 Research Article
Research Article
A Blended Learning Develops the Basic Physical Exam Practice Skills for Nursing Student
Wanna Sanongdej1*, Sukanya Tantiprasoplap1, Jantra Keawpugdee1 and Panita Wannapiroon2
1Ramaithibodi school of Nursing, Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University,Thailand
2King Mongkut University of Technology north Bangkok, Thailand
Wanna Sanongdej, Ramaithibodi school of Nursing, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand.
Received Date: March 05, 2022; Published Date: March 17, 2022
Abstracts
This student determined the blended learning course that can improve basic physical examination practice. This study is one group pre-posttest design. The development of teaching materials as 7 basic physical examination video pace on Moodle platform. Teaching management is based on information theory by learners determine for self-learning. The purposive sample is 130 second-year nursing students. The student studied by selflearning and demonstrated back to the instructor (Face to face). When the course finish, learning outcomes were evaluated. The level of score test scores (mean 28.26, SD 3.76) t (102) = 7.06, p = 0.48) and examination scores (mean 200.03, SD 12.10, 16.737, p =0.00) were higher the 70%. The considering separated blended and online learning were tested path analysis by Amos. The hypothesized model is in accordance with real data (χ2 = .641 .18, df 1, p = .423, RMSEA = .00, RMR .013, GFI 1.00, CFI .995). Blended learning model can account for 89%. It was shown that blended learning have direct to perception of ability to basic examination and satisfaction at statistically significant (.49, p < .001), in contrast, specific online learning had no direct effect to nurse’s basic physical examination ability and satisfaction (.06, p > .05). This study reflected that learning improving well nursing skills should use a blended learning method that uses both online learning and a demonstration model (face to face).
Keywords:Blended learning; Self-directed learning; Basic physical examination skills.
Introduction
Blended learning, redesigning education of educational environment, is integrate online lessons combining with classic learning by teacher teaching (face to face) [1]. Blended learning, online lessons, is learning management through a technology medium or online through the Internet network [2]. Blended teaching was managed in conjunction with self-learning management. It is a concept that learners determine for self-learning [3]. Students take the initiatives to take responsibility for their learning.
As Instructors have played a role in the development of teaching materials, planning, creating online courses/lessons by composing content, creating a video and uploading online, and evaluating student’s competency. The teacher develops teaching materials by used video, the video media served as a stimulant with its features of image, sound, and movement, and those stimulate learning in the brain faster than letters; they have been shown to contribute to a better and longer thinking process and memorization [4,5,6]. Media was uploaded on the platform. Online learning is widely used for teaching nursing students in the era of the coronavirus pandemic. Especially subjects need to create professional practice such as health assessment. This requires basic physical examination skills.
Basic physical examination practice was a significant competency for nurses. Nurse has to health assessment for patients. Nursing students need to learn and have basic physical examination practice skills. However, basic physical examination practice skills need to be rehearsal several times. Nursing instructors created a blended learning course that learners determine for self-learning to improve basic physical examination practice.
Initially, students were self-study online by watching videos. Initially, students were self-study online by watching videos. This method reduces constraints on time and place to study. Self-learning manages by the learners and applied together with the teaching of online learning management. In teaching and learning management, learners must have access to the Internet network1. All 100% online or only partially taught online. It has been reported that online use alone does not improve clinical skills [7,8]. Therefore, students come to class to ask questions and discuss with the teacher. This will make the students understand better. Blended learning is used in both theoretical and practical learning for nursing students. Some research reports show that the use of blended instruction can improve skills in nursing practice [9-12].
According to the research report, it was found that blended learning increases skills in clinical practice in nursing. There are still conflicting results of studies on the outcomes of clinical teaching in nursing using blended learning [2,9]. In addition, studies on this issue are limited [6]. The researcher, therefore, conducted research to compare before and after clinical nursing practice skills, find the relationship between specific online and clinical nursing practice skills. The results of the research will be used to develop the nurses’ teaching and learning management.
Objective of Study
The objective of the study is the developing blended learning for improving basic physical examination practice skills.
