 Short Communications
Short Communications
Optimal Blocking of Undesired Nodes in Digraph
Tsitsiashvili Gurami,Institute for Applied Mathematics FEB RAS, Russia.
Received Date: April 14, 2020; Published Date: May 18, 2020
Abstract
This paper provides a complete solution to the problem of minimizing the number of edges in the protein network, the removal of which blocks all paths that pass through a set of undesirable nodes. The minimization problem is reduced to the problem of minimum cut and maximum flow in a specially constructed weighted digraph with a source and a drain.
Keywords: Digraph;Ford-Fulkerson Theorem;Sub-graph; Optimal Blocking.
Problem Statement
Consider a digraphG, representing a protein network with finite sets V and E of nodes and edges respectively. In the setV there is a subset W ⊂V of undesired nodes. Contrast to the set W the subset Q ⊆W of output nodes from which edges exit to the subset U =V \W and the subset P ⊆W of input nodes to which edges enter from U.
Denoten( p) a number of edges, entering to p∈P from U, and N(q) a number of edges, exiting from q∈Q to U. Our problem is to find subsets 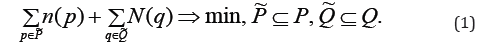 so that their removing from the
sets
so that their removing from the
sets breaks all paths, which transit to W from the set U , pass through W and exit back. And the number of edges to delete
is minimal:
breaks all paths, which transit to W from the set U , pass through W and exit back. And the number of edges to delete
is minimal:
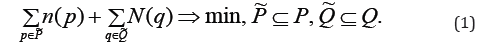
In [1] the digraphG*with the nodes set W and edges, connecting them in digraph G, is constructed. The set W of the digraph G* nodes is divided into classes of cyclical equavalence (clusters) and a relation of partial order between these clusters is defined a* ≥ b* if in the digraph G* there is a path from clustera*to clusterb*. A bipartite digraphΓ with the set of input clusters P* , the set of output clustersQ* , and the set of edges: R: (p*,q*), if p*≥q*, if p* ≥ q* This design allows for simultaneous input and output clusters, to be included into the sets P* , Q* and an edge between them is to be introduced.
The bipartite digraphΓ is divided into connectivity componenets (after deleting of edges direction) and isolated clusters are removed. In each connectivity component input or output edges are removed, depending on which number is less. But this solution is not optimal.
Search for an Optimal Solution by the Ford- Fulkerson Theorem


The Ford-Fulkerson algorithm [2] with improved additions of Edmonds-Carp [3] and Dinits [4] is used to find the maximum flow f . All algorithms for determining the maximum flow consistently find paths that increase the amount of flow. For the maximum flow found, the minimum cut is determined using well known recurrent algorithm [2].
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest exists.
References
- Tsitsiashvili G Sh (2019) Improved Algorithm of Blocking the Selected Edges in the Digraph.Annals of Biostatistics and Biometric Applications 3(3).
- Ford L R ,Fulkerson DR (1956) Maximal Flow Through a Network. Canadian Journal of Mathematics 8: 399–404.
- Edmonds J,Karp RM (1972) Theoretical Improvements in Algorithmic Efficiency for Network Flow Problems.Journal of the ACM 1(2): 248–264.
- Dinits EA (1970) Algorithm for solving the problem of maximum flow in the network with power estimation.Reports of the USSR Academy of Sciences 194(4): 754–757.
-
Tsitsiashvili Gurami. Optimal Blocking of Undesired Nodes in Digraph. Annal Biostat & Biomed Appli. 3(5): 2020. ABBA. MS.ID.000578.
Digraph;Ford-Fulkerson Theorem;Sub-graph; Optimal Blocking.
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






