 Research Article
Research Article
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Video Games and Simulations for Designing Learning Experiences for Nursing Student and Educators
Klaudia Ćwiękała Lewis* and Brandon H Parkyn
Department of Nursing, York College of Pennsylvania, USA
Klaudia Ćwiękała Lewis, Department of Nursing, York College of Pennsylvania, USA.
Received Date: February 07, 2020; Published Date: April 15, 2020
Background
Background: Technological applications, games and simulations are already extensively incorporated into the traditional educational process. Lately, the interest in investigating games and simulation use in nursing education has been amplified. The alteration, from lecture-centered to student-centered environments and the growing use of games as innovative learning technologies, demands a renovation in nursing education. In regard to this, games and simulations are projected to play an important part in the nursing learning process. Virtual simulation and gaming offer a sustainable, lucrative teaching alternative for nursing students and nursing educators.
Objectives: The purpose of this paper is to discuss present Advantages and Disadvantages of utilizing games and simulation for designing learning experiences for nursing.
Methods: An electronic database search was conducted of five electronic databases PubMed, CINAHL, Web of Science, Embase, and Google Scholar (January, 2007 – December, 2019) limited to English. Studies that discuss application of games and/or simulation for designing learning experiences for nursing students and educators.
Results: The search strategy identified 168 papers of which 34 were retrieved for full review. Nineteen articles were removed based on the exclusion/inclusion criteria, leaving 18 articles for final analysis. During this literature review this author noted three key advantages and three key disadvantages.
Keywords: Games; Simulations; Learning experiences; Nursing; Education
Introduction
The term video game generally means the interaction of games played utilizing a specialized electronic device or any other type of screen that it is programmed on (video game, n.d.). The term ‘video game,’ has been recorded in history as early as 1948 with the invention of the “Cathode-Ray Tube Amusement device” (Brookhaven National Library, n.d.). This particular device utilized manual pictures placed on the screen as an overlay and the game was played under the overlay. In 1952 the first recorded, full-screen video game, without the picture overlay, was developed and titled “OXO” or a version of tic-tac-toe (Brookhaven National Library, n.d.) This device fully displayed the processed output of a game onto a screen. As the years and eventually decades progressed, video games have progressed from something that is played casually, to simulations, educational games, and full virtual reality types of games. Although in earlier times, video games had the stigma of being for pure entertainment value only, the literature has conveyed the utilization of video games, specifically in nursing, as early as the 1980’s [1]. This was preceded with the idea of multiple constraints with video games to use in nursing education. The primary reasoning was deeply rooted in the nursing tradition from the founder Florence Nightingale of being educated in the classroom and supported that method of education for nursing [1]. Secondary reasoning for the resistance to the utilization of video games in education stemmed around the lack of knowledge and research surrounding them as being utilized as an educational tool for nursing students. That is the main purpose of this paper, not to show that games can be utilized as a tool within the nursing education scheme, but rather to illustrate specific advantages and disadvantages of utilizing video games as presented within the articles based upon using gaming as an adjunct in the education of nursing students.
Methods
A literature search was conducted in two ways. First a systematic literature search was conducted using six popular health science databases. Secondly a Google Scholar (http://scholar.google.com/) search was conducted. The second search allowed the researcher to explore more publications in a less structured manner. During the second search, abstracts were reviewed carefully, as this database provides more low- quality material. The search was conducted to answer the research question: What advantages and disadvantages of using video games and simulations for designing learning experiences for the nursing student and educators are discussed in current literature? An electronic search was conducted of the published research studies examining the advantages and disadvantages of using video games and simulations for designing learning experiences for the nursing student and educators. Electronic databases included: PubMed, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Web of Science, and Embase, from January, 2007 to December, 2019. Search terms included: “Video Games” or “Gaming Simulation” AND “Nursing Education”. Articles were limited to English. The abstracts of all research studies were reviewed to determine the relevance to the presented topic.