To assess the academic achievement of nursing students who studied using blended learning by demonstrating through a digital learning platform.
Review Literature
Teaching and learning management follow Information processing theories. Information processing theory is a cognitive theory that is processing for the workings of the human brain [13]. The theory explained learner selected information which they select to know, then they will encode it into their memories. This Information encoded goes through into long term memory sensory memory short term and long term memory. When external stimuli or events influence learners, they will search, retrieve the pre-coded cues, and recall them to respond via a specific performance. Learners will execute an action and/or a skilled movement sequence. Learning management based on Information processing theories, teacher need create media and learning styles that stimulate learners’ curiosity [14]. The learning process occurs within the brain. Online learning is learning processes directly influenced the physical examination ability of nursing students [15]. However, some research reported that online learning did not enough to improved performance or activity. Blended learning approach was presented for teaching and learning to develop practical skills [11, 12].
Blended learning refers to the systematic integration of Internet, digital media and classic teaching or face to face instruction [9]. There are different forms of blended learning, including: faceto- face driver, rotation, self-blend, flex etc. Flex is the most popular model which curriculum is delivered via a digital platform and teachers are available for face-to-face consultation and support. Teacher Blend learning may have some potential improved clinical competencies among healthcare students [16] However, students have to plan their studies and control themselves to study according to the plan. The concept of self-directed was used to organize in conjunction with online learning program. Self-directed is a learning process in which the learner determines the learner’s own learning plan [11]. There four steps: step 1 Instructor had to assess reediness, state the necessity and importance of the subjects that will be used for future work, mutually set objectives together with learner, inform instructional methods and, evaluate learning Re-evaluate and alter goals as required during your unit of study.
Methodology
The blended learning process by demonstrating through a digital learning platform was one group pre-posttest design. This study has three steps:
Developing a video media
The video Developing video materials on all physical examination systems. The physical examination systems media compose of HEENT, lung, heat, abdominal, and muscle skeleton. The videos have been examined by 3 experts including one nursing teaching, 2 media experts. Video materials on all physical examination systems were examined from the Education Service Division of Mahidol University. Video will be placed on the MOODLE Platform in the assessment nursing course. The Instructor will provide questions or MCQs (multiple choice questionnaires) for each section.
Teaching management of basic physical examination course
Educational blended learning process through demonstration through the digital learning platform teaching about systematic physical examination, seven topics in online lessons through MOODLE platform, teaching and learning to have a theoretical step, information processing theories, self-directed learning, consisting of nine steps.
1. Step 1: online classroom; encouraging learners to focus on the lessons. The instructors developed an interesting video on physical examination system. The teacher persuaded the students to study the video that these content is useful for applying to patients in the future.
2. Step 2: online classroom; State the purpose of the lesson. The instructors inform students about objectives of each video in each section.
3. Step 3: online classroom; before reviewing the previous knowledge (Recall previous knowledge). Before teaching the demonstration of physical examination in each system. The video will present a review of the anatomy of each system for learners to review anatomy before physical examination.
4. Step 4: online classroom; Present the material to be learned. Use video demonstrations demonstrating the physical examination of each system, motion picture, sound.
5. Step 5: online classroom; the lesson presents knowledge about anatomy along with physical examination. This make students connect knowledge of anatomy with physical examination. This makes it easier to understand and remember the methods of physical examination.
6. Step 6: Online classroom; Provide link knowledge of physical examination in VDO. The Instructors will provide links to find out more knowledge for students.
7. Step 7: Online classroom; Provide feedback on the web, teachers can contact learners in case they don’t understand what period of physical examination. The teacher will bring the questions to the class again for learners to understand more
8. Step 8: online classroom; Knowledge test (Testing) to test the knowledge of learners. Using multiple-choice or subjective exams, able to test on the web via network.
