 Research Article
Research Article
Strategic Orientation and Employee Performance: The Role of Organizational Support. A Study of Primary Health Care Centres in Jos North LGA of Plateau State, Nigeria.
Danjuma Kusa1, Ruth Agwom Panle1, Shitnaan E Wapmuk1, Ibrahim M Auwal1 and Arinzechukwu Jude Okpara2*
1The Department of Business Administration, Faculty of Management Sciences, University of Jos, Jos, Nigeria
2Department of Marketing, Faculty of Management Sciences, University of Jos, Jos, Nigeria
Arinzechukwu Jude Okpara, Department of Marketing, Faculty of Management Sciences, University of Jos, Jos, Nigeria.
Received Date: June 27, 2024; Published Date: July 08, 2024
Abstract
In order to utilize human resources fully and augment organizational success, an effective employee performance management system is imperative for any organization to succeed in the long run. In order to achieve this superior performance, this study determine the extent to which perceived organizational support (POS) can mediate between strategic orientation and employee performance of primary health care workers in a bid to develop more lucrative incentive schemes for motivating the employees toward meaningful job participation. A total population of 254 employees of the primary health care centers in Jos North (PHC) was surveyed. The data were analyzed using multiple linear regression with the aid of SPSS. It was discovered that strategic orientation has a positive and significant relationship with employee performance. The extent of the relationship between organizational support and employee performance was also positive and significant. Perceived organizational support also mediates the relationship between strategic orientation and employee performance of organizations. The implication of these findings is that strategic orientation and organizational support are strong forces of employee performance. The study recommended that for optimal employee performance, the primary health care centers should best serve their employees by developing policies and strategies that contribute to positive employee beliefs and attitudes about the centers.
Keywords: Strategic orientation; Organizational support; Employee performance
Introduction
Organizations are facing increased competition due to globalization, changes in technology, political and economic environments and therefore prompting these organizations to train their employees as one of the ways to prepare them to adjust to the increases above and thus enhance their performance. It is important to not ignore the prevailing evidence on growth of knowledge in the business corporate world in the last decade. This growth has not only been brought about by improvements in technology nor a combination of factors of production but increased efforts towards development of organizational human resources. It is therefore every organizations responsibility to enhance the job performance of the employees and certainly implementation of effective strategic orientation is one of the major steps that most companies need to achieve this. As is evident that employees are a crucial resource, it is important to optimize the contribution of employees to the company aims and goals as a means of sustaining effective performance. This therefore calls for managers to ensure an adequate supply of staff that is technically and socially competent and capable of career development into specialist departments or management positions [1].
Employee performance plays an important role for organizational performance. Employee performance is originally what an employee does or does not do. Performance of employees could include: productivity, quantity of output, quality of output, timeliness of output, presence at work, cooperativeness [2]. Harvy [3], pointed that improved individual employee performance could improve organizational performance as well. If viewed in this way, performance is represented as a distribution of outcomes achieved, and performance could be measured by using a variety of parameters which describe an employee’s pattern of performance over time. Good employee performance has been linked with increased consumer perception of service quality, while poor employee performance has been linked with increased customer complaints and brand switching. Employee performance could be simply understood as the related activities expected of a worker and how well those activities were executed. Then, many business personnel directors assess the employee performance of each staff member on an annual or quarterly basis in order to help employees identify suggested areas for improvement. Due to increased globalization and rapid changes in business environments, organizations way of transacting business is increasingly becoming turbulent. Under such an environment, business units should align their internal resources with their strategic focus such as marketing orientation, so as to remain competitive and also to achieve a superior organizational performance [4]. Strategic Orientation focuses on the way an organization adjusts and interacts with its external environment. It has also been termed as strategic fit [5].
Today’s changing work environment, replete with job uncertainty and frequent mergers and acquisitions, contributes to a lack of trust and concern for the mutual welfare between employees and employers. Many employers have yet to fully understand the central importance of favorable relationships with employees to reducing absenteeism as well as enhancing dedication to organizational objectives and increasing performance.
For the benefit of employees and organizations alike, it is crucial for organizations to recognize employees as valuable sources of human capital. Perceived organizational support (POS) an employee’s perception that the organization values his or her work contributions and cares about the employee’s well-being has been shown to have important benefits for employees and employers. For instance, studies have found that employees with high POS suffer less stress at work and are more inclined to return to work sooner after injury [6]. Therefore, organizations can best serve their employees and their bottom line by developing policies and strategies that contribute to positive employee beliefs and attitudes about the organization.
The Primary health care (PHC) is the backbone of a health system. Furthermore, quality PHC initiatives have been recognized as fundamental to improving health outcomes. PHC also has improved population health in low- and middle-income countries.
The contribution of primary care to health and health systems
in low- and middle-income countries: a critical review of major
primary care initiatives and the 2006 Abuja call for accelerated
action towards universal access to HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and
malaria services in Africa. 2–4 May 2006 all emphasized the
importance of investing in PHC for health. Following the World
Health Report, the World Health Organization’s World Health Report
“Primary Health Care (Now More Than Ever) in 2008 asserted that
PHC reforms can deliver equitable health services and secure the
health of communities Given that PHC is essential to strengthening
health systems [7]. However, the performance of the PHC system
is hindered by (1) segmented supply chains; (2) a lack of financial
access to PHC; (3) a lack of infrastructure, drugs, equipment,
and vaccines at the facility level; and (4) poor health worker
performance. Altogether, these factors reflect two overarching
system-level challenges financing and governance that are key root
causes of the dysfunctions observed in the PHC system in Nigeria.
Compared with peer African countries, Nigeria ranks low on
nearly all PHC performance indicators. The government has taken
important steps to address these root causes of underperformance,
but policy gaps remain in achieving sustainable and equitable
provision of PHC for the people of Nigeria. The question that arises
over here is, if monetary incentives are incongruent on one’s effort
and performance, then what are the other associated behavioral
factors that influence enhancing employee performance? At
the same time, with the changing organizational requirements,
the ability to adapt stands as one of an important measure to
assimilate in performance. Unfortunately, little efforts have been
made to verify those subdued variables together empirically.