Results
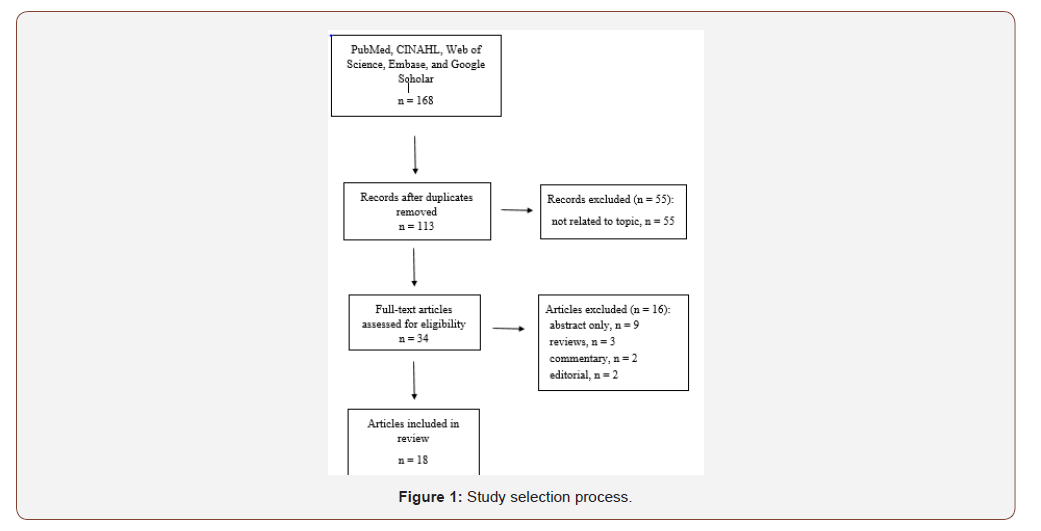
The search of five databases yielded 138 articles for screening for potential inclusion. After removing duplicate articles and those not related to the topic, a total of 34 studies were reviewed in depth for eligibility. The 34 articles were reviewed based on inclusion and/or exclusion criteria, yielding 18 articles included in this review (Figure 1). illustrates the study selection process. Fifteen articles were examined to create a list of potential advantages and disadvantages of using games and simulations for designing learning experiences for nursing students and educators.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
The researched articles that were found revealed a vast amount of information pertaining to video game usage with the education of nursing students. Upon further examination, specifically looking for the advantages of using games, the following list was developed based upon the main themes of the articles presented.
• Errors are not harmful to patients
• Simulated training leads to clinical improvement
• Video games allow for specific designs and patient interactions specific to a specialized skillset
This author will delve further into the explanation of these advantages in relation to the research that presented the concepts of utilizing video games in nursing education.
Errors are not harmful to patients: Medical errors are a very serious problem within the United States of America’s healthcare system. Overall medical errors that involve all types of errors including physician, nurse and unlicensed professional errors account for over 130,000 patient deaths a year [2]. Specifically, pertaining to nursing, the majority of nursing errors are related to medication errors. It was deducted within a research study performed in 2009 that in upwards of 65% of nursing errors were related to medication errors [3]. These errors range from the occurrence of minor issues such as increased discomfort to more serious consequences such as allergic reactions and increased length of stay. There is, estimated to be, over $70 million a year of increased healthcare costs associated with medication errors alone [3].
The advantage of utilizing gaming in relation to errors is that gaming is not using real-life subjects. This alone is beneficial due to the fact that if a video game character has a medication error, a human is not harmed by that error. Robyn and Simon (2009), within their review, showed that 50% of their reviewed research studies pertaining to simulation had a significant effect on a nursing student’s confidence with their skills and critical thinking. Utilizing simulation for education assistance with nursing education can boost the nursing student’s confidence and critical thinking which can lead to fewer errors. One issue with clinical scenarios that may occur, according to Sleeper and Thompson[4], is that students may have a fear of performing skills or even communicating on how to perform skills due to the fear of causing harm to patients, even when in a supervised environment. Gaming and simulations can help quell those fears by providing an environment of no fear of harm to the patient. Multiple research articles specifically mention the importance of the creation of that type of environment of not harming a patient [1,5-12]. [5,9] continue to press that issue of errors not affecting humans and that simulations create a supervised session that allows the students to practice, experience and try new skills in different ways to help them learn how to perform those skills in a controlled manner. That can help decrease the anxiety related to trying new procedures and increase the comfort level of the students to try to learn more easily.
Simulated training leads to clinical improvement: Simulation and education are synonymous with each other to provide a new method of training outside of the traditional classroom method of education. This type of training helps expand the situation and knowledge that is being transferred to the student to allow for placement of the knowledge in a more realistic context [12,13]. The benefits to the simulation-type of education can be attributed to the idea that the students can retain more knowledge utilizing simulation versus the traditional classroom-type of style. In a classical work by Edgar Dale, he developed a ‘Cone of Experience’ that outlined the hypothetical amount of knowledge retained during an educational session. To simplify the cone, it lists the hypothetical percentage of knowledge retained with the various types of learning experiences beginning with (a) 10% of knowledge remembered with reading, (b) 20% of knowledge with what they hear, (c) 30% of knowledge remembered with what they see, (c) 50% of knowledge remembered with what they see and hear, (d) 70% of knowledge remembered of what they say and write, (e) 90% of knowledge remembered of what they do as they perform the task [14].
