 Review Article
Review Article
Developing Test System in Academic Nursing School
Yael Tal Hof*
Nurse Educators in Wolfson Academic Nursing school, Holon, Israel
Yael Tal Hof, Nurse Educators in Wolfson Academic Nursing school, Holon, Israel.
Received Date: August 12, 2019; Published Date: August 28, 2019
The Article Goals
To describe the development of a school system dealing with building tests and controlling the process of producing test in the academic nursing training center in central Israel. By the end of the process, a model was built, and a work instruction was developed to guide uniform work methods among the organization staff members.
Background
There are several study courses in the academic nursing training center:
Academic training of four years, 2.5 years retraining courses and 10 to 12 months advanced courses (advanced training) in specific domains for nurses as: intensive care, operation rooms, infections prevention. Most of the tests in these courses take place in nursing school.
Evaluation of learners’ achievements is part of the training process in nursing school. There are many ways to evaluate learners’ achievements, but the most common way is a test. There are different types of tests. Tests have many advantages. The test results enable to identify the weak and strong learners and the missing disciplines in a specific group of learners. The teaching and learning processes can be deduced from test results. All tests in the nursing school are of a multiple-choice type (including a stem and four distractors, one of which is correct). There is an increase in the required number of tests to be produced for students in the nursing school and therefore there is a need to establish a system that regulates the test producing procedure. The tests are prepared by a team of teacher nurses and lecturers who participate in teaching these courses.
The reasons influencing the need in establishing a school test system:
Increase in the amount of test producing:
1. The nursing administration in the Ministry of Health defined a national target to increase the number of nurses in Israel that claims:
2. To increase the number of learners in all study courses. b. To increase the number of study courses opening each year (working plan, nursing administration, 2018).
3. According to the academic study regulations, each test has two sessions (A and B). In some cases, students get approval to have a special exam session. A fact that creates a need to compose additional tests.
The test quality: The lecturers are expert professionals in their fields: nurses, doctors, dietitians, physiotherapists, pharmacologists. They have to be taught how to write questions in a correct and structured way. They have to know the principals and instructions of composing a qualitative test.
Therefore, we have to:
1. Prevent a situation in which the learners appeal the test questions that find to be correct in a second check and cause the lecturer to cancel questions in the test or accept more than one correct answer.
2. Prevent a situation in which the examinees report during the test that: the question is not clear, the distractors are not clear, there is more than one correct answer or distractors of the answers is correct.
3. Prepare the learners to answer the test simulates the external qualification test during their studies
4. Manage a computerized tests database that will provide a professional solution to composing a qualitative test.
To start this process there is a need in a structured process which recruits the whole teaching staff to the organizational change.
Keywords: Nurse training center; Nursing school; Nurse educators; Tests, Multiple choice tests; Nursing administration; Test map
Introduction
A written test has various goals. The test is a communication tool between the teacher, the course and the student. The test results may indicate lacks in teaching and the need to improve the core or teaching methods. The test has a structure called the test map. This map outlines the relative part of each topic in the course, in accordance with its importance. It is also determining the questions difficulty that will be defined according to the test map and to the required level the student must meet due to his studies stage (Workshop for item writers, 2015) [1]. There are many different types and styles of tests. A multiple-choice test is more commonly used in nursing schools. This kind of test includes the question called stem, and the part that contains the answer options, i.e. the distractors which include the correct answer and the incorrect answers. There are rules and principles to composing multiple choice test items and the items writers must know and implement them. The procedure is not simple and requires proficiency [2].
Organizational change works for several reasons. The external environment, as: technological changes, changes in the structure of the external licensing test, and the need to know it and simulate it. A change as a result of the Ministry of Health and the nursing administration policy to increase the number of students in nursing schools as a national goal. The internal environment of the organization is influenced by the external changes and the training staff is being pressured. Therefore, it is requirement to uniform work according to the same criteria. Internal organizational changes arise from an internal crisis or dissatisfaction and from the desire to successfully perform personal tasks and lead the organization to success and manage tasks more easily due to technological changes [3,4].
