 Review Article
Review Article
Investigate and Analyzing of Loaded Beam-Columns with Initial Deviation by AGM Method
M R Akbari1*, Sara Akbari2 and Esmaeil Kalantari2
1Department of Civil Engineering and Chemical Engineering, Germany
2Department of Pharmaceutical Technical Assistant, Dr. Kurt Blindow Vocational School, Germany
2Department of Chemical Engineering, Islamic Azad University, Ghaemshahr, Iran
M R Akbari, Department of Civil Engineering and Chemical Engineering, Germany.
Received Date: January 04,2023; Published Date: January 20, 2023
Abstract
Euler–Bernoulli beams theory (also known as engineer’s beam theory or classical beam theory) in general it can be a nonlinear theory of elasticity which provides a means of calculating the load-carrying and deflection characteristics of beams. It is thus a special case of Timoshenko beam theory that accounts for shear deformation and is applicable for thick beams. It was first enunciated circa 1750 , but was not applied on a large scale until the development of the Eiffel Tower and the Ferris wheel in the late 19th century. Additional analysis tools have been developed such as plate theory and finite element analysis, but the simplicity of beam theory makes it an important tool in the sciences, especially structural and mechanical engineering.
Theorical Formulation
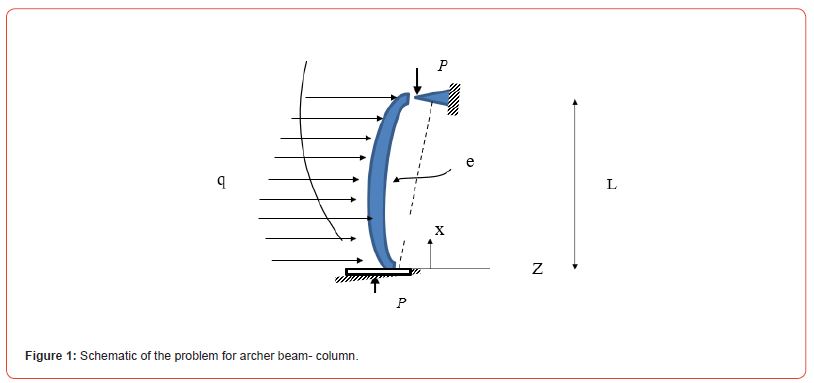
We consider beam-column with no constant cross -section I (x ) and initial deviation (e ),and so Applying two loaded (distribution load q and axial force P ) affecting of it , weight of column (W ) also with separate loading affecting on it and it’s shown in this Figure1.
According to above beam-column Figure1,we have two external force (axial (P) and vertical load on beam(q)) and so beam- column have initial deviation than before, in this situation we have non linear differential equation of complicated as follow :
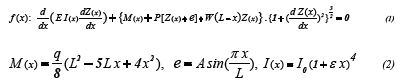
W= column-beam weight
The boundary conditions in fixed side ( x = 0 )are as follows: Z(0) = 0 , Z′(0) = 0 (3)
Solving the nonlinear differential equation by AGM
The answer of Eq. (1) in this method is considered by AGM as polynomials of series with constant coefficients as follows:
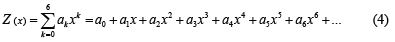
The constant coefficients of Eq.(4) which 0 1 6 {a ,a ,...,a } can easily be computed by applying boundary conditions. Applying boundary conditions in AGM:
The constant coefficients 0 1 6 {a0,a1,...,a6}in Eq.(4) are just achieved with respect to the given boundary conditions are applied in two manners in AGM.