9. Step 9: Face to face classroom; remembering and Applying (Providing Enrichment or Remediation). The learner must return to demonstrate the physical examination in the classroom what the learner sees in the video and show it to the teacher, if there is some part that perform incorrect, the teacher will suggest again suddenly. The classroom was managed about 5 times Number of practicing procedure depend on students convenient. Student can entry in program depend on themselves. During the demonstration students returned to the instructor. The teacher will introduce the shortcomings what students do correct or wrong; Students will practice the physical examination correctly following teacher’s suggestion.
Assessing physical examination practice skills
• Face to face classroom; assessing physical examination practice skills of nursing students who studied using blended learning by demonstrating through a digital learning platform. In the last week of studying, students demonstrate physical examinations to instructors in each body system topic by using a rubric score physical examination assessment.
• Online classroom; the student must do a quiz including a physical examination. The students do a short clip video on basic physical examination. Moreover, students complete an achievement questionnaire including self-assessment on physical examination.
Measurement
The Demographic Questionnaire was used to obtain the demographic information of the senior nursing students; information gathered included sex, age, number of times studying online, and online entry study period each time. The achievement was measured by:
1. Basic physical examination ability was measured by the students’ self-assessment using visual rating scales (VRS). The question was “you think that level of physical exam proficiency did you have before/after studying blended learning? and “you think that level of physical exam proficiency did you have before/ after studying online learning? VRS has a long straight line, divided into 10 spaces or 1 point each (1-10). The scores are in order from least (1) to (10) greatest. If the students are very talented, they will rate themselves highly (7-10). VRS was Cronbach’s alpha coefficient .89.
2. The satisfaction of teaching before and after online learning was measured using visual rating scales (VRS), measured using a long straight line, and divided into ten boxes, 1 point each. you think that level of satisfaction did you have before studying online/blended learning? and “you think that level of satisfaction did you have after studying online/blended learning? The scores are in order from least (1) to (10) greatest. If the students are very satisfied, they will score as many points along the line according to their preferences. VRS was Cronbach’s alpha coefficient .87.
3. Measure scores in physical examination practice were measured by Physical assessment rating scales with rubric scale four. Each item is rated on a 4-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (very good) to 4 (need to improve), with a higher score indicating excellent online content. The individual construct reliability of items was .53–.63. The Cronbach’s alpha reliability was .77.
4. MCQ are used measured on the physical examination test (quiz) the total score of the physical examination score IOC =1.00 The students review their knowledge from watching videos in each episode. Students did quiz online physical examination.
5. A number of visit online: the nursing student entry website to see video in physical examination practice.
6. A number of visit classroom (face to face): The nursing student entry in classroom to consult instructors and demonstrated physical examination back.
Sample group
The purposive sample was a second-year nursing student at nursing Ramathibodi school of nursing who attended an online initial physical examination course. The sample selection was simple random according to the specified properties by calculating the sample. The sample was calculated from the paired t-test the formula, using G power program, Effect size .05, α err prob, Power (1-β err prob) = 0.095, N1/N2 =1, thus df is 44, got non-centrality parameter 3.35 critical t 1.68, required a sample of 45 samples. Therefore, the samples will be collected from 130 second-year students to prevent data loss.
According to statistics, the best sample for our study design should be 5-10 times the number of parameters (i.e., 10 x 3 =30 in our study in the path analysis [17] thus, a sample size of 130 would have been enough for a path analysis using the software AMOS, Therefore, the samples will be collected from 130 second-year students to prevent data loss. Inclusion criteria is a second-year nursing student of the academic year 2021 who has passed all 7 videos and willingness to participate in research. Exclusion criteria: nursing student has not watched all seven videos, or is non-willingness to participate in research
Method of collecting data
Data were collected for 4 weeks at the Nursing School of University in the Ramathibodi hospital region of Salaya, Mahidol university, Thailand. After the students finished watching the video, they did the Quiz every week. The researcher informed the nursing students about the details of the present study. After students completed the health assessment course. They demonstrated tests with their instructors. The questionnaires were distributed, one hundred and thirty were returned used for the final analysis.
Statistic method.