In leading organizational change, it is necessary to recruit the employees and provide them the knowledge and skills in order to promote the organization’s goals for its clients, who in this case are the learners. Training and developing the human factor are perceived as an investment in the employee that will lead to quality. Therefore, providing knowledge is the first stage in leading the change [5].
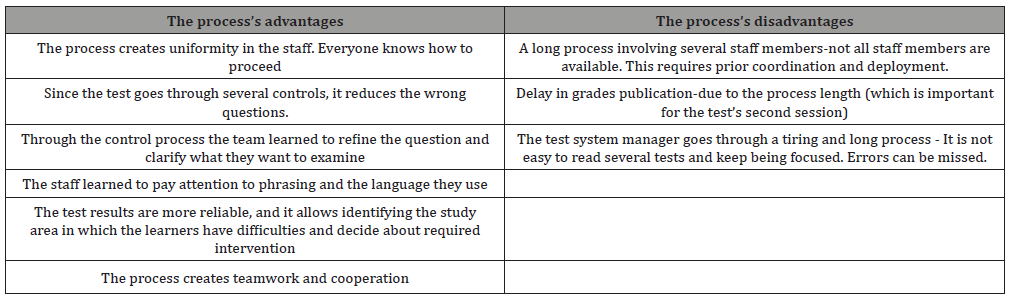
After several attempts to build a test according to the studied principles, required changes were done to obtain satisfaction with the process that was settled in institutional work instruction and a model. A working procedure is an internal organizational document that specifies and defines the policy and implementation methods. The procedure serves as a control standard, defines areas of responsibility and authority, and internal communication means. The procedure has advantages and disadvantages. Its advantage is the regulation and clear and institutionalized division of organizational activity between the staff members it causes, and it prevents misunderstandings and intra-organizational struggles. Keren claims that in small organizations, communication is often good and open, and therefore there is only a small need in procedures. The larger the factory, the bigger the units, and therefore, there are many partners that may cause tensions between them. The management enables control and supervision of the activity [6].
At the Nurses Training Center where was developed a building and testing tests system, there is an ISO9001 certification process designed to achieve a quality organizational culture. It is important to understand that procedures have been created to serve the goal. Sometimes the goals change and therefore must be updated or improved [6].
The method description
The process was performed in several stages in order to lead the whole staff and to achieve organizational uniform performance. The test items writing training was performed in big classrooms allowing a large group of people to be taught at the same time. The lecture method was used, and computerized examples and exercises was integrated. Then, the training program was evaluated. The evaluation goal was to examine the knowledge assimilation and the implementation method.
Stage 1-Knowledge impart: A team of nurse educators in the organization was trained in Tel Aviv University in the Faculty of Nursing in the supervision of Dr. Koren, who was the head of the licensing and certification exams department in the Nursing Administration. In this meeting the public had a presentation and explanation of the principles of writing multiple choice items, goals, structure, criteria for a good test and other relevant information. They had an explanation about the item analysis results, about the significance of α Cronbach, the meaning of a positive and negative correlation to each question, and more. At the end of the meeting they practiced composition of questions that are considered “good” and diagnosis of questions considered “not good” and had an explanation.
About two months after this meeting, there was a workshop dealing with building items for the government licensing test of the Licensing Examination Division in the Nursing Administration. This workshop was also attended by the training center staff members in order to strengthen the knowledge and understanding about writing test items and in order to lead and mediate the change and innovations in the nursing school. In this workshop the Licensing Examinations Department roles and the examination producing process were presented. They had an explanation on the test structure, the question structure, and formulation of question and distractors.
The importance for nurse educators to know and understand the principals of writing multiple choice items is:
a. To know the guiding principles in creating external certification test.
b. To follow those principals and use it in the daily work in school internal tests.
c. The learners in the training process will be exposed to questions/tests similar to the licensing test.