One of the reasons may be that performance is a difficult concept
to outline and measure. Moreover, Lack of continuous guidance
and coaching, Not wanting to appear incompetent, some people
may try to struggle through their difficulties on their own, either
taking more time or making mistakes along the way, which could
impact overall productivity. Instead, it’s important to develop
a culture of continuous learning so people feel able to ask
questions and empowered to learn on the job. Another problem
this study intends to address is the Performance of public health
care facilities in terms of productivity mixed with a range from
shortages of doctors as indicated by the ratio of doctors to patients
of 5 doctors per 100,000 people in the year 2016, a decrease from
12 doctors per 100,000 people in the year 2012 which is still
below the national rate of 10 doctors per 100,000 people. PHC’s
also face erratic supplies with 38.6% of the patients being asked
to buy their own drugs and equipment to access healthcare. This
poor performance of public health facilities in Jos North leads to
asking questions of whether the strategic orientation dimensions
being implemented by the management have a significant influence
on their performance. This study was also motivated by existing
conceptual and contextual knowledge gaps in previous studies
on the topic such as a study by Matsumo [8]. The studies were
conducted in sectors other than the public health sector thus
presenting contextual knowledge gaps. Contextual knowledge
gaps presented by these studies motivated this study to focus on
the effect of strategic orientation dimensions on performance of
primary health care centers in Jos North LGC. While studies have
been undertaken with regard to establishing the link between a
firm`s strategic orientation and performance, the findings have
sometimes been contradictory and therefore complicating the
assessment of the robustness of concepts used to support the
model that links strategic orientation to employee performance.
In addition, several studies that focus on a specific orientation
or on the direct effects of each respective orientation; ignore the
consideration for the possibility of interaction that they function
as a system. This therefore created an interest in undertaking this
study so as to determine whether strategic orientation dimensions
with the help of organizational support can play significant role on
employee performance in the primary health care sector. The study
raised the following questions, objectives and hypotheses:
i. To what extent does Strategic orientation influences
employee performance of primary health care centers in Jos
North.
ii. What is the relationship between strategic orientation
and organizational support on employees of primary health
care centers in Jos North.
iii. What is the effect of Organizational support on employee
performance of primary health care center in Jos North.
iv. To what extent does organizational support mediate
strategic orientation and employee performance of primary
health care centers in Jos North.
Literature Review
Conceptual Review
The conceptual review section reviews all the variables that cut across the research area (strategic orientation, organizational support and employee performance) in order to have a general view of contemporary issues that made up this study.
employee performance: Improvement of productivity is a central issue in present-day organizations. Productivity through job performance stands as a widely researched domain in literature of organizational behavior (OB) and human resource (HR) development [9]. Job performance as in the form of performance assessment and management is an essential part of effective HR management and it is a most sought-after developmental intervention in HR portfolio [10]. The term “employee performance” signifies individual’s work achievement after exerting required effort on the job which is associated through getting a meaningful work, engaged profile, and compassionate colleagues/employers around [11]. In order to utilize HR fully and augment organizational success, effective employee performance management system is imperative for a business organization. The performance-driven objective is expected to be aligned with the organizational policies so that the entire process moves away from being event-driven to become more strategic and a people-centric perspective [12]. The question that arises over here is, if monetary incentives are incongruent on one’s effort and performance, then what are the other associated behavioral factors that influence enhancing employee performance? At the same time, with the changing organizational requirements, the ability to adapt stands as one of an important measure to assimilate in performance. Unfortunately, little efforts have been made to verify those subdued variables together empirically. One of the reasons may be that performance is a difficult concept to outline and measure.
dimensions of employee performance: Performance is a multi-component concept and on the fundamental level one can distinguish the process aspect of performance, that is, behavioral engagements from an expected outcome [13]. The behavior over here denotes the action people exhibit to accomplish a work, whereas the outcome aspect states about the consequence of individual’s job behavior [14]. Apparently, in a workplace, the behavioral engagement and expected outcome are related to each other [13], but the comprehensive overlap between both the constructs are not evident yet, as the expected outcome is influenced by factors such as motivation and cognitive abilities than the behavioral aspect. Performance in the form of task performance comprises of job explicit behaviors which includes fundamental job responsibilities assigned as a part of job description. Task performance requires more cognitive ability and is primarily facilitated through task knowledge (requisite technical knowledge or principles to ensure job performance and having an ability to handle multiple assignments), task skill (application of technical knowledge to accomplish task successfully without much supervision), and task habits (an innate ability to respond to assigned jobs that either facilitate or impede the performance) [15].
It is believed that an engaged employee works with a sense of passion which leads to translation into not only high performance but extra role behavior as well [17]. The contextual performance is elaborated on the ground of “feeling and viewpoint” that employee embraces about their colleagues, which is termed as espritde- corps (team spirit). A kind of fellow feeling gets intensified through team-spirit, wherein employees are able to share their issues and problems willingly and freely with each other within the organization [18]. Esprit-de-corps is an excellent endeavor for deriving organizational success and earlier researchers in this context have advocated that growth in team spirit within an organization results in better employee performance and a happier workplace [19].
Contextual performance is a kind of attitude like volunteering for extra work, helping others in solving difficult task, upholding enthusiasm at work, cooperating with others at the time of need, sharing critical resources and information for organizational development, abiding by the prescribed rules and regulations, and supporting organizational decisions for a better change. This kind of behavior contributes for creating a stimulating culture and climate of the organization which aids in achieving individual productivity and organizational effectiveness. For selecting and inducting the right personnel in organizations, introducing personality tests and group discussion for measuring a prospective candidate’s ability for contextual performance along with the efficiency tests (ability and experience tests) to measure their task performance is proposed.
strategic orientation: Strategy implies choice and the notion of strategic choice recognizes that given the same environment, similar firms may employ different competitive methods or strategies to address the environment [19]. Competitive strategy is synonymous with the term strategic orientation and the concept of strategy is central to the effectiveness of an organization [20]. In other words, strategic orientation refers to how organizations use strategy “to adapt and/or change aspects of its environment for a more favorable alignment” [21] or how firms strategically position themselves to achieve and sustain competitive advantage It also refers to how strategy is used to improve the organization’s chances of success [22].
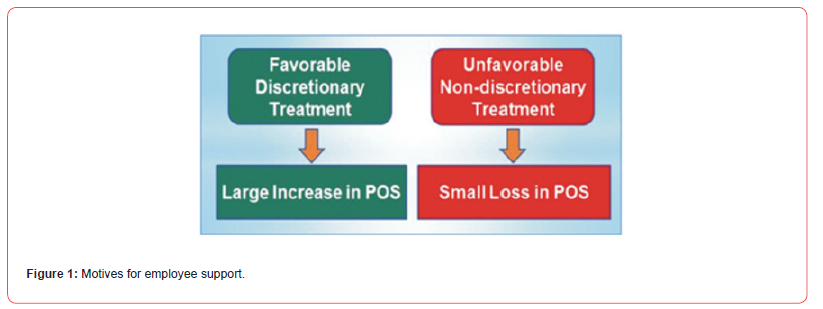
Favorable treatment received by employees from an organization can be of many different kinds, such as recognition for good work, opportunities for promotion and job security. However, such treatment does not necessarily translate into high POS. Employees understand that benefits received from the organization can arise from a variety of motives, not all of which are concerned with employees’ welfare. Research found that when employees received favorable job conditions, POS was six times stronger if employees believed the organization had high control over the job conditions [23]. Therefore, employee perceptions of favorable treatment associated with organizational free choice have a powerful influence on POS. This scenario can be illustrated in the diagram below:
.
