Opinion Article
Opinion Article
Statistical Analysis on Occupational Health in a Sample of 240 Workers
Abdoulaye Diouf*
Department of Statistical and Decision Computing Engineering, Web Developer, Senegal
Abdoulaye Diouf, Department of Statistical and Decision Computing Engineering, Web Developer, Senegal.
Received Date:August 04, 2025; Published Date:August 13, 2025
Abstract
This study focuses on a sample of 240 workers and aims to explore the distribution of sociodemographic characteristics, medical history, reported symptoms, and their association with certain occupational risk factors. It is part of a broader initiative for workplace health promotion and risk prevention.
Keywords:Smoking, PPE, Symptoms, Chi-square, Occupational health, Statistical analysis, Gender, Age group, Seniority
Introduction
Sociodemographic and Anthropometric Data
- The average age of participants is 35.1 years. Over half
(54.4%) are aged between 30 and 45, while 31% are under 30.
- The sample is predominantly female (60.67%).
- The average anthropometric measures are: height 1.71 m,
weight 72.6 kg, and BMI 24.97 kg/m². Women have a slightly higher
BMI than men.
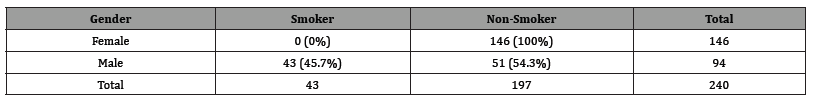
Smoking and Gender
Table 1:This difference is highly significant (p-value < 0.0001).
Job Roles and Gender
Women mostly work as room attendants (50.21%), while men are mostly gardeners (28.33%). The association is highly significant (p-value < 0.0001).
Medical History
- 70.3% of individuals report no medical history.
- Allergic conditions dominate among those who do: allergic
rhinitis (17.15%) and asthma (7.95%).
Symptoms and Associated Factors
- Nearly half (46.86%) report no symptoms.
- The most frequently reported symptoms include cough
(18.41%), nasal discharge/sneezing (16.32%), and eye irritation
(11.3%).
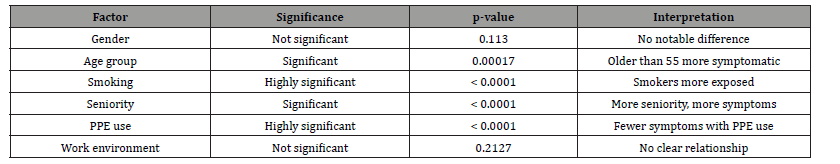
Table 2:Correlation analysis.
Conclusion
The study highlights several strong associations between occupational factors and perceived health among workers. Smoking, seniority, and the use (or not) of personal protective equipment (PPE) significantly influence the presence of symptoms. These findings call for strengthened prevention policies, including improved PPE access, anti-smoking campaigns, and medical monitoring for long-serving personnel.
-
Abdoulaye Diouf*. Statistical Analysis on Occupational Health in a Sample of 240 Workers. Mod Concept Material Sci. 7(3): 2025. MCMS. MS.ID.000663.
-
Smoking, PPE, Symptoms, Chi-square, Occupational health, Statistical analysis, Gender, Age group, Seniority
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.