i) In general, the initial conditions are applied on Eq.(4) in the form of:
Z(x = 0) = 0 → a0 = 0 (5)
Z′(x = 0) = 0 → a
ii) The application of boundary conditions on the main differential equation which in this case is Eq.(1) and also on its derivatives is done as follows:
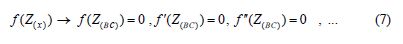
Therefore, after substituting Eq.(4) which has been considered as the answer of the main differential equation into Eq.(1), the boundary conditions are applied on the obtained equation and also on its derivatives on the basis of Eq.(7) as follows:
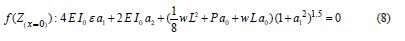
Then for the first derivative of the achieved equation, we will have:
\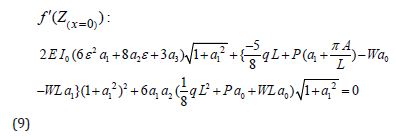
And so second derivative:
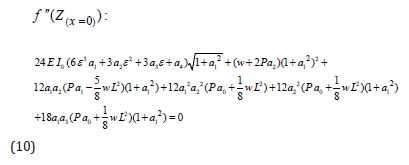
Then we can apply the initial condition to high derivative of differential equation as follow:
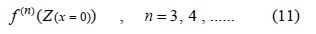
By solving a set of algebraic equations which is consisted of seven equations with seven unknowns the constant coefficients 0 1 6 {a0,a1,...,a6}from Eq. (4) can easily be yielded as follows:To simplify, the following new variables are introduced as:
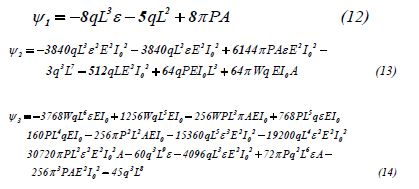
Therefore, the constant coefficients of Eq. (4) are achieved as follows:
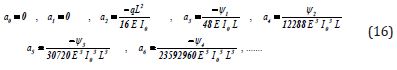
By substituting the obtained values from Eqs. (16) into Eq.(4), the solution of the mentioned problem Eq.(1) will be obtained as follows:
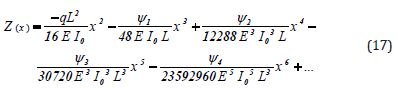
By selecting the following physical values:
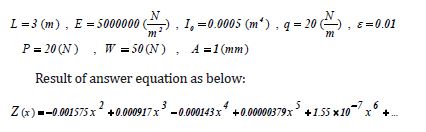
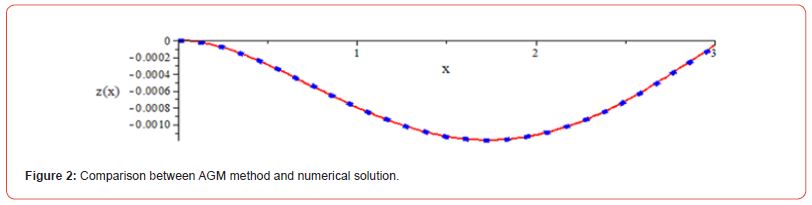
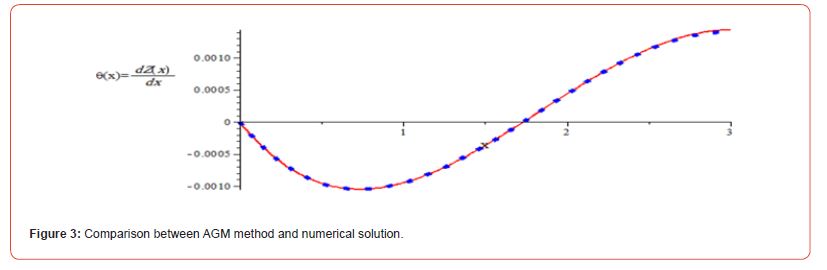
Comparing the achieved solutions between Numerical Method and AGM: (Figure 2 and Figure 3)
Figures (2,3) illustrated that the AGM method is precise and reliable and capability to solve complex nonlinear differential equation when compares to numerical method.