The simulation utilizes the knowledge learned and applies that directly towards a situation where the student can perform the action on a training dummy while ‘educating’ the instructor [15]. This method of learning and knowledge retention is up in the highest percentage, according to the cone of experience, which can translate into increased clinical competence [16]. This improvement in the clinical competency of the students has been researched fairly extensively over the years. In a Systemic Review of just 12 research studies surrounding the usage of simulationbased learning, Cant and Cooper [16] found that all 12 of the studies, consisting of a total sample size of 1533 study participants showed a significant improvement in the clinical competency of the research participants. In another study researching undergraduate nursing student’s experiences, they continued the trend of the increased knowledge and increased feeling of having better knowledge towards being able to perform their clinical functions within their skills [10].
Video games allow for specific designs and patient interactions specific to a specialized skillset: One of the great concepts surrounding video games is that they are a game. Games can be made to show anything that they are programmed to show. The only limitations to this would be the hardware limitations on what can be processed for the graphics and the limitations pertaining to the method of delivery [12]. This relates to the simulation equipment and the capabilities of these to process and adequately simulate what needs to be simulated [15]. Video games and simulations can be made to order depending on the topic that is being educated, the specialty that needs to be learned and the imagination of the programmer [15]. Specialists within the individual fields will need to be present during the programming of the game or simulation to ensure that the information being presented is sound and the research is based upon that specialty.
In one study performed by Boctor [17], she utilized a Jeopardytype of game, as a general review specialty for her class information, to help students reinforce the nursing knowledge that was taught to them. After the study was completed, a statistically significant number of students reported enjoying the game and requested to see more. This was also found in a study performed by Cremonini [18] that nursing students’ satisfaction was high with the usage of video games in education. Multiple other studies also concur with the flexibility and adaptability of video games and simulation towards any specific specialty [5,6]. Two studies were performed specifically with the pediatric nurse specialty and gaming. The first study performed by Verkuyl, Atack, Masatrilli and Romaniuk [19] studied virtual gaming to develop pediatric nursing skills and was successful in showing increased knowledge retention towards pediatric information and caring for pediatric patients. The second study performed by Verkuyl, Romaniuk, Atack and Mastrilli [20] researched the usage of virtual serious games and the clinical competency of nursing students within the pediatric population. They found that the knowledge gained by utilizing virtual serious games proved to be a statistically significant gain in knowledge and expertise. This illustrates that even specialized nursing can benefit from video games and simulation.
Disadvantages
Despite the advantages of utilizing video games and simulation for the education of nursing students, there are still disadvantages that exist. These must be weighed when attempting to decide whether to incorporate this tool into nursing education. The main disadvantages that were found during the research includes:
• Costs
• User Interface Issues
• Real-life patient care is irreplaceable
This author will now discuss the disadvantages associated with utilizing video games and simulation within nursing education based upon the listing above.
Costs: Costs of everything have to be accounted into anything that is being done, whether in real life or within business. Budgeting, cost, profits and more must be carefully considered when needing or wanting to do just about anything in life. Video games are no exception to cost. Typical costs include the equipment to be able to program the software, manpower to perform the programming, manpower to test the software as well as the marketing for the products and have costs associated with them. Those associated costs are then passed onto the purchaser to keep the developer and publishing company in business. Costs are associated with a large barrier to the adoption of video games and simulation technology integration into a nursing program as well [13]. Typical costs associated with pure video games can range from a few dollars to millions of dollars. For instance, the video game “Grand Theft Auto V” which was produced and released in 2013 ultimately cost $137.5 million dollars to produce (Sinclair, 2013) for a high visibility and very popular video game. This puts into perspective the potential costs of video games from the cheapest to one of the most expensive games to date. The actual cost of an education video game will depend on the simulation type, graphics, and interface [15]. There is the quality issue pertaining to ensuring that the video game or simulation contains the appropriate information and presents the quality and expectations of the nursing program and nursing in general. This is where nursing regulation would have to step in to make sure that the information is sound and that regulations are produced and being followed when utilizing video games. Some of the concepts that are needed for appropriate development of games for nursing education, as provided by Lemermeyer [21]
• Method of learning is to be engaging and valid
• Nurses should be involved in the development
Some of the regulatory components, associated with the content that would need to be considered as well include, as provided by Lemermeyer [21]
• Governance
• Requirements for registration and practice permit renewal
• Scope of nursing practice
• Practice standards and ethics
• Continuing competence
• Professional Conduct
All of these concepts would need to be included within the development of the video game and simulation and would need to be accounted for within the budget due to the time constraints needed for someone to assure that these are followed to ensure that the highest standards and quality is met with the video game.