For the descriptive statistics of participants, we used frequency, percentage, mean, standard deviation, and SPSS software version 24.0. The t-test set the mean value of 70% of score test significantly at .01. The t-test, pair t-test statistics analyzed differences between before and after learning significance at .01. The path analysis analyzed before and after the online and blende learning used the AMOS 24.0 software. The assumption of path analysis, including normality, multicollinearity, linearity, and homoscedasticity were examined using SPSS. To analyze the influence of online teaching affecting the ability to perform basic physical examinations, we used Path Analysis Statistics, statistical maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) of AMOS. The model was verified based on χ2, χ2/ df, the goodness of fit index (GFI), comparative fit index (CFI), and root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA). Amos statistics analyze the model before and after online learning. The model is harmonious with the hypostasized model, set significance at .05.
Result of this study
All of the participants were women (100%) and between 19 to 22 years old with 46.9. % studying each online lesson twice times. 46.9. % of them saw VDO on online about 30-60 min. They entries classroom for consult and practice (Table 1-3). This study reported the scores of basic examination skill was higher the 70 % of the score (175) (mean 203.03, SD 8.35) t (37.89) = 16.737, p <.00. The higher level of test scores was higher the 70 % of the score (38) (mean 28.72, SD 3.16, t (2.62) = 7.06, p .01. After finish course, the nursing student evaluated themselves about ability basic physical examination practice and satisfaction. They perceived that they had the basic physical examination practice (M=7.24, SD= 3.36) and satisfaction (M=7.88, SD= 3.36) were significantly higher than before blended learning at statistical significance = .01. In contrast, there were not a significant increase in basic physical examination practice skills (p=.53), and satisfaction (p=.17) after only seeing video and entry online course (Table 4).
Table 1:Personal Information of Senior Nursing Students
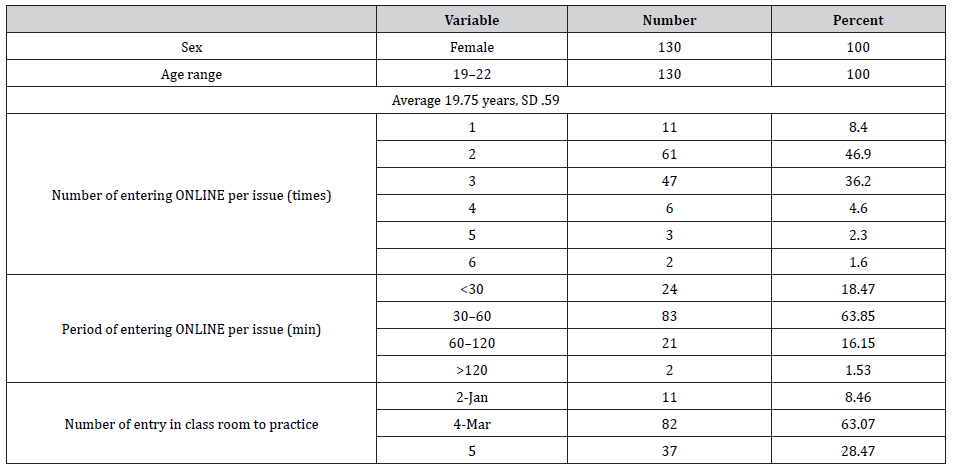
Table 2:show result of examination score.
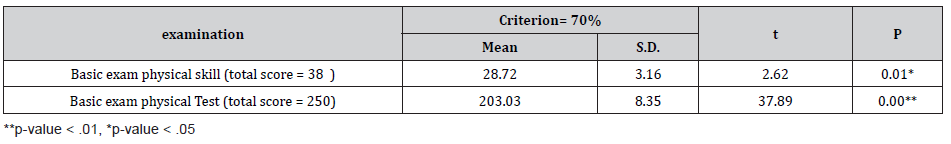
Table 3:show result of student’s self- evaluation to ability physical examination and satisfaction.
