 Research Article
Research Article
Effect of 12-week Rehabilitation Exercises on Body Self-Descriptive and Social Unrest Students with Lordosis
Mohammad bagher Forghani Ozrudi*
MA Sport, PE Teacher, Education Office, Babol, Iran
Corresponding AuthorMohammad bagher Forghani Ozrudi, Master of bachelor, Department of Physical Education, Education Office, Babol, Iran.
Received Date: March 02, 2022; Published Date: April 06, 2022
Abstract
The aim of this research was to effect of 12-week rehabilitation exercises on body self-descriptive and social unrest students with lordosis. The research was conducted by pretest-posttest method. Statistical society of research includes 20 boy students than selected randomly and voluntarily and has been divided in the two groups of test and control. In order to gather datum, we have used of multi-dimension relations of self-body questionnaire and social unrest questionnaire. The method of research is tested in the pre-test, post-test kind and by control group. The result of the study All findings using the statistical software in SPSS23 and evaluated p<0.05. The result of variance analysis showed there is meaningful difference among test groups and control. It means, reforming practices are influential on improving body self-descriptive and social unrest, Rehabilitators can use the proposed research protocol to rehabilitate students with lordosis.
Keywords: Rehabilitation Exercises, Self-Description of Body, Social Unrest, Lordosis, Student
Introduction
Having a good physical condition is one of the essential needs for human beings. Proper body posture in any person in the first place indicates his health and well-being. Optimal physical condition refers to a condition in which the body engages in daily work and activity with the least amount of energy and produces less fatigue [1]. Behavior development and learning is concentrated on understanding and internal and external factors influential on knowledge completeness [2,3]. Self-imagination as a one of these factors is deterministic on understanding and sensation completeness of a person. Self-imagination is collection of characteristics in which person applies for his own description and is one of important aspects of social growth in which has been achieved gradually through social experience and relation to others [4].
Self-imagination does have multi-dimensions structure in which could be divided in the two levels of educational and noneducational. Educational self-imagination or scientific is related to self-imagination in the grounds of lessons like mathematic, English language. Non educational self-imagination is divided to social level, sensation and body in which any of them does have some dimensions [5,6].
Bodily self-imagination or self-description of body as a one of non-educational self-imagination shows person view to bodily dimension, abilities, bodily skills like body appearance, fat content, flexibility, coordination, stability, power [7]. Body condition and figure structure is related to body and mental health, existence of figure rudeness does have undesired effects on understanding and body image, especially in youth (Alnabi, 2000). It could influence on persons self-confidence [8].
There are so many research about spinal column and mental factors. [9] Boomgeraphner and Soker (1990) showed there is relation among body condition and mental factors [9]. [10] showed the effect of mental characteristic on those who have spinal column rudeness [10]. Against Balzini et al, studies (2003) in which examined the behavior of persons by spinal column rudeness and showed there is relation among these variables and spinal column status rudeness [11].
[12] in a study on Tehran university student has not found meaningful relation among Kyphosis mean and mental factors [12]. From clinical view, agitation in different levels of behavioral, bodily and understanding has been observed. But, because any agitation mode does have mental and bodily indicator, therefore, agitation requires some bodily signs [13]. It has been found in a study, more than 90% of patients affected by body rudeness has experienced one period of basic depression in their life. About 70% does have agitation disorder and about 30% have some kinds of piloctic [14]. Mosburger & Egel has done some studies for finding characteristic disorder in patient affected by spinal column disease and determined all of them do have agitation characteristic and depression [15].
Balzini et al, (2003) has studied clinical behavior on those who have had body status rudeness. The result showed those who had more bended figure, does have more depression and lower interest than the groups in which does have lesser bended figure (Balzini et al, 2003). According to the above mentioned and less research related to current topic in global level and Iran. Lordosis or lumbar arch is a curvature in the posterior of vertebral column. This curvature is situated at the lowest part of vertebral column right above the sacrum [16]. Reforming practice as a try for removing body rudeness like back Kyphosis, Scoliosis, back Lordosis through coordination of agreed muscular groups, non-agreement and by vigor and tension practices. Reforming practice includes tension practice, power and facilitating nerve-muscular practices [17]. The question of the present study is whether effect of 12-week rehabilitation exercises on body self-descriptive and social unrest students with lordosis?
Methods
This study has been done in semi-experimental method. Statistical society of research includes students in high school in Babol city, about 20 has participated voluntarily in research (test participate = 10, control group = 10). All tastes have completed written satisfaction form informed before participating in research procedure. The measures for participation were having Kyphosis disorder and converting Lordosis. Also, participator does not have past record in continuous practice three times in a week for three months and in other cases has been omitted.
The method of research is to gather two groups students in a sport saloon and after explaining the object of research and satisfying tastes, body image and social unrest questionnaire has been provided to students and after completing and returning questionnaire, the member of experimental group has been obliged to perform Williams reforming practice including tension and power practice for removing rudeness for 12 weeks and every day in two times and control group has done re-creative sport. At last, the two groups have completed questionnaires. Then after gathering information, datum has been analyzed by multi-variables analysis method.