Conclusion
In this article, we proved that with this new method, all kinds of complex practical problems related to nonlinear differential equations can be easily solved analytically for beam-column in the mechanics and civil engineering. Obviously, most of the phenomena in dynamics and aerodynamics are nonlinear, so it is quite difficult to study and analyze nonlinear mathematical equations in this area, also we wanted to demonstrate the strength, capability and flexibility of the new AYM method(Akbari-Yasna Method).This method is newly created and it can have high power in analytical solution of all kinds of industrial and practical problems in engineering fields and basic sciences for complex nonlinear differential equations.
Acknowledgment
History of AGM , ASM , AYM , AKLM , MR.AM and IAM methods:
AGM (Akbari-Ganji Methods), ASM (Akbari-Sara’s Method) , AYM (Akbari-Yasna’s Method) AKLM (Akbari Kalantari Leila Meth od), MR.AM (MohammadReza Akbari Method)and IAM ( Integral Akbari Methods), have been invented mainly by Mohammadreza Akbari (M.R.Akbari) in order to provide a good service for researchers who are a pioneer in the field of nonlinear differential equations.
*AGM method Akbari Ganji method has been invented mainly by Mohammadreza Akbari in 2014. Noting that Prof. Davood Domairy Ganji co-operated in this project.
*ASM method (Akbari Sara’s Method) has been created by Mohammadreza Akbari on 22 of August, in 2019. *AYM method (Akbari Yasna’s Method)has been created by Mohammadreza Akbari on 12 of April, in 2020. *AKLM method (Akbari Kalantari Leila Method)has been created by Mohammadreza Akbari on 22 of August, in 2020.
MR.AM method (MohammadReza Akbari Method)has been created by Mohammadreza Akbari on 10 of November, in 2020.
*IAM method (Integral Akbari Method)has been created by Mohammadreza Akbari on 5 of February, in 2021.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
References
- (2014) Book Nonlinear Dynamic in Engineering by Akbari-Ganji's MethodISBN-13: 978-1514401699, ISBN-10: 151440169X.
- MR Akbari, Sara Akbari, Esmaeil Kalantari (2020) ‘Akbari-Ganji‟s method “AGM” to chemical reactor design for non-isothermal and non-adiabatic of mixed flow reactors’Journal of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science 11(1): 1-9.
- MR Akbari, DD Ganji, M Nimafar (2014) Significant progress in solution of nonlinear equations at displacement of structure and heat transfer extended surface by new AGM approach. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering Journal.
- K Rostami, MR Akbari, DD Ganji, S Heydari (2014) Investigating Jeffery-Hamel flow with high magnetic field and nanoparticle by HPM and AGM. Cent Eur J Eng 4(4).
- R. Akbari, D. D. Ganji, A. Majidian , A. R. Ahmadi (2014) “Solving nonlinear differential equations of Vanderpol , Rayleigh and Duffing by AGM. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering.
- DD Ganji, MR Akbari, AR Goltabar (2014) Dynamic Vibration Analysis for Non-linear Partial Differential Equation of the Beam - columns with Shear Deformation and Rotary Inertia by AGM. Development and Applications of Oceanic Engineering (DAOE).
- MR Akbari, DD Ganji, AR Ahmadi, Sayyid H Hashemi kachapi (2014) Analyzing the Nonlinear Vibrational wave differential equation for the simplified model of Tower Cranes by (AGM). Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering 9(1): 58-70.
- MR Akbari, M Nimafar, DD Ganji, MM Akbarzade (2014) “Scrutiny of non-linear differential equations Euler Bernoulli beam with large rotational deviation by AGM” Springer
- MR Akbari, Sara Akbari, Esmaeil Kalantari (2020) A Study about Exothermic Chemical Reactor by ASM Approach Strategy”Crimson Publishers Wings to the Research.
-
M R Akbari*, Sara Akbari and Esmaeil Kalantari. Investigate and Analyzing of Loaded Beam-Columns with Initial Deviation by AGM Method. Insi in Chem & Biochem. 2(3): 2023. ICBC. MS.ID.000540.
-
Civil Engineering and Chemical Engineering, Pharmaceutical Technical, Investigate, Analyzing, Beam-Columns, AGM Method, derivatives
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