Another issue to note when considering cost is if the video game or simulation is associated with the usage of a real simulation mannequin. This is another cost that would have to be accounted for within the total cost for the video game or simulation. This would depend on the complexity of the simulation. For example, a half body, CPR only mannequin would cost $1580.00 whereas a full body mannequin would cost $2061.00. [22]. In a product called “Sim Man 3G” produced by Laerdal, this mannequin is very complex allowing it to be used for CPR training, seizures, neurological examination, secretions, IV placement, Medication administration, trauma and more. This, very advanced, mannequin can cost up to $60,000 [23]. These prices do not include the additional equipment that is necessary to maintain and utilize it for multiple students as well. One last very important issue associated with cost is the equipment, rooms to house the equipment, costs for training the trainers, maintaining the equipment and the costs associated with paying the employees to train on the equipment. All of these things can add up.
User interface issues: This type of software issue can be broken down into two main categories. The first being actual user interface issues surrounding the user themselves and the second being the platform for distribution.
user issues: This includes barriers with the language, ease of use of the software, usage of the software, understanding how to navigate within the software as well as the visual presentation of the software [15]. The software would have to be easy enough to pick up and utilize with some instructions, but complex enough to maintain interest in the game to keep attention for adequate learning and knowledge retention. From the complexity point-of-view, if a game is too complex there is a possibility for students to lose interest and risk not learning anything. If a game is too simple, there is the possibility for students to become bored and risk not learning anything. Granic, Lobel and Engels [24] mention about complexity in video games, indicating that the better games tend to be dynamic on the complexity of the game and adapted to the ability of the player while increasing in difficulty and other aspects of the game. Other ideas to be included within the game are the feedback mechanisms for both positive and negative choices made within the game. Reinforcement for positive choices, when performed in a correct fashion, has been found to be the most successful in adapting and learning new behaviors [24] Another issue is the accessibility of the game. Accessibility of software must accommodate students with special needs, and alternative languages as well as students with learning difficulties. This is extremely important to incorporate into the software as it allows for more students to utilize the game and still learn the same information as everyone else. Some of the issues that surround accessibility include alternative methods for obtaining the information, such as alternative text, additional tutor or screens for explanation, text-to-speech, visual enhancements as well as the ability for the game to accept different spellings for those times the students will need to type in an answer [25].
Platform for distribution: This issue revolves around the issue surrounding the number of different operating systems that are available. Currently for computers, three of the most popular operating systems are Windows, Macintosh and Linux. For gaming systems that are popular, there is the Microsoft Xbox, Sony PlayStation, and Nintendo Wii and Switch. For the mobile platform, the most popular are Android and Apple IOS. This list is far from being comprehensive as there are over 50 different ‘operating’ systems throughout the world with different and specific functions that they were designed for. This issue revolves around the decision on how the delivery of the game or simulation will occur. That ultimately would be up to the institution utilizing the software.
Real-life patient care is irreplaceable: It is safe to say that absolutely nothing can completely replace a real-life person sitting, standing or lying in front of the nursing student, who has that ability to utilize all five senses on that patient [26].Patients have different personalities as well as different ways to present signs and symptoms. Video games and simulated patients can only utilize the information that has been programmed into them. It would be impossible to program every single type of skin color, every condition or every symptom that someone can have [12,26] King-Henderson, 2018). In addition to those issues, students can ask real-life patients any type of questions and receive answers to those questions. With virtual or simulated patients, students can only ask questions that were pre-programmed for the game to answer [12,15,26-30]. Multiple research studies have mentioned that simulated patients are no replacement for real-life patients and that video games and simulations should be kept as a supplement to the education on and with real-life patients [1,9,10,12]. Simulations and video games can only show so much, with the educational content, up until the point the student is in a real-life situation and the patient is complaining, talking, coughing, gagging and becoming unstable in front of them and the student has to make a decision on how to treat them on the spot.