In this study, in order to evaluate body self-description, we have used of multi-dimension self-body, we could use this questionnaire for youth and adults, too. Short form of questionnaire includes 34 questions by 5 sub-scales: appearance evaluation, looking to appearance, mental occupation by the weight more than limit, understanding weight category and satisfaction from body areas (Mosburger & Egel, 2000). In evaluating social unrest, we have used of social unrest questionnaire including 24 questions and for evaluating agitation and avoidance to performance or social situation has been designed (Cash et al, 2004). In evaluating Lordosis rudeness, we have used of spinal column mouse, inner group stability and outer group has shown high in measuring general spinal column bow [18]. This program on test group is collection of Williams’s practices. Williams has published a program on reaction to clinical observance for patients by chronic back aches. These sports are for men under 50 years old and women under 40 years old in which does have increases in back Lordosis and decrease in disk space among back spinal and have low aches. The objects of these practices are to decrease aches and making stable under part of body and does have emphasis on back flexion [19,20]. Data analysis using SPSS24 software.
Result
According to table 1 the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test showed datum does have natural distribution (p>0.05). Therefore, we have used of parametric statistic for analyzing datum (Table 1) (Figure 1).
Table (1) is the mean and standard deviation of the two groups of test and control before and after exporting to independent variables. From Fig. (1) datum, we have the mean of test group does have positive effect after exporting to independent variable in body image and social unrest. In other words, body image of test group is more positive and social unrest of student in this group decreased (Table 2).
Table 1: The result of Kolmogorov- Smirnov test.


Table 2: The result of variance analysis for body image & social unrest in test and control group.
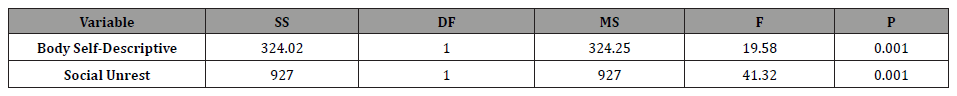
The result of table (2) shows there is meaningful difference among test and control group from body image (f=19.538; p=0.001) and social unrest (f=41.327; p=0.001). In other word, williams reforming practices according to the mean in two groups leads to positive body image and decreasing social unrest.
Discussion & Conclusion
Improper physical movements or long-term unfavorable postures in people cause postural abnormalities and as a result cause disorders in various systems of the body, including the musculoskeletal system and various complications such as pain and deformity [21]. Unfortunately, because the topic of research is not the same as current research and in this section, we have paid to the result of research and don’t compare them to the same research, too. In this research, we examined the effect of body image and social unrest in students. The result showed williams reforming practices are influential on body image and social unrest in students.
The result showed reforming practices does have positive effects on self-description and decreasing social unrest. The results of the present study are consistent with the findings of Singer (2021). In explaining this finding, we could say: doing reforming movement by establishing better muscular balance and increasing bodily efficiency in peoples by rudeness improves body image and decreases social unrest, too. It avoids non-self-confidence and inefficiency sensation because of laziness and muscular non movement and at last bad looking of rudeness and non-balance and non-feasible bodily figures and improves body image and selfimage and decreases agitation, too.
All mentioned above, are very important in reforming practice on body image. It seems participating in reforming programs does have medium role on increasing self-esteem and view to itself [22,23] In fact, doing reforming movement increases body ability level and body readiness and changes the kind of person evaluation from his own abilities. In general, the current research showed sport improves body image and decreases social unrest, but future research could declare the effects of this kind of practices [24-30].
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflicts of Interest
No Conflicts of Interest.
References
- Afroundeh R, Saidzanozi R (2017) Comparison of the Effect of Pilates and Traditional Corrective Exercises on Lumbar Lordosis in Female Students. The Scientific Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 6(3): 84-94.
- Gabbard C (2021) Lifelong motor development. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Renninger KA, Hidi S, Krapp A, Renninger A (2014) The role of interest in learning and development. Psychology Press.
- Biabangard E (2011) The methods of increasing self-esteem in children and adolescents. 4thed Tehran: Islamic Republic of Iran Guardians and Teachers Society 19.
- Ramirez-Granizo IA, Sanchez-Zafra M, Zurita-Ortega F, Puertas-Molero P, Gonzalez-Valero G, et al. (2020) Multidimensional self-concept depending on levels of resilience and the motivational climate directed towards sport in school children. International journal of environmental research and public health,17(2): 534.
- Marsh HW, Martin AJ (2011) Academic self‐concept and academic achievement: Relations and causal ordering. British journal of educational psychology 81(1): 59-77.
- Liefke K, Werning M (2020) Experiential Imagination and the Inside/Outside-Distinction. In JSAI International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence. Springer, Cham. pp. 96-112 .
- Daneshmandi H, Alizadeh MH, Gharakhanlou R (2018) Corrective movements: Identify and prescribe exercises. Samt publisher.