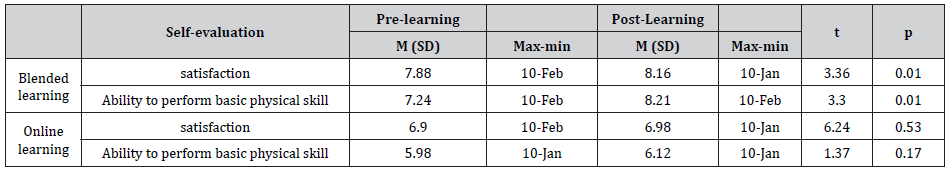
Table 4:The Results of the Influence of online and blended learning to basic physical examination performance and satisfaction.
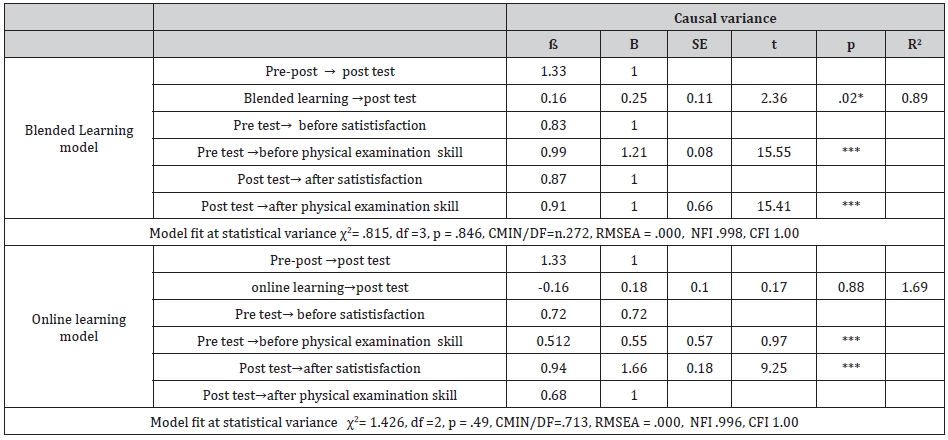
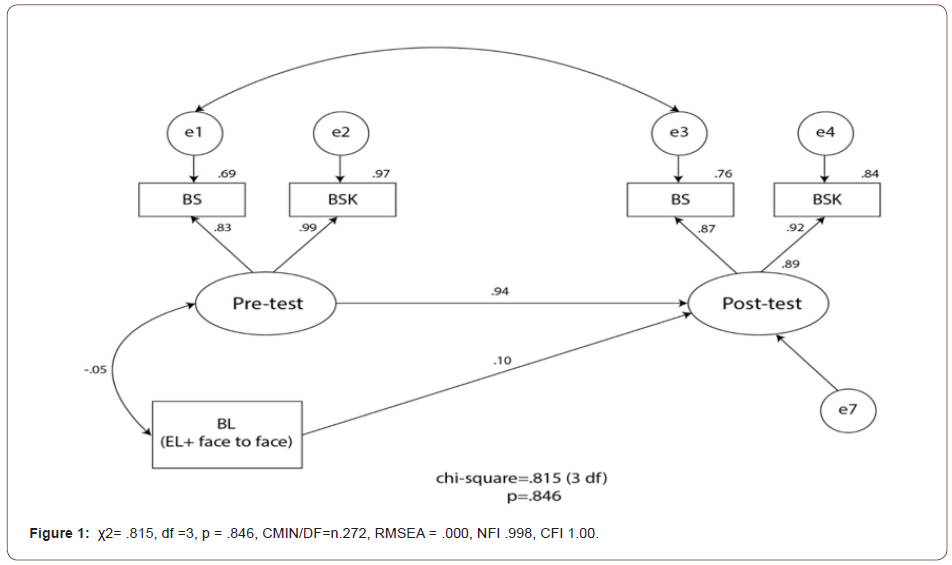
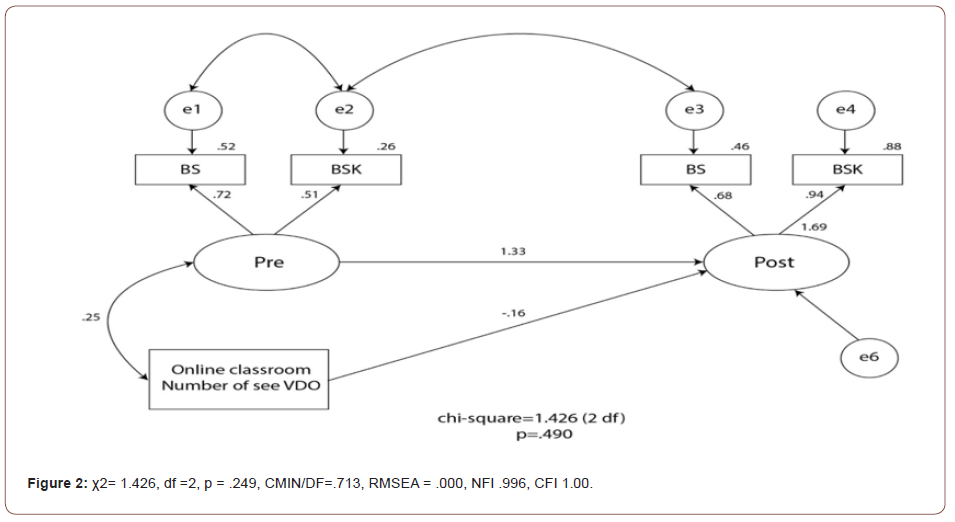
The results of blended learning model showed parameters affected the ability to perform basic physical examination and satisfaction among nursing students. The hypothesized model is in accordance with real data which was collected χ2= .815, df =3, p = .846, CMIN/DF=n.272, RMSEA = .000, NFI .998, CFI 1.00. This model could account 89%. Blended learning has affect to post test at statistically significant (.25, p =.02). Moreover, satisfaction before online and after online has relation with post- test statistically significant .87, .91, p < .001). Where as, the results of online learning model is in accordance with real data which was collected χ2= 1.426, df =2, p = .249, CMIN/DF=.713, RMSEA = .000, NFI .996, CFI 1.00. The online characteristics could not affect to nursing students’ perception effective basic physical examinations and satisfaction (.16, p = .88) (Figure 1 & Figure 2).
Discussions
The teaching and learning was managed by using blended learning by allowing students to schedule their own online attendance or self- learning management. This type of learning is suitable for students at the university level [18]. The effectiveness of learning in this way, improving knowledge was 70% higher than the specified criteria. He recognized the benefit that this knowledge could be applied in future work with patients. He can review the lessons as much as the objects set himself. Students are satisfied with their studies at a high level because they can control the study by himself.