Stage 2-Implementation: A system that responsible to test management was established in school. Its goal is to ensure that the composing tests process is uniform according to the required principles. This system was presented to the staff in a staff meeting.
The implementation was performed in two levels: a. the lecturer, b. the test
A. Performance in lecturer’s level
The lecturer work by himself with the study material he teaches. Each lecturer/nurse educator corrects or creates new questions according to the stages: planning, writing, validation, proofreading.
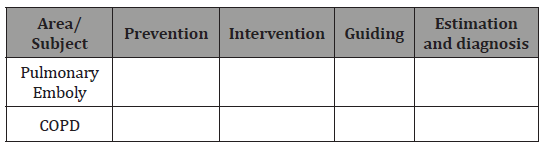
Planning-answers the question: “what do I actually want to test in each subject?” the area may be: prevention, estimation, diagnosis, treatment/intervention, patient’s guiding. Each course is divided to subjects in accordance with the study syllabus. To each subject a question is being written by the chosen area and we build a test map (Table 1&2).
Table 1: Course heart diseases.
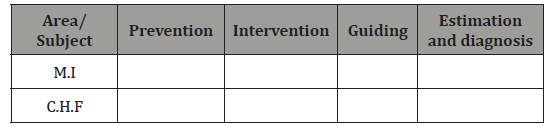
Table 2: Course respiratory diseases.
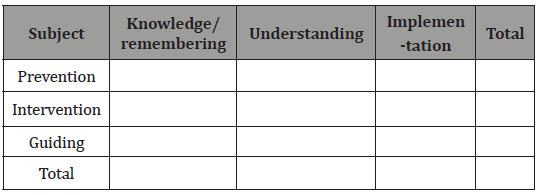
Then, we must decide about the question’s difficulty level according to Bloom’s taxonomy’s stages including six difficulty levels: remembering the knowledge, which is the most basic level, understanding, implementation, analysis, evaluation and production, which is the highest level. The questions difficulty in tests are usually in the three firs levels of the taxonomy (Table 3).
Table 3:
i. Writing-i.e. phrasing the multiple-choice question each question has stem and 4 distractors. Only one distractor is the correct and the others are not correct.
ii. Validation-the question’s stem and the correct distractor must be validated by the literature obligated by the syllabus. The same importance must be given to confirm that the other set distractors are not correct and do not appear in literature.
iii. Proofreading-conform that the question the lecturer wrote is structured as he intended, and it is unequivocal.
B. Performance in test level
In this level the process is very similar to the lecturer’s level process, which by its end a fair and valid test that reflects the learner’s knowledge in the study unit must be produced.
i. Planning-all the test domains are spread according to the syllabus and the number of questions in each domain is calculated. The number of questions is derived from the content and the time frame. A broader test map is built according to the domains included in the test.
ii. Writing and validation-the validated questions which was written in the lecturer’s level are entered to the test.
iii. Proofreading-is performed when the test is ready, and a MASTER form is issued and the base for printing the tests to the learners.
It was decided in the nursing school that prior to print, each test is check by the test system manager, who serves as a quality guard and as a gatekeeper, check the test in terms of: formulation, difficulty, structure, repeating questions, spelling errors, proofreading. If there is unclear distractor, or unclear question he stopes the process and the question is returned for clarification. The question may be fixed or replaced. If the questions are clear, the test is approved for further printing to the learners.
Stage 3-Control: This stage is done after the students answered the test and prior to the grades’ publication. The students’ response sheets are collected and sent to segmentation and test results. This stage is computerized and done outside the organization.
The study unit coordinator receives the test segmentation results and begins to review the statistical results of each question separately and of the entire test. At this stage, each question’s correlation (positive or negative) is examined. A question that its indices are not good goes back to the lecturer who wrote the question for reconsideration. At this stage, the phrasing, the distractions, and the answer the students chose are compared to the study material and the literature. After the review, they decide what to do about the question. If the question is good and the learners did not know to answer it, they think how to supplement/reinforce the learner’s missing knowledge. If there is an additional correct distractor, they accept it. At the end of the control stage, which may be a little long, the test results are published.