- Norris R, Carroll D, Cochrane R (1992) The effects of physical activity and exercise training on psychological stress and well-being in an adolescent population. Journal of psychosomatic research 36(1): 55-65.
- Noonan KJ, Dolan LA, Jacobson WC, Weinstein SL (1997) Long-term psychosocial characteristics of patients treated for idiopathic scoliosis. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 17(6): 712-717.
- Balzini L, Vannucchi L, Benvenuti F, Benucci M, Monni M, et al. (2003) Clinical characteristics of flexed posture in elderly women. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 51(10): 1419-1426.
- Asghari A (2006) Determines the positional relationship of spine disorders, with depression and anxiety in athletes and students. Non-athletes selected University of Tehran, Islamic Azad University, master's thesis 96.
- Forghani Ozrudi MB, Nikkhoo Amiri F (2021) The effect of correctional exercises on body image and social anxiety in students with lordosis disorder. Turkish Journal of Kinesiology 7(3): 87-91.
- Ozrudi MF, Faghanpour S, Goli RG, Podrigalo L (2021) Effect of depression among taekwondo students and its relationship with negative events due to COVID-19. Physical education of students 25(1): 10-19.
- Mosburger H, Egel S (2000) Determine of pain exercise: perceived competence, trait anxiety, trait depression and moderate effects. Pers Individ Dif 12: 1261-1266.
- Okhli H, Hojjati H, Akhoundzadeh G (2019) Comparing the Effect of the Corrective Exercises of America’s National Academy of Sports Medicine and Pilates on the Correction of Lordosis among Female High School Students in Golestan Province in 2018. International Journal of School Health 6(4): 1-6.
- Meyer DW (2011) Correction of spondylolisthesis by the correction of global posture. Clinical Chiropractic 22-23.
- Mollmann A, Dietel FA, Hunger A, Buhlmann U (2017) Prevalence of body dysmorphic disorder and associated features in German adolescents: A self-report survey. Psychiatry research 254: 263-267.
- Hematfar A, Sedaghati N (2013) Comparison of the effects Williams exercise & pick a water treatment on pain intensity and lumbar lordosis by female students. Journal of Sports Sciences 2(8): 21-11.
- Mannion AF, Knecht K, Balaban G, Dvorak J, Grob D (2004) A new skin-surface device for measuring the curvature and global and segmental ranges of motion of the spine: reliability of measurements and comparison with data reviewed from the literature. European Spine Journal 13(2): 122-136.
- Zagyapan R, Iyem C, Kurkcuoglu A, Pelin C, Tekindal MA (2012) The relationship between balance, muscles, and anthropomorphic features in young adults. Anatomy research international 1-6.
- Khanjani M, Bararzadeh M, Ozrudi MF (2014) Relaxation practice influence on mood competitive agitation in female Karate fighter. International Journal of Sport Studies 4(1): 67-71.
- Yousefi T, Shakeri F, Forghani Ozrudi MF (2014) Relationship between self-concept and self-esteem with Psychopathology in boy and Girl Students in Babol High Schools. International Journal of Sport Sciences 1(1): 1-5.
- Al-Nabi ST (2000) Evaluation of medical problems in children and adolescents in sport. Research report. Presented at the Second International Congress of Sport School in Tehran. Proceedings of the Second International Congress of print books with an emphasis on sports during elementary school. Publications physical education department. Ministry of Education.
- Ariapooran S, Godarzi A (2021) The Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction on Competitive Anxiety and Mental Toughness in Wrestler Adolescents. Sport Psychology Studies (ie, mutaleat ravanshenasi varzeshi) 10(35): 143-166.
- Cash TF, Theriault J, Annis NM (2004) Body image in an interpersonal context: Adult attachment, fear of intimacy and social anxiety. Journal of social and clinical psychology 23(1): 89-103.
- Lo CL (1998) The effects of extra-curricular activities on the self-concept of Taiwanese university students. University of South Dakota.
- Ozrudi MBF, Matmask EA (2019) A Survey of Self-esteem among Successful and Unsuccessful Student Athletes and this relationship by Achievement Motivation. Asian Exercise and Sport Science Journal 3(1): 1-7.
- Singer N (2021) How committed are you to becoming a translator? Defining translator identity statuses. The Interpreter and Translator Trainer 1-17.
- Zagyapan R, Iyem C, Kurkcuoglu A, Pelin C, Tekindal MA (2012) The relationship between balance, muscles, and anthropomorphic features in young adults. Anatomy research international 1-6.
-
Mohammad bagher Forghani Ozrudi. Effect of 12-week Rehabilitation Exercises on Body Self-Descriptive and Social Unrest Students with Lordosis . Glob J Ortho Res. 3(5): 2022. GJOR.MS.ID.000571. DOI: 10.33552/GJOR.2022.03.000571.
-
Rehabilitation Exercises, Body Self-Descriptive, lordosis, Multi-dimension, Self-Description of Body, Social Unrest, Lordosis, Student
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