Research suggests three useful ways to promote justice perceptions: (1) rewards and resources should be distributed fairly across employees and the rationale for the ways they are distributed should be effectively communicated; (2) employees should be provided with opportunities for active involvement in the development and application of organizational procedures and policies; and (3) supervisors and other representatives of the organization should treat employees with respect and sensitivity. These procedures should influence employees’ perceptions of organizational fairness and, as a result, serve to enhance their POS.
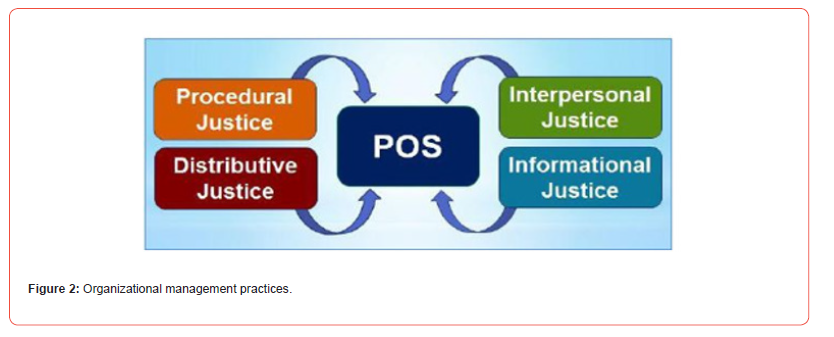
Set achievable goals and reward proportionately: Appropriate rewards and recognition for the achievement of high Performances are strong drivers of POS. When rewards and recognition for high performance are appropriately provided, organizations promote an environment that employees can expect to gain rewards for high performance. This expectation indicates that the organization values employee contributions and, thus, not only increases employees’ willingness to perform at a high level but also serves to enhance their POS [24].
Conceptual Framework
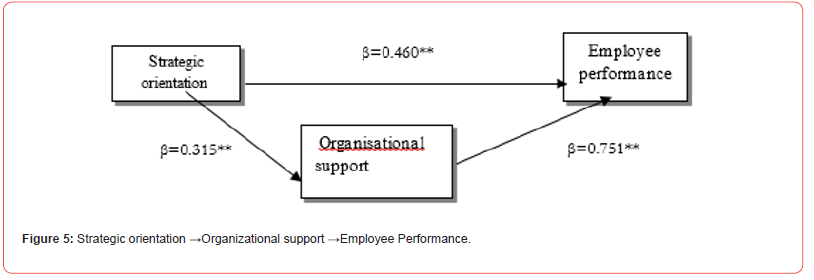
This research framework is configured from the review of literature as the floor plan blueprint for building this study foundation. This foundation blueprint alongside the theoretical framework is necessary in providing insight into the methodological structure and analysis of every research dissertation. The conceptual framework is shown in figure five.
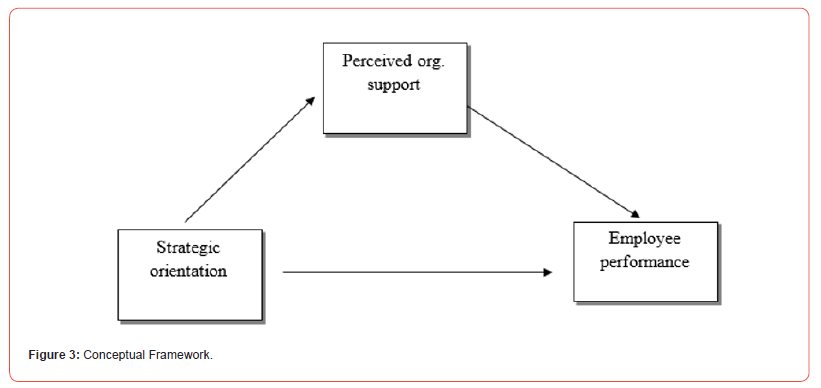
The framework of figure five has the independent variable as strategic orientation (SO). The independent variable has direct relationship with the dependent variable (employee performance). The IV also has a direct relationship with the mediating variable (organizational support).
Theoretical Review
This study will be anchored on the environment-strategyperformance theory, organizational support theory and configuration theory. According to the environment-strategyperformance theory [25], business entities select strategies in response to their external environment because a fit between strategic choice and environmental conditions enhances firm operations, which in turn improve firm performance. More recently, Slater, et al. [26] expanded the traditional environmentstrategy- performance theory to include internal characteristics and capabilities in explaining organizational performance and strategic focus. The second theory is the Configuration theory which posits that an organization will have superior performance if there is an appropriate fit between a firm’s internal organizational characteristics and its strategic focus. It further posits that a match between marketing function and strategic function of a firm will lead to a firm’s performance having a positive effect.
Emperical Review
strategic orientation and employee performance: Gupta [27] while researching on the business orientation and employee performance of Indian SMEs found that a strong entrepreneurial orientation can allow companies to gain from recognizing ways in which new product satisfies the unmet consumer requirements or at the same time demonstrate how it is greater to and exceptionally diverse from reasonable contributions in the eyes of customers. The findings further imply that entrepreneurial orientation has an overall constructive effect on firm performance in the budding economy of India. The findings reinforced other similar studies confirming a noteworthy and optimistic relationship concerning entrepreneurial orientation as well as company performance.
Lee, Choi, Kwak [28] investigated the impact of four scopes of strategic orientation on company innovativeness as well as performance in promising markets with reference to the Smalland Medium-Size Enterprises in South Korea. The study sought to establish the four constructs of strategic orientation namely, possessions of technology, entrepreneurial, market, and learning orientations on firm innovativeness. In count, the study wanted to determine the mediating role of firm innovativeness on these relationships, using a survey of 374 small-and medium-size enterprises in Korea. The findings were that, while technology, entrepreneurial, and learning orientations significantly influence firm innovativeness, firm innovativeness was found to have a noteworthy outcome on firm performance. In addition, the firm innovativeness was found to be statistically significant mediating role in the relationships of technology, entrepreneurial, and learning orientations to firm performance.
strategic orientation and organizational support: So many researches have been done in this area on different contexts but not on all the dimensions. An organization is a purposeful arrangement of resources to achieve a common goal through its established mechanism [29]. Organizations may be for-profit or not for profit purposes thus common goals could be financial, onfinancial or social. The achievement of goals is associated with the organizational performance which is firmly attached with its competitive advantage [30]. In strategic management literature, exploration of sources of sustainable competitive advantage has been at the heart of discussion [31] for superior performance. The extant literature highlights different perspectives to achieve and sustain competitive advantages but two of them are discussed persistently i.e .positional or strategy view and resource-based view of firms.