Discussion
It was presumed, by this author, that video games and simulation would be a truly welcome addition to the nursing curriculum as an additional tool for the education of nursing students. Based upon the listed advantages, the biggest advantage of the no chance of harm to real humans, while being able to practice, can help significantly decrease nursing student’s anxiety that could be generating a fear of trying new things out to learn. As nursing programs are trying to acquire and maintain clinical sites to help the students flourish and see as much as they can while they are in the safety net of their nursing program, not all types of patients and treatments are available during the clinical and schooling years of nursing students. This is where video games and simulations can help to introduce the students to new concepts and ideas with the ability to specialize and target specific patient populations or skills that students may not see very often and allow them to have some experience with the more specialized patient populations.
The disadvantages, however, are strong with the usage of video games and simulations. The cost is most likely the biggest barrier to many healthcare institutions and schools. The premise that video games can cost a few dollars to millions of dollars can be a threat to the advancement of video games into nursing education. This cost does include the development costs associated with programming, voice-overs, and music as well as testing. This, however, does not include hardware that the simulation may control such as the Sim Man 3G, which has the upward costs of over $60,000, depending on the features required for your institution [23]. There are methods to be able to afford the costs of software and hardware through grants that are offered through the federal government and other entities that offer money for technologies. The cost also doesn’t include the equipment storage, maintenance, rooms to educate and utilize the equipment as well as the cost for the education of the employees and students to benefit.
The other disadvantages such as the interface issues can easily be resolved with the educational facility or healthcare entity choosing one specific operating system to utilize the software as well as limiting the software to in-house usage only. The last disadvantage to gaming is that real patients are not able to be substituted. Although this is a disadvantage, gaming and simulations are not healthcare. Healthcare is the caring of humans that are sick and ill. Humans are not a video game, and thus, video games are not humans. Although video games are programmed by humans, it is nearly impossible to account for every sign and symptom that patients may experience with a disease state. This leads to the mention that video games and simulations are an additional tool in the toolbox for the education of students and nurses. It is not made to replace, but rather to assist in the education of nursing to help create a safe environment for the successful learning of new skills and increase the confidence of those learning. This leads us to the ultimate question, are video games and simulations worth it to utilize for the education of nursing students? Do the advantages outweigh the disadvantages? The appeal of the current research showing positive adjustments in the clinical behaviors and confidence with skills at the bedside is a great start at showing that video games and simulations are a great concept to help with nursing education. The other aspect is the ability to tailor the content of the video games to any specialty that you want it to cover. Nursing is a diverse job with an almost limitless application both inside and outside of the hospital to see any types of injury, illness and even those people that are healthy. However, the cost is one of the barriers to the full adoption of the video game and simulation tool. Looking at it from the patient perspective, with the cost of avoidable medical errors being $19.5 billion, even preventing one percent of that equates to a $195 million dollar savings to the healthcare system, more than enough to pay for even the most expensive $137.5 million dollar Grand Theft Auto video game and have some money left to pay for the marketing of the video game. With that figure in mind, depending on how the nursing school or hospital utilizes the video game and equipment, it will make up the cost of the video game within a year or two, hypothetically with the prevention of common errors.
Conclusion
Video games and Simulations are a valuable tool to both nursing schools and hospitals to help with the education of not just nurses, but anyone within the healthcare field. They offer many advantages to utilizing these modalities of education including no harm to a patient for performing an error, a possible increase in clinical improvement for the student utilizing the game and simulation, as well as the opportunity to tailor video games to multiple different types of specialties. However, despite the advantages, there are also disadvantages including cost, interface issues and the fact that a real-life patient is irreplaceable. The cost is the largest barrier to the adoption of these technologies due to it potentially costing over a million dollars. However, with medical errors, potentially, costing upwards of hundreds of millions to over a billion dollars a year for the US healthcare system, the utilization of video games and simulations can help decrease the preventable errors and, in the long run, pay for the video game and simulation just from those savings. Healthcare is present to take care of people, whether they are ill or healthy and having that ability to prevent errors from happening should be on the top of the priority list for the healthcare system. The personal experience of this author with simulation type of education has been a positive one and this author would like to see the expansion of those technologies and tools for education of all students and experienced professionals.
Acknowledgement
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
References
- Royse MA, Newton SE (2007) How gaming is used as an innovative strategy for nursing education. Nurs Educ Perspect 28(5): 263-267.
- Makary MA, Daniel M (2016) Medical error-the third leading cause of death in the US. BMJ 353: i2139.
- Cheragi MA, Manoocheri H, Mohammadnejad E, Ehsan SR (2013) Types and causes of medication errors from nurse's viewpoint. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res 18(3): 228-231.
