 Editorial Article
Editorial Article
Information in Biological Structures and Big Data Assisted Prediction as Informational Biostatistics/Biometric Tool for Pandemic COVID-19 Investigation
Florin Gaiseanu*
Science and Technology of Information Bucharest (Romania) and Barcelona (Spain).
Florin Gaiseanu, Science and Technology of Information Bucharest (Romania) and Barcelona (Spain).
Received Date: November 08, 2021; Published Date: November 24, 2021
Editorial
Information is powerful in our informational era, when the multitudes of mass-media communication systems are flooding our daily life with information and contribute to enlarge our cultural horizon, to understand our life and environment, not only in our nearest community, but also at the planetary scale. Little is known however about the information concept when we refer to the biological structures, although the techniques, methodologies and microelectronic/intelligent equipment as informational systems, able to improve the decision in operative management [1], the diagnostic and treatment in healthcare field, are now more and more penetrating in the daily use [2]. We have to connect therefore to the last discoveries concerning the role, intervention and the effect of information in human and biological structures in general. Developing the concept on information in human and living structures, it was shown recently [3-5] that information is not only a concept measuring in Bits our info-consumption during the communication by internet and audio-visual media, but also with an essential role in the functionality and the info-structuration of living entities [3,4]. We have to refers therefore to a virtual information expressed by language, concerning concepts, symbols, significance of various events and objects of our reality, but not only. Information is also a result of structuration/destructuration processes or configuration/ reconfiguration of a system of microparticles or parts of a macro-system.
The proteins are the structuration bricks of the biological structures, built in the body of the eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells – the units of life. The info-communication is based on the released information from the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of the genes by means of the messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA), combined with amino acids units [3,4].
Distinctly of the human language, or other manifestations of human and subhuman biological structures, which communicate each other by gestures, position/posture, vocalization or other (chemical, electrical, infra-sonic, pressure contact) signals, genetic information is expressed in a specific 4-letter-type “alphabet”, i.e. by the combination of a very large/various possible DNA sequences of the nucleotides combination, which are Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G), binding the two very large helix-type strands of carbon chains in the DNA molecule. In such a structure, A may only bind the complementary T base and C only the complementary base G, acting as YES/NO (Bit-type unit) informational operator pairs. The DNA sequences compose the basic “words” of the genetic “language”, able to determine the sort of proteins which are to be used for the building of body. This communication is achieved during the structuration/ destructuration chemical/physical processes, allowing the “embodiment”/“disembodiment” of specific information, which becomes an active/distinctive participating factor to form a certain structure.
The genetic process, communicating the development programmed “software” of a new biologic structure, is received as an input “embodied” (compressed “zip”-type) information from parents, and is transmitted to the next generation by the genetic output “terminal” [5]. Based on such mechanisms, it is possible to calculate the quantity of information contained by the cell, which was evaluated as [6]: 5.07×106 Bits for Staphylococcus aureus (bacterium); 1.08×108 Bits for Aegypti (mosquito); 4.13×108 Bits for Gallus (chicken); 5.28×108 Bits for Bos Taurus (cow); 8.38×108 Bits for Homo sapiens (human). showing that the more complex organism, more information is operable. The informational functionality of uni and multicellular organisms on the entire scale is similar, supported mainly by similar specialized organelles (either distinctive in eukaryotic and not in prokaryotic cells [4]) and organs respectively, where the inter-communication is based on the YES/NO type complementarity of the proteins as chemical messengers (including the neurotransmitters) and ionic-type transport in the nervous system-equipped biological structures.
The biologic structures are reactive systems operating with information, able to decide and stock information, sensing/ receipting information by means of the sensory elements of the info-input interface and emitting information to the execution elements of the info-output “terminal”, expressed as attitude [5]. The reactivity of the biological structures is supported by specialized reactive chains/networks in the cell and multicellular organisms, necessary for:
I. The body maintenance by metabolic processes of the
nutrients – air, water from environment, providers of energy
and substituting / reconstruction / reconfiguration elements
for the body structure.
II. The info-perception of internal/external signals,
memorization and info-analytic/decisional processing
allowing to “know”/determine the momentary self-status and
to elaborate and transmit the reactive adequate response for
survival necessities, according to the life experience and own
decision criteria.
III. Info-sentient reaction to information, felt as emotions in
human and detected/interpreted in subhuman organisms as
internal “sensations”/sentience [4,5].
Non-standard specific selection/separation/discriminant phenomena are manifested at human by near-death / mystic and religious experiences and “beliefs” criteria, allowing the decisional “navigation” among the high quantity of environmental information. At subhuman organisms, this is manifested by detection / communication of subtle information, allowing the synchronization of the geometrical configuration of bacteria colonies, the orientation of the migratory birds and premonitory detection of danger signals by various living species [5].
In human, the distinct informational functions described above are detected in mind as cognitive centers of consciousness, suggestively defined as I-know (memory), I-want (decision), I-love (the driving force of life, representing emotions), I am (self-status, vigor, health), I-create (genetic transmission), I-created (genetic inheritance), I-believe (beliefs, confidence, trust). We have to observe therefore that the biologic organisms are self-organized info-matter structures, working like an informational “device” with four terminals, two input/output terminals for info-reactive quick adaptation to environment conditions, and two genetic terminals for large-time adaptation and species survival, with cognitive properties on the entire evolution scale, from proto-cognition to evolved consciousness at human. Such results open a spectacular horizon for applications in the neurology, neuroscience, psychology, behavioral science, psychiatry, geriatrics, and life science [6], in particular for the biostatistics/biometric applications [7-9].
