNOT22 score off all 15 patients was 46.2 and the mean post-operative SNOT22 score was 9.2 with an overall of 70% improvement in patient’s symptoms.
Results
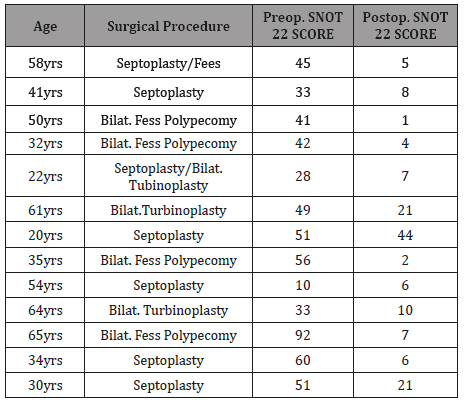
Summaries the Cohort of patients included in this audit comparing the preoperative with the Postoperative SNOT22 scores following each performed surgical Procedure (Table 1).
Table 1: Comparing the Preoperative and Postoperative SNOT 22 Scores of each patient.
Discussion
The 22-item Sino-Nasal-Outcome test (SNOT22) is a widely applied patient-reported outcome instrument used to assess the severity of symptoms associated with chronic Rhinosinusitis, However recent publication suggest that it is also a validated outcome that can measure the improvement of patient’s symptoms postnasal Obstruction Surgical procedures, as septoplasty, turbinoplasty [2]. Kennedy et al. [3] Grouped the SNOT 22 questions into 4 main categories: Nasal related (need to blow nose, sneezing, runny nose, nasal obstruction, loss of smell/taste and post nasal drip.), Ear/Facial related (ear fullness, dizziness, ear pain, facial pain&pressure), Quality of life related (difficult falling asleep, wake up at night, wake up tired, and fatigue, reduced productivity, reduced concentration), Psychologically related (frustrated/ restless, sad, embrassed), Kennedy et al. Concluded that SNOT-22 is helpful tool for quantifying changes in symptoms and can be used to predict extent of post-operative improvement. While all of the components of the SNOT-22 significantly improved after surgery, only runny nose, as well as cough were independent predictors of post-surgical SNOT22improvement. Harries etal. Published an article assessing the usefulness of SNOT22 test to measure the success of septal surgery. A Total of 40 patients were included in the study the mean total pre-operative SNOT-22 score was 36.3 compared to a mean post-operative score of 19.3 with a total of 47% improvement in patient’s symptoms. The study considered an improvement is defined as reduction of > one point [4].
Conclusion
This Audit of a single surgeon experience at Emersons Green/ Devizes NHS Treatment Centres reveals that SNOT-22 Questionnaire is a useful tool in nasal surgeries as it combines both nasal specific and general health questions that reflects patients’ symptoms both pre-and postoperatively. Based on this audit it is also recommended to document the scores of SNOT-22 questionnaire pre-and postoperatively in patient’s medical record as a validated measure of success or failure of any nasal procedure.
Acknowledgements
None
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest
References
- Snidvongs K, Heller GZ, Harvey RJ (2014) Validity of European Position Paper on Rhino sinusitis disease control assessment and modification in Chronic Rhino sinusitis. Otolaryng Head Neck Surg 150(3): 479-486.
- HH Kordjia (2017) Sixty-Three patient-based survey-Can SNOT-22: be a suitable evaluation method for septoplasty and turbinectomy Clin. Otolaryng 42(6): 1373-1377.
- Kennedy J, Hubbard, Huyett P (2013) SNOT-22: A predictor of postsurgical improvement in patients with chronic sinusitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 111(4): 246-251.
- Buckland JR, Thomas S, Harries PG (2003) Can the Sino-Nasal Outcome Test (SNOT-22) be used as a reliable outcome measure for successful septal surgery. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 28(1): 43-47.
-
Samir Gendy. An Audit of the Predictive value of SNOT 22 Test in Evaluating Nasal Surgeries Emersons Green /Devizes NHS Treatment Centers-UK. On J Otolaryngol & Rhinol. 1(3): 2019. OJOR.MS.ID.000515.
-
Septoplasty, Endoscopic turbinoplasty, Rhinosinusitis, Septal surgery, Polypectomy, Septal surgery, Dizziness
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.