Blended lessons influence clinical practice and learning satisfaction. The report is consistent with several critical reports 21. The presence of a teacher in providing guidance and demonstrations had a significant effect on practice and specially nursing students. It can be seen from the research results that students self-assessed that they had a statistically significant increase in their abilities before and after. Oppositely, when separating online learning from blended learning by using statics (AMOS). Instead, the number of visits online course did not make any difference in satisfaction and between before and after classes. A sense of self-examination increases the ability of the basic physical examination and satisfaction in learning. The results were consistent with research reporting that online learning did not improve practical ability [19]. This differed with Pavlov Antonino and college [5].
Only looking motion pictures creates visual recognition and retrieves the images when needed to be displayed, but not enough to make the mechanism of the brain lead to action. This can be seen from the number of sessions that have no effect on the ability to practice nursing. The students were not convinced that they had the basic physical examination abilities before and after. Students must take action several times or rehearsal in order to develop practical skills. And in this process, students need instructors to guide what he practiced many times was correct. Teachers are also needed for practice-based teaching and require students to acquire clinical skills. Thus, using only educational technology does not necessarily make medical education more effective [8] The blended learning group showed a significantly higher level of knowledge of medication and satisfaction with the comprehensiveness of their medication learning, but the self-efficacy of medication administration, medication-administration ability, related to their learning satisfaction did not differ significantly from that in the control group [19].
Online learning alone does not improve skills in nursing practice. This can be reflecting from the increasing in the number of visits online did not make the learner feel that he has the ability to practice nursing more. Practice also requires expressive practice and need a teacher to guide. This will make the learner feel confident and have the ability to practice more.
