 Research Article
Research Article
The Effect of Psychodrama Therapy on Impulsivity in Women with Comorbidity of Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) and Methamphetamine Abuse in Social Emergency Referrals in Organization
Elmira Hajaghaie*
Department of Clinical Psychology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Hamedan branch, Islamic Azad University, Hamedan, Iran
Elmira Hajaghaie, Department of Clinical Psychology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Hamedan branch, Islamic Azad University, Hamedan, Iran.
Received Date: April 14, 2022; Published Date: May 30, 2022
Abstract
The main goal of the current research is the effect of psychodrama on reducing the impulsivity of women with comorbidity. Borderline personality and misuse of methamphetamine in emergency social welfare patients of Tehran province. This research semi-experimental design of pre-test-post-test type with a control group and its statistical population is all women with disorders. The characteristic of borderline disorder and amphetamine abuse is kept in the social emergency center of Tehran. With the available sampling method, 40 people were selected equally and completely randomly in two experimental groups. And they were witnesses. Then only the experimental group underwent psychotherapy for 12 sessions of 90 minutes placed in a group. To collect data for the borderline personality variable from the Milon 3 Multiaxial Clinical Test (IIIMCMI) (1977) and impulsivity variable was used from Barat Impulsivity Scale (BIS) (1959) which was used in the pre-test. And the post-test was performed on both groups. The ANCOVA method was used to analyze the data Hypothesis results. The main one shows that the independent variable of dialectical behavior therapy has a significant effect on the dependent variables of impulsivity of women suffering from borderline personality disorder (F = 65.1985 and) P < 0.001) and impulsivity in women suffering from substance abuse (F = 291.58) and has (P<0.001); Therefore, the intervention has had an effect in reducing impulsivity and methamphetamine abuse. Results showed that the independent variable (group) had a significant effect on the dependent variable (decrease in impulsivity) of women. The patient had abused methamphetamine (F=299.52 and P<0.001); Therefore, intervention in reducing the impulsivity of sick women It has influenced the misuse of methamphetamine in the clients of social welfare emergency of Tehran province.
Keywords:Bipolar personality disorder; Impulsivity; Methamphetamine abuse; Psychodrama
Introduction
Personality disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by persistent patterns of thinking, behaving, and relating to oneself and others that deviate from cultural norms and cause significant distress or impairment in daily life. Personality disorders are maladaptive and persistent ways of perceiving, relating, and thinking about oneself and the world that interfere with one’s daily life, job, and education. Personality disorder is a common and chronic disorder that is estimated to be between 10-15% of the general population. Three general categories of personality disorders are introduced based on the common or obvious characteristics of the disorders Characteristics of (group a) strange and unusual ideas and behaviors are characteristic of (group B) disorders, emotional or irregular behavioral behaviors, and group C) is characterized by anxious or frightening behavioral tendencies. Impulsive behaviors and aggression are common features of group B personality disorders (DSM5). Borderline personality disorder is one specific type of personality disorder of group B that is characterized by emotional instability, impulsive behavior, and difficulty in maintaining stable relationships [1].
Nearly half of patients with mental disorders have personality disorders, and among the clinical population with personality disorders, borderline personality disorder is seen in 30% to 60% of cases. The term borderline was first used by Adolf Stern (1938) to describe a group of patients on the borderline between psychosis and psychosis. Neuro-hormones such as oxytocin opioids mediate the exaggerated fears of rejection and abandonment that characterize BPD. It seems that environmental effects are also important in the pathogenesis of this disorder. Lack of communication security, periods of delirium, self-injurious behavior with overeating or anorexia nervosa, and major depressive disorder are more common in these patients [2].
The prevalence of this disorder is higher than other disorders The main feature of borderline personality disorder is emotional instability, which includes low mood and severe mood swings, and refers to a specific pattern of behavior that is seen among people with borderline personality disorder [3]. This behavioral pattern is characteristic, and this emotional vulnerability causes the patient with borderline personality to be sometimes emotionally aroused, resulting in high arousal, behavioral instability, and poor control over emotion, physiological arousal, and manifestations. Face is body language and interpersonal communication.