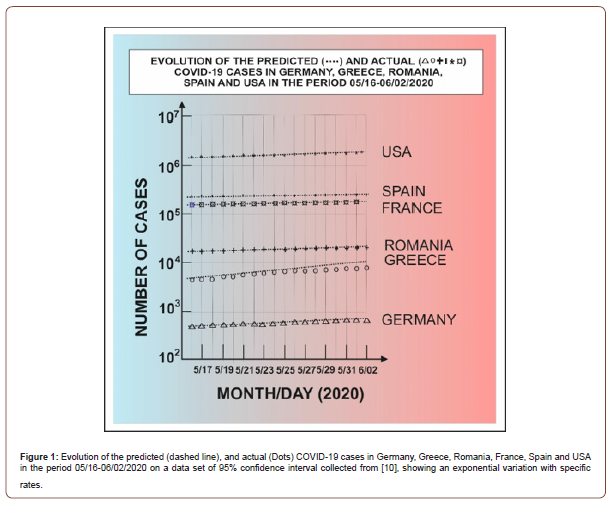
The penetration of the informational and artificial intelligence, assisting the human intelligence/investigation effort in the biological field, is already a necessity for healthcare domain in general and in particular for biostatistics and biometric applications in immediate/due-time interventions. A spectacular development is represented by the big data analysis for prediction and decision/ management [1], with particular applications in pathology and radiology for fast exploration, psychiatric disorders, in the deep investigation of the molecular behaviors within the frame of the so called “omics” (genomic, proteomic, epigenomic, metabolomic or organimics) domains [2,4,5]. An example of efficiency of such an application is given in Figure 1, where are represented the predicative results showing the evolutive tendency of COVID-19 contamination cases in Germany, Greece, Romania, France, Spain and USA during the pandemic period 05/16 – 06/02/2020, with data collected from [10]. According to such results, it can be deduced that the autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model is the most suitable when an exponential increasing trend is operable in each particular case, generating the best prediction, as it can be seen from the comparative results shown in this figure. The power of the big data predicative processing becomes a recognized useful tool for prediction, based on the learning machines and models, allowing an adequate info-assistance and appropriate decision on the pandemic wave at the global level, for the avoidance of the negative effects on economy, finances and industries, and especially on the human health, at planetary scale. An additional benefit consists in the due-time operability, avoiding the indirect negative effects referred to undesirable social behaviors like anxiety, depression and even violence, induced by restrictive adopted measures and individuals’ isolation.
Conclusion
Degree based topological indices like General fifth M1 and General fifth M2 Zagreb indices for Dyck-56 Network are found in this paper. These indices are useful in study of QSAR/QSPR. Furthermore, General fifth M1 and General fifth M2-Zagreb polynomials for Dyck-56 Networks are found. These indices and polynomials are useful for the study to understand correlation between physical structures with chemical properties.
Acknowledgement
To my family, to Adrian Gaiseanu and Ana-Maria Gaiseanu.
Conflict of Interest
No financial or conflict of interests.
References
- Filip Florin Gheorghe (2020) DSS-A class of evolving information systems. In: G Dzemyda, J Bernatavičienė, J Kacprzyk (Eds.), Data science: New issue, challenges and applications. Springer, pp. 253-277.
- Lidong Wang, Cheryl Ann Alexander (2020) Big data analytics in medical engineering and healthcare: methods, advances and challenges. J Med Eng Technol 44(6): 267-283.
- Gaiseanu F (2020) What Is Life: An Informational Model of the Living Structures. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 5(2): 18-28.
- Gaiseanu Florin (2021) Information as an essential component of the biological structures and their informational organization. Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology 6(2): 1-9.
- Gaiseanu Florin (2021) Human as an Informational Device. Archives in Biomedical Engineering & Biotechnology 6(1): 1-8.
- Gaiseanu Florin (2021) Information in the Universal Triangle of Reality for Non-living/Living Structures: From Philosophy to Neuro/Life Sciences. Philosophy Study 11(8): 607-621.
- Gaiseanu Florin (2021) Information, Info-Creational Field, Creativity and Creation, According to the Informational Model of Consciousness. International Journal on Neuropsychology and Behavioural Sciences 2(3): 75-80.
- Gaiseanu Florin (2020) Attitude as an Expressible Info-Operational Reaction to a Perceived/Purposed Object/Objective. International Journal on Neuropsychology and Behavioural Sciences 1(1): 12-16.
- Gaiseanu Florin (2021) Evaluating Attitude and Behavior: An Info-Operational Procedure Related/Supported by the Cognitive Centers of Mind. International Journal on Neuropsychology and Behavioural Sciences 2(1):1-5.
- Ismail L, Materwala H, Znati T, Turaev S, Khan MAB (2020) Tailoring Time Series Models For Forecasting Coronavirus Spread: Case Studies of 187 Countries. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 18:2972-3206.
-
Florin Gaiseanu. Information in Biological Structures and Big Data Assisted Prediction as Informational Biostatistics/Biometric Tool for Pandemic COVID-19 Investigation. Annal Biostat & Biomed Appli. 4(4): 2021. ABBA.MS.ID.000592. DOI: 10.33552/ABBA.2021.04.000592
Biological structures, Methodologies, Symbols, Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), Nervous system, Sensory elements
-

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