organizational support and employee performance: Most researches on organizational support have been linked with employee performance and how most of the organizations support their employees. For instance, studies have found that employees with high POS suffer less stress at work and are more inclined to return to work sooner after injury [6]. In addition, high POS positively relates to performance [32,33]. For instance, traffic patrol officers with high POS made more DUI arrests, and steel company managers and line workers with high POS made more creative suggestions for improving operations [34]. Therefore, organizations can best serve their employees and their bottom line by developing policies and strategies that contribute to positive employee beliefs and attitudes about the organization.
strategic orientation, organizational support and employee performance: Manyasi, Kibas & Chep [35] conducted research on the moderating role of organizational support on employee’s efficiency in the banking sector. The study indicated that organizational support positively affects improving employees’ performance. In a meta-analysis of 70 studies, Rhoades et al. demonstrated that employees’ OS could increase job performance [33]. Conversely some previous studies have indicated contradictory findings. Stamper et al. reported that OS was unrelated to task performance among sales people [36]. Therefore, it is not clear whether OS is directly related to job performance. The study, investigate the role of organizational support in improving employees ‘performance specifically in Jordanian maritime transport companies.
Research Gap(S)
The gap in this research begins with one of the criticisms of Moores strategic triangle theory that the strategy is more of event-driven rather than being more strategic and a people (employee) centric perspective. This in turn emphasizes more on the organization rather than on the employees [12]. The gap here is that firms prefer preferential treatment to only their shareholders and ignoring the important role played by employees hence the need to research on how organizations value their employee wellbeing and their work contributions.
On the whole, the strength of this study gap(s) evolves out of the studies done on strategic orientation dimensions and organizational performance outside this country on settings like the hospitality industry, telecommunication industry and other SMES [29]. Moreover, Primary Health Care Centers especially in Jos North LGC have paucity of literature as well as plateau state and Nigeria in general. Therefore, this study is carried out in the Nigerian context particularly in Jos North LGC the plateau state capital. Also, a mediator (perceived organizational support) is also introduced with a proposition to use quantitative method of analysis to address this study problem.
Methodology
Research Design
Research design is a comprehensive plan for data collection in an empirical research project that outlines a blueprint for answering specific research questions and for testing specific hypotheses, and must specify some processes ranging from the data collection process to data analysis [37].
The design of this study is the survey research design. This design has been chosen because the study utilizes the use of standardized questionnaires to collect data about the behaviors of people in a systematic manner. A) Purpose of the study is a survey study comprising of descriptive and explanatory study. This is because the study is undertaken to ascertain and be able to describe the characteristics of the variables of interest. B) Time horizon is cross-sectional because it is studies that gather data just once in order to answer a research question. Data collected in just one-shot. C) The unit of analysis is at the individual level (employee level). D) The research uses the non-contrived setting whereby work progresses with minimal interference while the study was conducted. This study population comprises of all the employees of the 24 primary health care centers in JOS North LGC of Plateau state. Moreover, the unit of analysis is at the employee level so that all employees of the selected PHC will be surveyed about their performance, effectiveness of strategic orientation and the role of organizational support. The study uses the 5-point Likert scale comprising of strongly disagree (1), disagree (2), neutral (3), agree (4), strongly agree (5). Cronbach’s alpha is most widely used method. It may be mentioned that its value varies from 0 to 1but satisfactory value is required to be more than 0.6 for the scale to be reliable. Therefore, the scales adapted for this study had established good reliability. The Cronbach’s alpha for strategic orientation was 0.818, organizational support was 0.815 while employee performance was 0.758. On the other hand, the modified scale suitable for this study has proven reliability value of 0.873. The adapted scales have undergone confirmatory and exploratory factor analysis to determine their construct validity and this gave good factor loading values for convergent and discriminant validities. Strategic orientation produces a convergent validity value of 0.727, organizational support 0.716 while employee performance 0.752. on the other hand, the discriminant validity remained satisfactory as their person correlation coefficients (SO=0.5567, OS=0.476, EP=0.5816.0) in addition to this, the correlation coefficients all exceeded the threshold of 0.5.
The multiple linear regression analysis was adopted for the testing of hypotheses via the statistical package for social sciences (SPSS) statistics 26. According to Sekaran and Bougie, multiple linear regression analysis is an analysis of association between two or more independent variables on a single, interval-scaled dependent variable.
Result
In addition to the manual screening of data, certain pilot checks are conducted with SPSS before test of hypotheses analysis was carried out, in order to ensure appropriate fitness for data and model development. This research work was carried out on the topic Strategic orientation and employee performance: The role of organizational support. A total of 254 questionnaires were personally administered to the respondents. A total of 233 (91.73%) questionnaires were successfully retrieved while 21 (8.27%) were missing.
Respondents’ Data
The respondents’ response by sex for the study, the result shows that 73.82% (172) of the respondents were females while 26.18% (61) were males. The result of the respondents’ response by age is presented in Figure 7. The result reveals that 49.36% (115) of the respondents falls between the age bracket of 18 – 30 years of age, 32.19% (75) were between the ages of 31 – 43 years, 12.88% (30) between the ages of 44 – 57 years and 5.58% (13) were 58 years and above. The response of the respondents by marital status is presented in Figure 8. The result indicates that 108 (46.35%) respondents were married while 87 (37.34%) and 38 (16.31%) were single and divorced respectively shows the percentage response of the respondents by their positions at the primary health care. The result reveals that 46% of the respondents were senior attendants at the primary health care, 23% were deputies in charge, 17% and 14% of the respondents are the heads in charge and volunteers respectively.
Test and Analysis of Hypotheses
Linear regression
Regression analysis describes and evaluates the relationships between a specified dependent variable and one or more independent variables. One can therefore assume that regression is an appropriate statistical method in order to confirm or disconfirm the chosen hypotheses. In regression analysis, important assumptions for a valid regression are elaborated and tested in order to ensure that the final regression model is not flawed. Four hypotheses were proposed in this study in order to measure the relationships among strategic orientation, employee performance and perceived organizational support based on the objectives set out to fulfill this study.
Table 1:Regression Result for IV (SO) and DV (EMP).
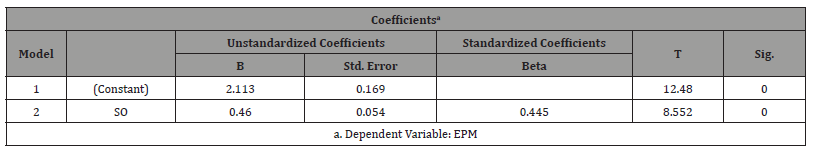
SPSS 26.0
H1: Strategic orientation significantly influences employee performance of primary health care centers in Jos North.