Impulsivity is one of the human personality states. Impulsiveness in showing anger is a good indication that something has caused these women chronic discomfort and raised their level of frustration and despair. In other words, the term impulsivity refers to behaviors such as haste, impotence, impatience and lack of attention to the consequences of an action. Based on research, they introduced four personality dimensions in relation to different dimensions of impulsive behaviors, which include lack of planning, urgency, excitement, and lack of perseverance. These individuals have widespread problems with purposeful and self-regulatory behaviors. On the other hand, different aspects of impulsivity appear to be associated with different high-risk aspects and poor therapeutic outcomes in substance abusers, for example, lack of planning, but not urgency. In addition, negative emotions are associated with severe problems and involvement in a variety of high-risk behaviors such as alcohol consumption, gambling, and morbid overeating. Finally, in substance abusers, negative emotional motivations, rather than unplanned, are strong predictors of psychological, social, family, and substance use problems. Addiction is a biological, mental, and social disease. Human history in different eras testifies to the existence of substances whose consumption has changed consumer behavior and caused anxiety. Today, with the emergence of different types of these drugs and their increasing consumption among people in different societies, and the transportation and trafficking of drugs has become a lucrative business [4].
Table 1:Protocol of psychodrama therapy sessions.
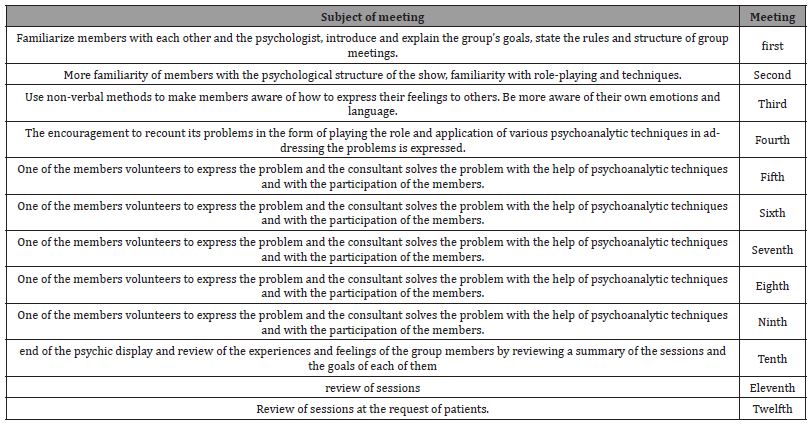
Nowadays, combating drug use, identifying patients who use drugs. It is one of the serious activities of the mental health system of most governments in the world. Humans take medicine to treat their physical and mental illnesses and to cure the disease or relieve its symptoms. Substances that affect the mental state and emotions of the consumer are abused. These changes are caused by the effect on the individual’s system (DSM-5). Various factors are related to substance use. Some of these traits are more likely to predict probability and generally represent a person who is not related to values or social structures such as family, school, or religion or adaptation. Treat, control, or painful emotions such as emotions. Angry, and dangerous, Guilt of Methamphetamine, marketed on the black market as Crystal Glass, is a powerful central nervous system stimulant with the potential for side effects that can be seriously misused for a specific pastime. Negligence - carelessness. Chronic hyperactivity and obesity are used to a limited extent in medicine (DSM_5) [5-7].
In basic and low doses, methamphetamine stimulates brain receptors to increase energy and concentration, euphoria, decreased appetite and insomnia, but in high doses can cause dangerous side effects such as seizures, cerebral hemorrhage, and psychosis. Prolonged use of methamphetamine also has many physical, psychological, and social consequences for consumers. The main composition of this substance is taken from amphetamine C9H13N. This white powdery substance is like odorless, bitter glass crystals that dissolve easily in soft drinks and alcoholic beverages. To the extent that they are accompanied by tolerance and signs of quitting. The pattern of this category is not mandatory.