- Sleeper JA, Thompson C (2008) The use of hi fidelity simulation to enhance nursing students' therapeutic communication skills. International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship 5(1): 1-12.
- Durham CF, Alden KR (2008) Enhancing patient safety in nursing education through patient simulation.
- Kleinheksel AJ, Ritzhaupt AD (2017) Measuring the adoption and integration of virtual patient simulations in nursing education: An exploratory factor analysis. Computers & Education 108: 11-29.
- Nehring WM, Lashley FR (2009) Nursing simulation: A review of the past 40 years. Simulation & Gaming 40(4): 528-552.
- Rodriguez KG, Nelson N, Gilmartin M, Goldsamt L, Richardson H (2017) Simulation is more than working with a mannequin: Student’s perceptions of their learning experience in a clinical simulation environment. Journal of Nursing Education and Practice 7(7): 30.
- Stokowski LA (2013) A digital revolution: Games, simulations, and virtual worlds in nursing education. Medscape.
- Sundler AJ, Pettersson A, Berglund M (2015) Undergraduate nursing students' experiences when examining nursing skills in clinical simulation laboratories with high-fidelity patient simulators: A phenomenological research study. Nurse education today, 35(12): 1257-1261.
- Xu JH (2016) Toolbox of teaching strategies in nurse education. Chinese Nursing Research 3(2): 54-57.
- Aksoy E (2019) Comparing the Effects on Learning Outcomes of Tablet-Based and Virtual Reality–Based Serious Gaming Modules for Basic Life Support Training: Randomized Trial. JMIR Serious Games 7(2): e13442.
- Alinier G, Hunt WB, Gordon R (2004) Determining the value of simulation in nurse education: study design and initial results. Nurse Educ Pract 4(3): 200- 207.
- Dale, Edgar (1969) Audio-Visual Methods in Teaching. New York, USA, p. 108
- Salovaara Hiltunen M, Heikkinen K, Koivisto JM (2019) User experience and learning experience in a 4D virtual reality simulation game. International Journal of Serious Games 6(4): 49-66.
- Cant RP, Cooper SJ (2010) Simulation‐based learning in nurse education: systematic review. J Adv Nurs 66(1): 3-15.
- Boctor L (2013) Active-learning strategies: the use of a game to reinforce learning in nursing education. A case study. Nurse Educ Pract 13(2): 96-100.
- Cremonini V, Ferri P, Artioli G, Sarli L, Piccioni E, et al. (2016) Nursing students’ experiences of and satisfaction with the clinical learning environment: the role of educational models in the simulation laboratory and in clinical practice. Acta Biomed 86(3Supp): 194-204.
- Verkuyl M, Atack L, Mastrilli P, Romaniuk D (2016) Virtual gaming to develop students' pediatric nursing skills: A usability test. Nurse education today 46: 81-85.
- Verkuyl M, Romaniuk D, Atack L, Mastrilli P (2017) Virtual Gaming Simulation for Nursing Education: An Experiment. Clinical Simulation in Nursing: 13(5): 238-244.
- Lemermeyer G, Sadesky G (2016) The gamification of jurisprudence: Innovation in registered nurse regulation. Journal of Nursing Regulation 7(3): 4-10.
- Laerdal (2017a) QCPR Resusci Anne manikin.
- Laerdal (2017b) SimMan®
- Granic I, Lobel A, Engels RC (2014) The benefits of playing video games. American Psychologist 69(1): 66
- Rice K (2012) Supporting learners with special needs. In: Making the move to K-12 online teaching: Research-based strategies and practices. Boston, USA, pp. 208-237.
- King Henderson P (2018) A Quasi-Experimental Study: The Role of Virtual Simulation on Self-Efficacy, Learning and Confidence in a Central Texas BSN Degree Program, USA.
- Andel C, Davidow SL, Hollander M, Moreno DA (2012) The economics of health care quality and medical errors. J Health Care Finance 39(1): 39-50.
- Brookhaven National Library. BNL, History: The First Video Game.
- Sinclair B (2013) GTAV dev costs over $137 million, says analyst, USA.
- (2017) video game. Dictionary.com Unabridged.
-
Klaudia Ćwiękała Lewis, Brandon H Parkyn. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Video Games and Simulations for Designing Learning Experiences for Nursing Student and Educators. Iris J of Nur & Car. 3(1): 2020. IJNC.MS.ID.000555.
-
Florence nightingale, Learning experiences, Potential inclusion, Patient interactions, Medication, Critical thinking, Confidence, Clinical competency, Manpower, integration
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