Decision Rule
The decision rule is that if the p-value is less than the level of significance of 0.05, the null hypothesis will be rejected while the alternate hypothesis is accepted. But if the p-value is greater than the level of 0.05, accept the null hypothesis and reject the alternate. The result in Table 1 indicated that the relationship is statistically significant (β = 0.460, t-value = 8.552, p-value = 0.000). This means that strategic orientation has a positive influence on employee performance. Hence, there is a significant relationship between strategic orientation and employee performance of PHCS in Jos North.
Table 2:Regression Result for IV (SO) and mediator (POS).
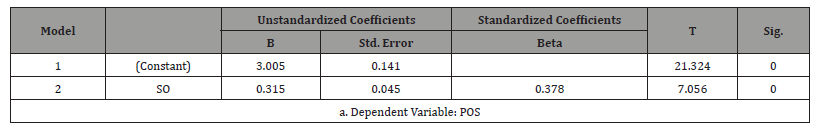
SPSS 26.0
H2: Strategic orientation significantly influences organizational support of primary health centers in Jos North.
Decision Rule
The decision rule is that if the p-value is less than the level of significance of 0.05, the null hypothesis will be rejected while the alternate hypothesis is accepted. But if the p-value is greater than the level of 0.05, accept the null hypothesis and reject the alternate. The result in Table 2 indicated that the relationship is statistically significant (β = 0.315, t-value = 7.056, p-value = 0.000). This means that strategic orientation significantly influences organizational support. Therefore, there is a significant relationship between strategic orientation and perceived organizational support of primary health care centers in Jos North.
Table 3:Regression Result for Mediator (POS) and Employee Performance (EMP).
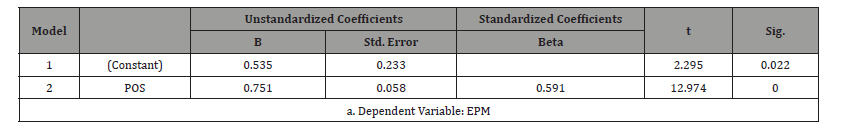
SPSS 26.0
H3: Organizational support significantly influences employee performance of primary health centers in Jos North.
Decision Rule
The decision rule is that if the p-value is less than the level of significance of 0.05, the null hypothesis will be rejected while the alternate hypothesis is accepted. But if the p-value is greater than the level of 0.05, accept the null hypothesis and reject the alternate.
The result in Table 3 indicated that the relationship is statistically significant (β = 0.751, t-value = 12.974, p-value = 0.000). This means perceived organizational support has a positive influence on employee performance.
The Mediating Effects
This study also tested for the mediating effect of perceived
organizational support (pos) to the relationship between strategic
orientations (SO) and Employee Performance (EMP). In other to
test for the mediating effect of Perceived Organizational Support
(POS), the Sobel method of mediation was applied (Sobel 1982).
Mediation occurs when:
(1) The IV significantly affects the mediator,
(2) The IV significantly affects the DV in the absence of the
mediator,
(3) The mediator has a significant unique effect on the DV, and
(4) The effect of the IV on the DV shrinks upon the addition of
the mediator to the model.
This study inserted the a, b, sa, and sb into Figure 4 and this program calculated the critical ratio as a test of whether the indirect effect of the IV on the DV via the mediator is significantly different from zero.
Mediation Effect of perceived organizational support
H4: Organizational support mediates the relationship between strategic orientation and employee performance of primary health centers in Jos North.
Decision Rule
The decision rule is that if the p-value is less than the level of significance of 0.05, the null hypothesis will be rejected while the alternate hypothesis is accepted. But if the p-value is greater than the level of 0.05, accept the null hypothesis and reject the alternate.
Sobel Test
Regression Coefficient between IV and the Mediator
a = 0.315
Sa= 0.045
Regression Coefficient between DV and IV with the Mediator
b = 0.632
Sb= 0.060
Sobel z-Test = 5.3800
P-value = 0.00000
Since the p-value is less than 0.05, it shows that perceived organizational support (POS) is a good mediator between strategic orientation and employee performance. Hence, perceived organizational support does significantly mediate the relationship between strategic orientation and employee performance of primary health centers in Jos North.
Discussion
The result of the major findings from the research work shows that 73.82% (172) of the respondents were females. This implies female employee dominance over their male counterparts in the study area. This result is contrary to Singh & Vinnicombe [38] in their study that women are almost if not completely absent when it comes to occupying senior positions in organizations. They argued that this is a matter of concern, because the talents of women are not being fully utilized. The private sectors is seen and characterized as influential, powerful, financially important and generally not controlled by the state might be the reason why females surpass male employees. Although women work in organizations purporting to have policies that offers equality of pay and opportunities, and though they most of the time appear to be well qualified, the career ladder for women in large organizations appear to be often shortened, while the male ladder extends to top of the career tree. Similarly, Arokiasany [39] observed that many organizations prefer to hire more of the male workers than the female workers because they are of the opinion that male workers have the ability to perform their jobs and can manage their jobs well. As such, quite a number of employers recognize that older workers signify a massive potential pool of high-quality applicants. Thirdly, the regulations set by some countries that outlaw mandatory retirement e.g. the USA. It is a common to assume that as people get older, their skills in terms of agility, strength, speed and coordination begins to decline and job could become boring and lack of intellectual stimulation all contributes to reduced productivity. On the contrary, researches conducted find that the age of employees and their job performance are not correlated and older workforce are more likely to take part in citizenship behavior. This commitment is seen more in older employees than younger environment seeing that they have lower rates of avoidable absence and thus equal rates of unavoidable absence, e.g. sickness absences.
Studies shows that organizations with high levels of well managed diversity are effective and steering ultimately producing corporate cultures that have new perspectives, pioneering capabilities and fresh ideas necessary to survive. Strategic orientation significantly (P≤0.001) influences employee performance of primary health centers in Jos North. While researching on the business orientation and employee performance of Indian SMEs found that a strong entrepreneurial orientation can allow companies to gain from recognizing ways in which new product satisfies the unmet consumer requirements or at the same time demonstrate how it is greater to and exceptionally diverse from reasonable contributions in the eyes of customers.
The result shows that organizational support is highly and positively correlated with strategic orientation (P≤0.001) and employee performance (P≤0.001). Strategic orientation and employee performance together accounts for 73.2% (R2 = 0.732) of the variance in the organizational support. Manyasi, Kibas & Chep [35] conducted research on the moderating role of organizational support on employee’s efficiency in the banking sector. The study indicated that organizational support positively affects improving employees’ performance.
Summary Conclusion and Recommendation
Summary Of Findings
Strategic orientation has a positive and significant relationship with employee performance of primary health care workers. It has a positive and significant effect on organizational support of primary health care workers.
Organizational support has positive and significant effect on employee performance of primary health care workers, and Organizational support can greatly mediate the relationship between strategic orientation and employee performance.