However, it has harmful and destructive consequences for substances. Among these cases, I can mention absenteeism from school and work, conflicts with colleagues and friends, lack of social success, and similar neglect of children and families. Each thesis has an antithesis that ultimately leads to the synthesis of the contrast between the thesis and the opposite. Simply put, any idea is the opposite. After a while, these two opposing ideas come up with a new idea called synthesis., That is, instead a friend, lover or spouse can be human. Consider a set of positive and negative features. Psychodrama: Psychodrama is one of the psychotherapy techniques that helps clients to express their daily experiences through theater techniques and its purpose is to promote coherence and cognitive structure about emotional experience in theatrical structure. Psychodrama is one of the branches. Art therapy is a different perspective in the field of psychotherapy. This method was proposed by Morno as a therapeutic tool in the early 1990s, based on discoveries related to conflicts in the individual in order to release repressed emotions [8-10].
Psychodrama is one of the group psychotherapies used in the treatment of chronic diseases and is considered as a combination of psychiatric, social skills, and also showing mental problems in which members are not the actor group and all the curtains are flexible. And it is not read from any text either. In essence, members play their own private world group. Psychodrama is a collective method of correcting behavior and a relationship-oriented approach that helps the patient discover the psychological dimension of the problem, so that the patient not only through dialogue but also by displaying the problem reviews them.
During psychodrama, the patient learns how to act better when communicating with the environment and interpersonal and social relationships and helps to discover the psychological dimensions of the problem., Even when one plays the role of the problems of the distant past. In this treatment, the therapist examines, recognizes, and recognizes the personality structure of the patient’s interpersonal relationships, internal conflicts, and emotional issues, not only through dialogue but also through “active action” and “active observation” and provides insight, personality development and treatment. They show that psychodrama is effective in reducing the rate of depression and so on. Sexual abuse in order to adapt to trauma and treat major depressive disorder. Psychodrama is widely used in the treatment of addicted patients. Moreno himself treated alcoholics with psychodrama. The effect of this treatment in changing the place of control and prevention of relapse to addiction treatment of alcohol and substance abuse, as well as creating a negative attitude towards addiction and quitting, as well as prevention of recurrence accepted. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of psychodrama psychotherapy on reducing impulsivity in women with borderline personality comorbidity and glass abuse in social welfare emergency. Expressing the issue of drug addiction as the most serious social issue in Iran has various aspects of sociology, psychology, law, politics, etc. [11-13].
According to social analysts, drug addiction is one of the most complex social issues in the present age, which is the cause of many harms and social deviations. In other words, the relationship between addiction and social issues is a two-way communication; On the one hand, addiction leads society to stagnation and decline, and on the other hand, it is a phenomenon that is rooted in social, economic and what requires more interaction in our country today. The shift of young people from traditional narcotics such as opium and cannabis to industrial narcotics such as ecstasy, glass and crack is an industrial narcotic belonging to a large group of narcotics that are not of natural origin and are made through complex chemical processes in industrial laboratories. Personality traits are one of the components related to substance abuse, and these characteristics are not just drug use.
Before addiction, they have many mental and personality disorders that appear and become more destructive after addiction, so the issue of abuse is not only drugs but also the relationship between personality and addiction. Personality disorder is a heterogeneous category of disorders. Which are defined by an age-old pervasive and inflexible pattern of behavior and inner experience that contradicts the expectations of one’s culture. These problematic patterns are manifested in at least two contexts. Cognition, Emotions, Relationships, and Impulse Control Explain that difficulty in impulse control is an important element in the development of abuse, which is also a prominent feature of group B personality disorder. Group personality disorders are manifested by impulsivity, self-destruction, unstable emotions, and disruptive attachment patterns, of which borderline personality disorders have received the most attention. In this regard, borderline personality disorder is a severe personality disorder that is characterized by a lack of anger control, stress and mood swings, impulsive actions, disturbed interpersonal relationships and risky behaviors. According to studies on the prevalence of personality disorders in drug users, the average prevalence of personality disorders in drug and alcohol addicts was estimated at 44% and in opioid addicts at 79%. According to this study, personality disorders of type two are antisocial, narcissistic, and dramatic borderline are more common in these people than other disorders. Given what has been said, substance abuse is a very challenging and important issue in today’s societies that has many destructive individual and social effects [14-16].