This study was a single quasi-experimental study. Therefore, the strength of research is less. In subsequent studies, research should be conducted with a control group and an experimental group before and after the experiment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study examined a blended learning course that aimed to improve basic physical examination practices for nursing students. The management of such a course is based on information theory by learners determine for self-learning. The results show that blended learning has a direct effect on the perception of physical examination practice in terms of ability and satisfaction while online learning alone does not improve skills in terms of nursing practice. To improve the quality of nursing clinical skills there is a need for a blended learning approach that uses both online learning and face-to-face guidance involving a teacher.
Acknowledgement
I would like to express my sincere thanks to School o Nursing, Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital and Division of Academic Affairs, Mahidol University.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
References
- D Randy Garrison, Norman D (2008) Vaughan Blended Learning in Higher Education: Framework, Principles, and Guidelines (2008) San Francisco. Wiley
- Mary K, TallentRunnels JA, Thomas WY, Lan S, Cooper TC (2006) Teaching Courses Online: A Review of the Research. Review of Educational Research 76: 93-135.
- Loeng S (2020) Self-Directed Learning: A Core Concept in Adult Education. Hindawi Education Research International 3816132: 12.
- McDaniel MA, Einstein GO (1986) Bizarre imagery as an effective memory aid: The importance of distinctiveness. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 12(1): 54-65.
- Pavlo C SPELLING A, Serkan T, Niederhauser D (2021) Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic Learning Environment: What Open Source Has to Offer.
- Davis T, Xue G, Love BC, Preston AR, Poldrack RA (2014) Global Neural Pattern Similarity as a Common Basis for Categorization and Recognition Memory. The Journal of Neuroscience 34(22): 7472-7484.
- Jang HW, Kim KJ (2014) Use of online clinical videos for clinical skills training for medical students: benefits and BMC Medical Education 14(56): 2-6.
- Yavner SD, Pusic MV, Kalet AL, Song HS, Hopkins MA, et al. (2015) Twelve tips for improving the effectiveness of web-based multimedia instruction for clinical learners. Medical Teacher 37: 239-244.
- McCutcheon K, Lohan M, Traynor M, Martin D (2015) A systematic review evaluating the impact of online or blended learning vs. face-to-face learning of clinical skills in undergraduate nurse education. Journal of Advanced Nursing 71(2): 255-270.
- Rowe M, Frantz J, Bozalek V (2012) The role of blended learning in the clinical education of healthcare students: A systematic review. Medical Teacher 34(4): e216-e221.
- Noh GO, Kim D (2019) Effectiveness of a self-directed learning program using blended coaching among nursing students in clinical practice: a quasi-experimental research design. BMC Med Educ 19: 225.
- Young Hee Sung, In Gak Kwon, Eunjung Ryu (2008) Blended learning on medication administration for new nurses: Integration of e-learning and face-to-face instruction in the classroom. Nurse Education Today 28(8): 943-952.
- Slate JR, Charlesworth JR (1988) Information Processing Theory: Classroom Applications.
- Gange RM (1985) The conditions of learning and theory of instruction (4th). The Dryden Press Saunders.
- Sanongdej W (2021) Investigating Learning Process Factors Related to Online Learning and Physical Examinations Among Nursing Students. Archives in Neurology & Neuroscience 9(5): 2021.
- Garrison DR, Kanuka H (2004) Blended learning: Uncovering its transformative potential in higher education. Internet High Educ 7(2): 95-105
- Bentler PM (1992) On the fit of models to covariances and methodology to the Bulletin. Psychological Bulletin 112(3): 400-404.
- Narong S (2018) Learning Management System for Creative Thinking Skill Development with Collaborative Learning of the Graduate Students in Kasetsart University. International Journal of Environmental &Science Education 13(6): 527-532.
- Young HS, InGK, Eunjung R (2008) Blended learning on medication administration for new nurses: Integration of e-learning and face-to-face instruction in the classroom, 2008 Nurse Education Today 28(8): 943-952.