Conclusion
Strategic orientation is significantly related to employee performance of primary health care centers. The strategic orientation components in this study suggest that no primary health care center can sustain an efficient and effective employee performance without the appropriate combination of market, customer, entrepreneurial and technological orientations. This means that the strategic orientation dimensions of Zhou & Li [5] have holistic approach to performance factors in the field of management. It can be concluded that an employee cannot benefit much by applying the strategic orientation dimensions in isolation and this has satisfied part of the objectives in a bid to ascertain the relationship between strategic orientation and employee performance of workers [40-108].
The study also established the individual relationship effect of strategic orientation dimensions on employee performance. It suggests that for optimal employee performance in terms of productivity and job satisfaction there must be a more cognitive ability and task skill facilitated through task knowledge and habits (an innate ability to respond to assigned jobs that either facilitate or impede performance).
The strong mediating effect of organizational support between strategic orientation and employee performance justifies the presence of consistent findings. The implication is that organizations that tends to prioritize their employee well-being is likely to see positive employee perception that the organization values his or her contributions and in turn contributes more positively to the development of the organization. Theories selected for this study have also supported through the direct effect of the organizational support theory on employee performance which has the highest regression value between the independent and dependent variables.
Recommendations
The following suggestions are made from the outcome of
this study to help improve the employee performance of most
organizations if applied judiciously.
i. Organizations in the health care sector should appropriate
the multi-dimensional attributes of strategic orientation
dimensions for sustainable employee performance. This can
always be done by diagnosing and their strategies whenever
the current one seems no longer effective using the employee
performance appraisal scale.
ii. Employees in the primary health care centers need to
be familiar with all the strategic orientation dimensions for
optimal result. Effective employee performance management
system is imperative for any organization to succeed.
Organizations should adopt a more lucrative and incentive
schemes for motivating the employees toward meaningful job
participation.
iii. The health care sector should put more emphasis on
the context of task performance as effectiveness with which
job occupants execute their assigned task that realizes the
fulfillment of organizations vision while rewarding the
employee and the firm proportionately.
iv. Organizations should set achievable and recognitive
rewards for high performance thereby providing an
environment that employees can expect to gain rewards for
higher performance. A compensation strategy in organizations
could serve as a strong contributor to perceived organizational
support by an employee because of its versatility to
appropriately reward and recognize high performance.
v. The health care sector should provide an effective
workplace social network that provides a web of interpersonal
relationships that offer information about how to become a
successful organization member as well as provide friendships that
make work-life more pleasant.
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Afshan S, Sobia I, Kamran A, Nasser M (2012) Impact of training on employee performance: a study of telecommunication sector in Pakistan. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business 4: 6.
- Guest DE (1997) Human resource management and industrial relations. Journal of Management Studies 24(5): 503-521.
- Harvey M, Myers M, Novicevic MM (2002) The Role of MNCs in Balancing the Human Capital “Books” between African and Developed Countries. International Journal of Human Resource Management 13(7):1060-1076.
- Ahlstrom D (2012) On the types of papers, the Asia Pacific Journal of Management. Asia Pacific Journal of Management 29(1): 1-7.
- Zhou KZ, CB Li (2010) How Strategic Orientations Influence the Building of Dynamic Capability in Emerging Economies. Journal of Business Research 63(3): 224-231.
- Shaw WS, Reme SE, Pransky G, Woiszwillo MJ, Steenstra IA, et al. (2013) The pain recovery inventory of concerns and expectations: a psychosocial screening instrument to identify intervention needs among patients at elevated risk of back disability. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine / American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 55(8): 885-894.
- (2016) Nigerian National Primary Health Care Development Agency. Public health facilities.
- Matsumo GL, Mentzer W (2000) The External Control of Organizations: A Resource Dependence Perspective. Harper & Row: New York.
- Bommer WH, Johnson JL, Rich GA, Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB (1995) On the interchange ability of objective and subjective measures of employee performance. Personnel Psychology 48(1): 587-605.
- Bateman TS, Snell SA (2007) Management: Leading & collaborating in a competitive World. Boston: McGraw-Hill.
- Karakas F (2010) Spirituality and performance in organizations: A literature review. Journal of Business Ethics 94(1): 89-106.
- Jena LK, Pradhan RK (2014) Deliverables towards Human Resource sustainability: A conceptual review. European journal of Business Management 6(23): 95-102.
- Borman WC, Brush DH (1993) More progress toward a taxonomy of managerial performance requirements. Human Performance 6(1): 1-21.
- Campbell JP (1990) Modeling the performance prediction problem in industrial and organizational psychology. In Dunnette MD, Hough LM (Eds), Handbook of industrial and organizational psychology pp. 687-732.
- Conway JM (1999) Distinguishing contextual performance from task performance for managerial jobs. Journal of Applied Psychology 84(3): 3-13.
- Kahn WA (1990) Psychological conditions of personal engagement and disengagement at work. Academy of Management Journal 33(1): 692-724.
- Jaworski BJ, Kohli AK (1993) Market orientation: Antecedents and consequences. Journal of marketing 57(3): 53-70.
- Cohen SG, Bailey DE (1999) What makes teams work: Group effectiveness research from the shop floor to the executive suite. Journal of Management 23(3): 239-290.
- Dess GG, Davis PS (1984) "Porter's (1980) Generic Strategies as Determinants of Strategic Group Membership and Organizational Performance." The Academy of Management Journal 27 (3): 467-488.
- Evered R (1983) "So What is Strategy." Long Range Planning 16(3): 57-72.
- Manu FA, Sriram V (1996) "Innovation, Market Strategy, Environment, and Performance." Journal of Business Research 35(1): 79-91.
- Miller A, Camp B (1985) "Exploring Determinants of Success in Corporate Ventures." Journal of Business Venturing 1(1): 87-105.
- Eisenberger R, Cummings J, Armeli S, Lynch P (1997) Perceived organizational support, discretionary treatment, and job satisfaction. Journal of Applied Psychology 82(5): 812-820.
- Eisenberger R, Rhoades L, Cameron J (1999) Does pay for performance increase or decrease perceived self-determination and intrinsic motivation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 77: 1026-1040.
- Child J, Kieser A (1972) Development of Organizations over Time. Handbook of Organizational Design. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Slater FS, Olson EM, Hult GTM (2006) The moderating influence of strategic orientation on the strategy formation capability-performance relationship. Strategic Management Journal 27(12): 1221-1231.
- Gupta N, Shaw JD (2014) Employee compensation: The neglected area of HRM research. Human Resource Management Review 24(1): 1-4.
- Lee DH, Choi BS, Kwak JW (2015) The effects of four Dimensions of strategic Orientation on Firm Innovativeness and Performance in Emerging Market Small-and medium size Enterprises. Emerging Markets Finance & Trade 50(5): 78-96.