Therefore, prevention in this field can be very important. In this regard, determining the predictors of abuse is not useless. On the other hand, due to the importance of the issue and the psychological, social, economic and physical adverse effects of substance use, a lot of research is done to identify risk factors and factors that can contribute to the occurrence of addiction and thus take appropriate measures to prevent the occurrence Prevent it, because despite the high cost of treating addiction, the chances of recurrence and relapse and the tendency to use drugs are still very high It can be said that addiction is a chronic and insidious disease that can never be cured. These findings emphasize the need for active participation of patients in the process of change, the main role of psychotherapy and the need for a clinical psychologist for primary care. In this study, we seek to determine whether psychology-based psychology drama interventions can reduce the ongoing damage caused by borderline personality disorder and glass abuse throughout a person’s life from work, education, marriage, and interpersonal relationships or not?
Research Method
The research method is a quasi-experimental design of pretest- post-test with a control group and its statistical population is all women with disorders. The characteristic of borderline disorder and amphetamine abuse is kept in the social emergency center of Tehran. With the available sampling method, 40 people were selected equally and completely randomly in two experimental groups. The selected sample members will be randomly divided into experimental and control groups. Thus, there will be 20 people in each group. The reason for selecting this volume of sample for each group is to eliminate the effect of possible loss of members, and they were witnesses. Then only the experimental group underwent psychotherapy for 12 sessions of 90 minutes placed in a group. To collect data for the borderline personality variable from the Milon 3 Multiaxial Clinical Test (III-MCMI) (1977) and impulsivity variable was used from Barat Impulsivity Scale (BIS) (1959) which was used in the pre-test. And the post-test was performed on both groups. The ANCOVA method was used to analyze the data. Hypothesis results. And finally statistical analysis by analysis of covariance on the data obtained from these people were assessed. The research tool is a questionnaire. Borderline personality scale (STB): borderline personality scale is a part of the schizotypal trait questionnaire (STQ) and STQ includes two schizotypal personality scales (STA) and Kalrich and Brooks borderline personality scale STB. This questionnaire is by Coleridge and Brooks. Created at Oxford University and by Rawlings Coleridge and Freeman revised. In addition to the 18 basic materials, there are also 6 other materials for covering diagnostic owners of this disorder added to it. Therefore, the STP scale has 24 items as follows. Yes/No is answered. A yes answer gets a score of one and a no score gets a zero score. This scale has three factors. It measures frustration 6, impulsivity 7 and dissociative and paranoid symptoms related to stress 8. Rawlings. They reported an alpha coefficient of 0.80 for STB [17,18].
Milon’s Clinical Multiaxial Questionnaire (III_MCMI): This questionnaire is a standardized self-assessment questionnaire. It measures a wide range of information related to the personality, compatibility, and attitude of test takers. Milon’s III questionnaire is one of the unique tests in which personality disorders and symptoms are often associated with these disorders. The original version of this test was compiled by Theodore Milon in 1977, and it was presented, and it has been reconsidered since then. The current version MCM III contains 175 items which. It is scored under 28 separate scales and based on the following classifications: Variable indicators, pattern, Clinical personality, severe personality pathology, clinical symptoms, and severe symptoms.
Impulsivity questionnaire prepared by Ernst Barthes et al in 2004. Bart’s impulsivity analogy correlated very well with the Eysenck impulsivity questionnaire, and the structure of the questions collected from both questionnaires showed the dimensions of hasty decision making. And there is a lack of foresight. This theory is based on Bart’s personality theory, which consists of three questions and evaluates the three factors of cognitive impulsivity, motor impulsivity, and unplanned. Options are scored on a four-point Likert scale. Rarely, never, almost always does this scale have 10 negative questions that are scored in reverse. Validity and reliability of impulsivity questionnaire. This scale also has a total score. Cognitive Impulsivity Scale: Includes rapid cognitive decisions. This subscale measures complexity tolerance and strength, including items 6, 5, 9, 11, 20, 24, 26, and 28. Motor impulsivity: involves action without thought. This subscale measures the tendency to act immediately and under stress, which states: 25, 17, 21, 22, 30 and 23, 19, 16, 4, 3, 2: These are the degree of unplanned: with an immediate feature is specified. Orientation or lack of foresight. This subscale slightly measures emotions about the future. The items of this subscale are: 29,27,18,15,14,13,12,10,8,7,7. Cronbach’s alpha is also above 70% [Table 1].