After several experiences like this, an institutional work directive was written describing and documenting proper conduct in the process of producing a uniform and agreed test. The procedure was written in cooperation with the Quality Control and Risk Management Department in to make it clear and detailed (Figure 1, 2) (Table 4).
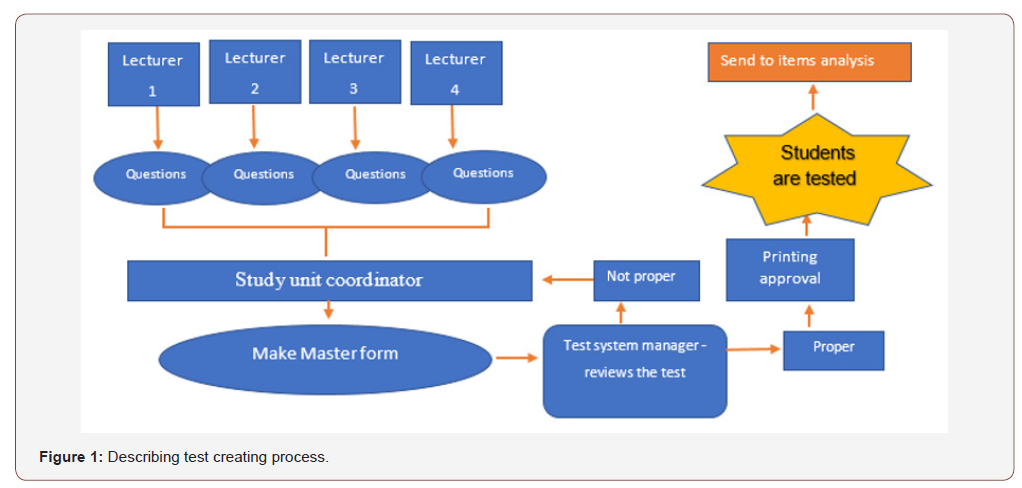
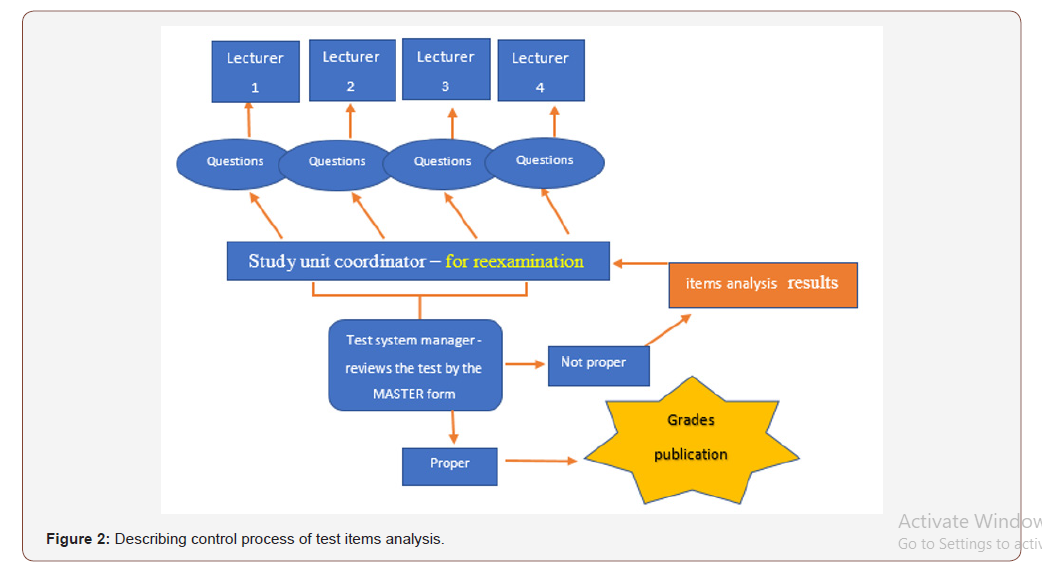
Table 4:
Recommendations
Develop in each organization a test system including several staff members who are skilled in development and refresh this field.