- Miles RE, Snow, CC, Meyer AD, Jr Cleman HJ (1978) Organizational Strategy, Structure and Policies. The Academy of Management Review 3(3): 546-562.
- Ismail AI, Rose RC, Abdullah H, Uli J (2010) The relationship between organizational competitive advantage advantageand performance moderated by the age and sizeof firms. Asian Academy of Management Journal 15(2): 157-173.
- Porter ME (1991) Towards a dynamic theory of strategy. Strategic Management Journal 12(8): 95-117.
- Kurtessis JN, Eisenberger R, Ford MT, Buffardi L, Stewart KA, et al. (2015) Perceived organizational support: A meta-analytic evaluation of organizational support theory. Journal of Management.
- Rhoades L, Eisenberger R (2002) Perceived organizational support: A review of the Literature. Journal of Appl Psychol 87(4): 698-714.
- Eisenberger R, Fasolo P, Davis-LaMastro V (1990) Perceived organizational support and employee diligence, commitment, and innovation. Journal of Applied Psychology 75: 51-59.
- Manyasi J, Kibas PB, Chep KR (2011) Effects of organizational support for career development on employee performance: A case of Kenyan public universities. Kabarak University First International Conference pp. 1-17.
- Stamper CL, Johlke MC (2003) The impact of perceived organizational support on the relationship between boundary spanner role stress and work outcome. Journal of Management 29(4): 569-588.
- Bhattacherjee A (2012) Social science research: principles, methods, and practices.
- Singh V, Vinnicombe S (2004) Why So Few Women Directors in Top UK Boardrooms. Evidence and Theoretical Explanations. Corporate Governance: An International Review 12(4): 479-488.
- Arokiasany AA (2013) Literature Review on Workforce Diversity, Employee Performance and Organizational Goals: A Concept Paper. International Refereed Research Journal IV: (4).
- Allen DG, Shore LM, Griffeth RW (2003) The role of perceived organizational support and supportive human resource practices in the turnover process. Journal of Management 29(1): 99-118.
- Atuahene-Gima K, Ko A (2001) An empirical investigation of the effect of market orientation and entrepreneurship orientation alignment on product innovation. Organization Science 12(1): 54-74.
- Austin JT, Villanova P (1992) The criterion problem: 1917–1992. Journal of Applied Psychology 77(1): 836-874.
- Baard SK, Rench TA, Kozlowski SWJ (2014) Performance adaptation: A theoretical integration and review. Journal of Management 40(2): 48-99.
- Bateman TS, Organ DW (1983) Job satisfaction and the good soldier: The relationship between affect and employee “citizenship.” Academy of Management Journal 26(1): 587-595.
- Bergeron DM (2007) The potential paradox of organizational citizenship behavior: Good Citizens at what cost. Academy of Management Review 32(4): 1078-1096.
- Bonner SE, Hastie R, Young SM, Hesford J, Gigone D (2001) Effects of monetary incentives on the performance of a cognitive task: The moderating role of skill. (Working Paper). University of Southern California. Los Angeles, California.
- Borman WC, Buck DE, Hanson MA, Motowidlo SJ, Stark S, et al. (2001) An examination of the comparative reliability, validity, and accuracy of performance ratings made using computerized adaptive rating scales. Journal of Applied Psychology 86(2): 965-973.
- Brief AP, Motowidlo SJ (1986) Prosocial organizational behaviors. Academy of Management Review 11(1): 710-725.
- Choi YR, Shepherd DA (2004) Entrepreneurs’ decisions to exploit opportunities. Journal of Management 30(3): 377-395.
- Chinawa J (2015) Factors militating against effective implementation of primary health care (PHC) system in Nigeria. Ann Trop Med Public Health 8(1): 5-9.
- Eisenberger R, Armeli S, Rexwinkel B, Lynch PD, Rhoades L (2001) Reciprocation of perceived organizational support. J Appl Psychol 86(1): 42-51.
- Eisenberger R, Huntington R, Hutchison S, Sowa D (1986) Perceived organizational support. Journal of Applied Psychology 71: 500-507.
- Eisenberger R, Stinglhamber F (2011) Perceived organizational support: Fostering enthusiastic and productive employees. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Eisenberger R, Wang Z, Mesdaghinia S, Wu H, Wickham R (2013) Perceived follower support: Contributions to supportive supervision and workgroup outcomes. Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology Houston TX.
- Eisenberger R, Huntington R, Hutchison S, Sowa D (1986) Perceived organizational Support. J Appl Psychol 71(3): 500-507.
- Elovainio M, Van den Bos K, Linna A, Kivimaki M, Ala-Mursula L, et al. (2005) Combined effects of uncertainty and organizational justice on employee health: Testing the uncertainty management model of fairness judgments among Finnish public sector employees. Social Science and Medicine 61(12): 2501-2512.
- Friedman D, Sunder S (1994) Experimental methods: A primer for economists. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Gannon JM, Doherty L, Roper A (2012) The role of strategic groups in understanding strategic human resource management. Personnel Review 41(4): 513.
- Gatignon H, Xuereb JM (1997) Strategic orientation of the firm and new product performance. Journal of Marketing Research 34: 77-90.
- Gouldner AW (1960) The norm of reciprocity: A preliminary statement. American Sociological Review 25: 161-178.
- Greenberg J, Baron RA (2008) Behaviors in organization. Dorling Kindersley (India) PVT. Ltd.
- Grinstein A (2008) The relationships between market orientation and alternative strategic orientations: a meta- analysis. European Journal of Marketing 42(1/2):115-134.
- Griffin M, Parker S, Mason C (2010) Leader vision and the development of adaptive and proactive performance: A longitudinal study. Journal of Applied Psychology 95(3): 174-182.
- Hambrick DC (1982) "Environmental Scanning and Organizational Strategy." Strategic Management Journal 32: 159-174.
- Hamel GP, Prahalad CK (1994) Competing for the Future. Harvard Business Review 72(4): 122-128.
- Hayton JC, Carnabuci G, Eisenberger R (2012) With a little help from my colleagues: A social embeddedness approach to perceived organizational support. Journal of Organizational Behavior 33: 235-249.
- Heneman RL, Coyne EE (2007) Implementing total rewards strategies: A guide to successfully implementing and planning a total rewards system. SHRM Foundation’s Effective Practice Guidelines Series.
- Hesketh B, Neal A (1999) Technology and performance. In Ilgen DR, Pulakos ED (Eds), The changing nature of performance: Implications for staffing, motivation, and development. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass pp. 21-55.
- House JS, Umberson D, Landis KR (1988) Structures and processes of social support. Annual Review of Sociology 14: 293-318.
- Huang JL, Ryan AM, Zabel KL, Palmer A (2014) Personality and adaptive performance at work: A meta-analytic investigation. Journal of Applied Psychology 99(1): 162-179.