Validity and reliability of Barat Impulsivity Questionnaire: The scale using Cronbach’s alpha for the whole test is 0.80 and for the subscales of motor, attention and unplanned are: 0.74, 0.74 and 0.73, respectively. This scale correlates well with impulsivity selfassessment questionnaires such as Zuckerman Emotion Scale, Eysenck Impulsivity Scale, and Behavioral Inhibition and Activation Scale. In this study, the total reliability of the questionnaire was 0.80.
Descriptive method the method of work and the method of data collection with full details in order to comply with the ethical criteria of the research, sufficient information about the purpose, how to implement and use the research findings will be provided to participants. Those who met the inclusion criteria will be selected into two experimental and control groups. For the experimental group, 12 sessions of 90 minutes per week, two sessions of therapy will be performed in the form of psychotherapy. It should be noted that 40 eligible clients were randomly selected and randomly divided into two groups.
They will respond to impulsivity as a pre-test. The experimental group then participated in a 12-session intervention session, each session lasting 90 minutes, as shown in Table 1, and the control group will not receive anything. In order to retest, the above scales will be applied to all subjects again. Data analysis: Description of the nature of the collected data and the type of statistical analysis required for the present research method was experimental with pre-test-post-test design with a control group. To collect data, Barat impulsivity questionnaire was used for statistical analysis using two methods of descriptive statistics and inferential statistics.
In order to analyze the data in the descriptive statistics section, the central index statistics of mean and median, fashion and standard deviation are discussed. In the inferential statistics section, analysis of covariance was performed on the data obtained from the measurements of the selected sample.
Findings
[Table 2] In the table (1-2), the average, standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis indices are observed in the research variables. As can be seen, the mean and standard deviation of the impulsivity variable among women with methamphetamine abuse. In the pre-test stage, it is 41.82 and 2.35, which in the post-test stage is equal to 17.97 and 0.946, respectively. It has been reported. Also, the mean and standard deviation of impulsivity variable among women with personality disorder. The pre-test stage is equal to 39.80 and 11.85 and in the post-test stage it is reported as 16.95 and 1.35 respectively [Table 3].
Table 2:Descriptive indicators in research variables
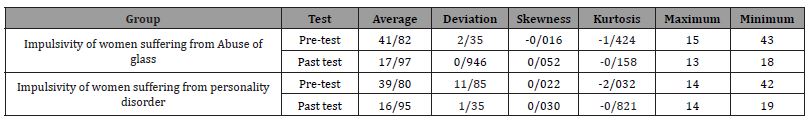
Table 3:Test of linearity of pre-test and post-test relationship.

According to the contents of the table (1-3), F is obtained and a significant value greater than 0.05 indicates the linear assumption. The relationship between the pre-tests and the independent variable is established [Table 4].
Table 4:Levine’s test to check homogeneity of variances.

According to the contents of the table (1-4), the condition of homogeneity of variances in all variables is not significant, therefore. The assumption of homogeneity of variances is established [Table 5].
Table 5:The result of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for the normality of the data distribution.

According to the results of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test in the table (1-5), it can be stated that the main variables of the research are normal, Because the significance level of Z values in each of the variables is greater than 0.05 (p < 0.05). Parametric tests can be used to analyze research questions.
Conclusion
Findings indicated that psychoanalytic approach could measure the consequences and disorders in patients. Reduce the borderline personality that psychodrama skills training provides by providing the ability to understand relationships with others. It can reduce impulsive behaviors and improve quality of life. This therapeutic approach can be a variety of areas of anxious efforts, combined with a rush to avoid real quit or imaginative, unstable and intense personal relationships as a pattern characterized by alternation between Bipolar is extreme, the obvious and constant instability of self-image or one’s feelings about oneself, at least impulsive in two of the areas that potentially harm the individual, behaviors and movements express or threaten suicide in the form of repeated, or repeated self-harm, emotional instability in the form of overt mood reactivity, chronic emptiness disproportionate and severe anger or difficulty in controlling anger and the occurrence of paranoid suspicious thoughts or severe symptoms. Transient decompression and occasionally reduce stress in these patients.