Survey description
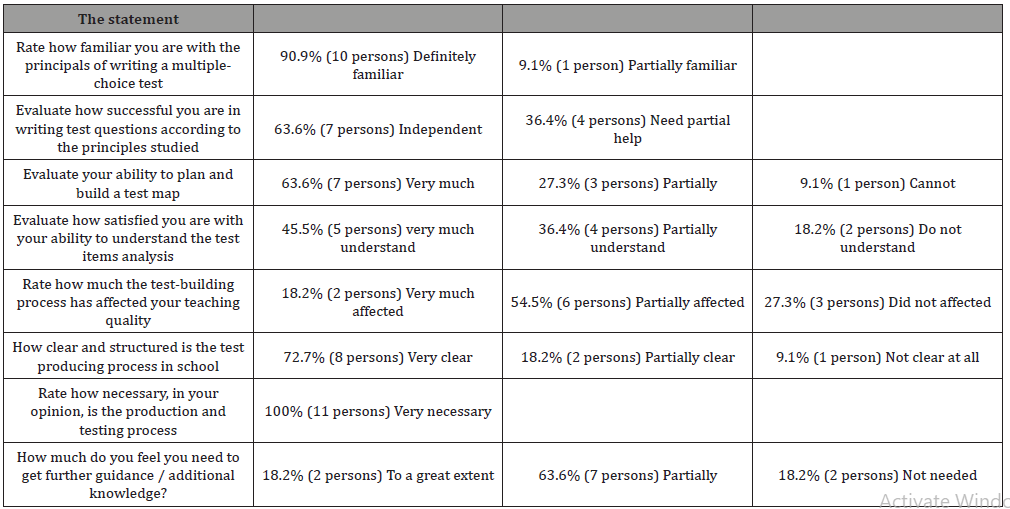
Following this process, a survey was performed among nurse educators in nursing school, which examines the process of assimilating test creation in school level, the survey’s results (Table 5).
Table 5: 11 nurse educators replied (n=11).
Conclusion
The process of writing a multiple-choice test requires knowledge and proficiency. This data shows:
It is necessary to strengthen the knowledge and widen the issue of test producing process beginning with the test structure and phrasing question and distractors to the level of understanding the test results analysis.
It may be seen that there is assimilation, but it requires continue working with the staff. may be the difficulty is in new staff members (which the survey did not check and therefore difficult to conclude)
There is a regulated institutional procedure describing the procedure, but staff members still have difficulty in this skill.
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
References
- Workshop for item writers (2015) Nursing Administration, Ministry of Health, India.
- Birenboim M (1997) Alternatives in assessing achievements. Ramot Publishing: Tel Aviv University, Israel.
- Levy A (2008) Management and leadership change and innovation. Published by: Rimonim, Israel.
- Work plan (2018) Nursing Administration, Ministry of Health, India.
- Meshulam A, Harpaz Y (2015) Resource management the strategic approach. Yedioth Ahronoth-Hemed Books, Israel.
- Yehezkealiy P, Shalev O (2012) Procedures: Essential but not holy, Israel.
-
Yael Tal Hof. Developing Test System in Academic Nursing School. Iris J of Nur & Car. 2(1): 2019. IJNC.MS.ID.000530.
-
Nursing, Health, Doctors, Dietitians, Physiotherapists, Pharmacologists, Qualitative Test, Nursing Administration, Intra-Organizational Struggles, Quality Organizational Culture, Nurses Training Center, Diagnosis, Analysis, Production, Formulation
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