- Hult GTM, Hurley RF, Knight GA (2004) Innovativeness: Its antecedents and impact on business performance. Industrial Marketing Management 33(5): 429-438.
- Ijadunola KT (2013) Free health services in Nigeria: how beneficial to the poor.
- Ilgen DR, Pulakos ED (1999) Employee performance in today’s organizations. In Ilgen DR, Pulakos ED (Eds), The changing nature of performance: Implications for staffing, motivation, and development. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass pp. 21-55.
- Jacobson JM, Jones AL, Bowers N (2011) Using existing employee assistance program case files to demonstrate outcomes. Journal of Workplace Behavioral Health 26: 44-58.
- Josef H (2010) Managing the Aging Workforce: A Challenge for Human Resource Managers. Germany: German National Library.
- Lambert SJ (2000) Added benefits: The link between work-life benefits and organizational citizenship behavior. Academy of Management Journal 43: 801-815.
- Lee C, Alonso A, Esen E, Schramm J, Dong Y (2014) 2014 employee benefits: A research report by SHRM.
- Lian LK (2012) Leadership styles and organizational citizenship behavior: The mediating effect of sub ordinates competence and downward influence tactics. Journal of Applied Business and Economics 13(2): 59-96.
- Lukas Bryan A, Orville C Ferrell (2010) “The Effect of Market Orientation on Product Innovation.” Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 28 (2): 239-247.
- Lumpkin, G. T., & Dess, G. G. (2006) Clarifying the entrepreneurial orientation construct and linking it to performance. Academy of Management Review, 21: 135-172.
- Macinko J, Starfield B, Shi L (2003) The contribution of primary care systems to health outcomes within Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)countries, 1970–1998. Health Serv Res 38(3): 831-865.
- Hamel GP, Prahalad CK (1994) Competing for the Future. Harvard Business Review 72(4): 122-128.
- Moore GC, Benbasat I (1991) Development of an instrument to measure the Perceptions of adopting an information technology innovation. Information Systems Research 2(3): 173-191.
- Motowidlo SJ, Borman WC, Schmit MJ (1997) A theory of individual differences in task and contextual performance. Human Performance 10(1): 71-83.
- Muindi F (2011) The Relationship between participation in decision making and job satisfaction among academic staff in the school of business, University of Nairobi. Journal of Human Resources Management Research 20: 9-34.
- Nadiri H, Tanova C (2010) An investigation of the role of justice in turnover intentions, job satisfaction, and organizational citizenship behavior in hospitality industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management 29(1): 33-41.
- Narver JC, Slater SF (1990) The Effect of a Market Orientation on Business Profitability. Journal of Marketing 54(4): 20-35.
- National Bureau of Statistics (2010) Nigeria Poverty Profile Report 2010.
- National Health Insurance Scheme (1999) National health insurance scheme decree No 35 of1999.
- Noruzy (2011) Investigation the relationship between organizational justice, and organizational citizenship behavior: The mediating role of perceived organizational support. Indian Journal of Science and Technology 4(7): 842-847.
- Noble CH, Sinha RK, Kumar A (2002) Market Orientation and Alternative strategic Orientations: A Longitudinal Assessment of Performance Implications. Journal of Marketing 66(4): 25-39.
- Class OA, Ngo J (2007) The effects of perceived industry competitive intensity and marketing related capabilities: Drivers of superior brand performance. Industrial Marketing Management 39(4): 571-581.
- Parnell JA (2015) Management and strategic orientation in Small and Medium-size Enterprises (SMEs) In Peru, Mexico and The United States. Journal of Contingencies Crisis Management Volume 23(4).
- Park BI, Ghauri PN (2011) Key factors affecting acquisition of technological capabilities from foreign acquiring firms by small and medium sized local firms. Journal of World Business 46(1): 116-125.
- Pfeffer J, Salancik GR (1978) The external control of organizations: A resource dependence perspective. New York: Harper & Row.Plateau State Ministry of Health. Annual health statistical bulletin. In: Planning Research and Statistics, editor. Jos: Plateau State Government 2006: 17-20.
- Renko M, Carsrud A, Brannback M (2009) The effect of a market orientation, entrepreneurial orientation, and technological capability on innovativeness: a study of young biotechnology ventures in the United States and in Scandinavia. Journal of Small Business Management 47(3): 331-368.
- Schwartz B (2009) Environmental Strategies as Automorphic Patterns of Behavior, Business Strategy and the Environment. 18: 192-206.
- Shin S, Aiken KD (2012) The mediating role of marketing capability: evidence from Korean companies. Asian pacific journal of marketing capability. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics 24(4): 658-677.
- Slater SF, Narver JC, (1994) Market Orientation, Customer Value, and Superior Performance. Business Horizons 37(2): 22-28.
- Stajkovic AD, Luthans F (2001) The differential effects of incentive motivators on work performance. Academy of Management Journal 44: 580-590.
- Teece DJ, Pisano G, Shuen A (1997) "Dynamic Capabilities and Strategic Management." Strategic Management Journal 18(7): 509-533.
- Tripathy SP (2014) Impact of motivation on job performance of contractual staff in Devi Ahilya University Indore (M.P.). Paripex-Indian Journal of Research 3(5): 1-5.
- Tsai Kuen-Hung, Shu-yi Yang (2013) Firm innovativeness and business performance: The joint moderating effects of market turbulence and competition. Industrial Marketing Management 42(8): 1279-1294.
- Werner J (1994) Dimensions that make a difference: Examining the impact of in-role and extra-role behaviors on supervisory ratings. Journal of Applied Psychology 79(3): 98-107.
- World Health Organization (2016) World Health Statistics 2016. Geneva: World Health Organization.
- Wollum A, Burstein R, Fullman N, Dwyer-Lindgren L, Gakidou E (2015) Benchmarking health system performance across states in Nigeria: a systematic analysis of levels and trends in key maternal and child health interventions and outcomes. 2000–2013 BMC Medicine 13:208.
- Worstall T (2015) The fed knows why Wal-Mart raised wages. Forbes.
- Ziobro P (2015) Target to increase wages to at least $9/hour for all workers in April. The Wall Street Journal.
-
Danjuma Kusa, Ruth Agwom Panle, Shitnaan E Wapmuk, Ibrahim M Auwal and Arinzechukwu Jude Okpara*. Strategic Orientation and Employee Performance: The Role of Organizational Support. A Study of Primary Health Care Centres in Jos North LGA of Plateau State, Nigeria.. Iris J of Eco & Buss Manag. 2(3): 2024. IJEBM.MS.ID.000539.
-
Financial access, Segmented supply chains, Lack of infrastructure, Strategic orientation dimensions, Behavioral aspect, Contextual performance, Mediating variable, Entrepreneurial orientation, Shareholders, Perceived organizational support
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