Psychodrama therapeutic training by inserting paradoxes, contradictions, using the metaphor of playing pro-devil and demon develop, active. Creating the wise mind of the clients, turning the negatives into the positives, allowing natural change and inequalities even in the environment Psychotherapy, evaluation, and diagnosis by asking the question, “What do you ignore here? Can reduce the rate of these disorders and injuries in patients with substance abuse, especially women and make them capable and resilient for enduring the pain caused by leaving the material.
Acknowledgment
None.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
References
- Lieb K, Zanarini MC, Schmahl C, Linehan MM, Bohus M (2004) Borderline personality disorder. The Lancet 364(9432): 453-461.
- Gunderson JG (2011) Borderline personality disorder. New England Journal of Medicine 364(21): 2037-2042.
- Corey G (2015) Theory and practice of group counseling. Boston: Cengag Learning.
- Dick DM, Smith G, Olausson P, Mitchell SH, Leeman RF, et al. (2010) Understanding the construct of impulsivity and its relationship to alcohol use disorders. Addiction biology 15(2): 217-226.
- Amraee M (2010) Ten set up psychoderama. Tehran Tahoora publication p.20-4.
- Andrada D Neacsiu, Shireen L Rizvi, Marsha, M Linehan (2010) Dialecal behavior therapy skills use as a mediator and outcome of treatment for borderline personality disorder and Therapy. Original Research Article Behaviour Research 48(9): 832-839.
- Stern, Aldoph (2009) borderline personality disorder treatment and management, published by the British psychological society and the royal college of psychiatrists, printed in Great Britain by Stanley I hunt(printers).
- Kroger C, Harbeck S, Armbrust M, Kliem S (2013) Effectiveness, response, and drop out of dialectical behavior therapy for borderline personality disorder in an inpatient setting. Behaviour Research and Therapy 51(8): 411-416.
- Dimeff LA, Koerner K (2007) Dialectical Behavioral Therapy in Clinical Practice. New York, Guilford.
- Geng F, Tu L, Zhan N, Zhang Y, Wang J (2021) Associations of substance abuse histories and gambling addiction history with post-traumatic stress symptoms and depressive symptoms among Chinese prisoners. European journal of psychotraumatology 12(1): 1906022.
- Harned MS, Rizvi SL, Linehan MM (2010) Impact of co-occurring posttraumatic stress disorder on suicidal women with borderline personality disorder. american Journal of psychiatry, 167(10): 1210-1217.
- Hinz, Tobais, Baid, Bloungen, Le, Boui, child mental health, Quarterly Journal of Child Mental Health, (2018) spring 5(1).
- Keller MB, McCullough JP, Klein DN, Arnow B, Dunner DL, et al. (2000) A comparison of nefazodone, the cognitive behavioral-analysis system of psychotherapy, and their combination for the treatment of chronic depression. New England Journal of Medicine 342(20): 1462-1470.
- Linehan M (1993) Skills training manual for treating borderline personality disorder (Vol. 29). New York: Guilford press.
- Linehan MM, Armstrong HE, Suarez A, Allmon D, Heard HL (1991) Cognitive-behavioral treatment of chronically parasuicidal borderline patients. Archives of general psychiatry 48(12): 1060-1064.
- Paris J, Gunderson J, Weinberg I (2007) The interface between borderline personality disorder and bipolar spectrum disorders. Comprehensive psychiatry 48(2): 145-154.
- McNally RJ. Personal Information Birthdate: April 17, 1954, Birthplace: Detroit, Michigan Marital Status: Married to Donna M. McNally.
- Wang Q, Ding F, Chen D, Zhang X, Shen K, et al. (2020) Intervention effect of psychodrama on depression and anxiety: A meta-analysis based on Chinese samples. The Arts in Psychotherapy 69: 101661.
-
Elmira Hajaghaie*. The Effect of Psychodrama Therapy on Impulsivity in Women with Comorbidity of Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) and Methamphetamine Abuse in Social Emergency Referrals in Organization. Open Access J Addict & Psychol 7(2): 2023. OAJAP.MS.ID.000659.
Bipolar personality disorder; Impulsivity; Methamphetamine abuse; Psychodrama; Borderline Personality Disorder; Psychodrama Therapy; Disorders; Hypothesis results
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






